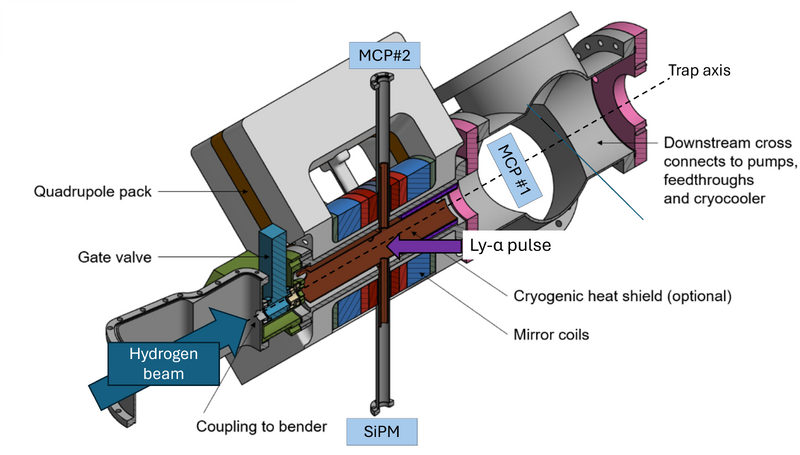
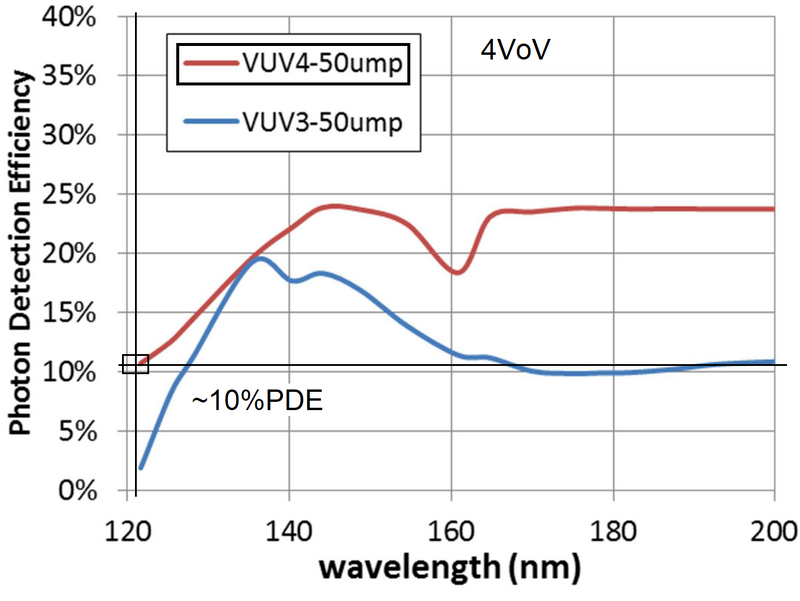
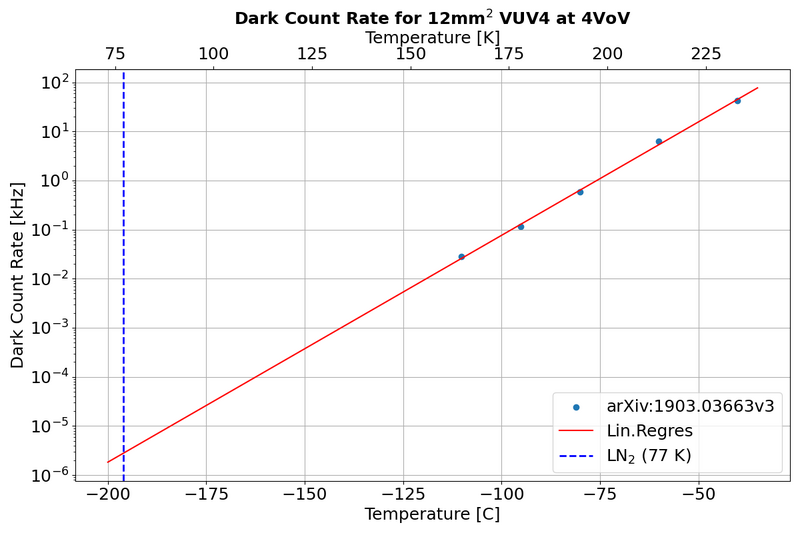
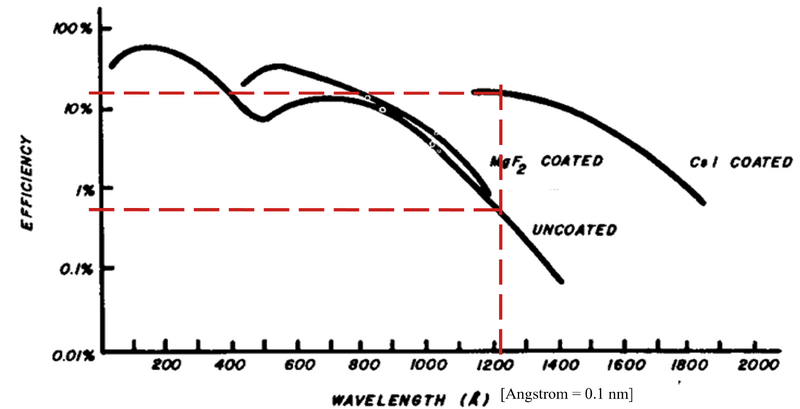
Detectors
SiPM
The Hamamatsu VUV4 is used to detect H fluorescence.
File:April 2017 VUV4-MPPC-HPK.pdf
The SiPM bias and the amplifier are powered by the so-called LoLX board
File:User Manual SiPM-FE-Rev1-A.pdf
The LoLX board is powered by a DC power supply.
File:HMC804x dat de en 3607-0169-3x v0200.pdf
Dark count rate from this paper
SiPM turn-on procedure
SiPM cooling procedure
MCP
Two InComm MCPs are used to detect H fluorescence.
The MCPs are biased by a custom made voltage divider.
HV PS
The HV power supply is a CAEN DT5533EN
If the MIDAS interface is unavailable, one can use:
`$ minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0`
[type "caen"]
the menu items can be accessed by typing the initials.
Digitizer
CAEN DT5730S - 8 Ch. 14 bit 500 MS/s Digitizer: 640kS/ch, Arria V GX, SE
Manual: File:WEB UMDT5730-DT5725 rev8.pdf
Registers Description: File:WEB UM5118 725-730 Registers Description rev4.pdf
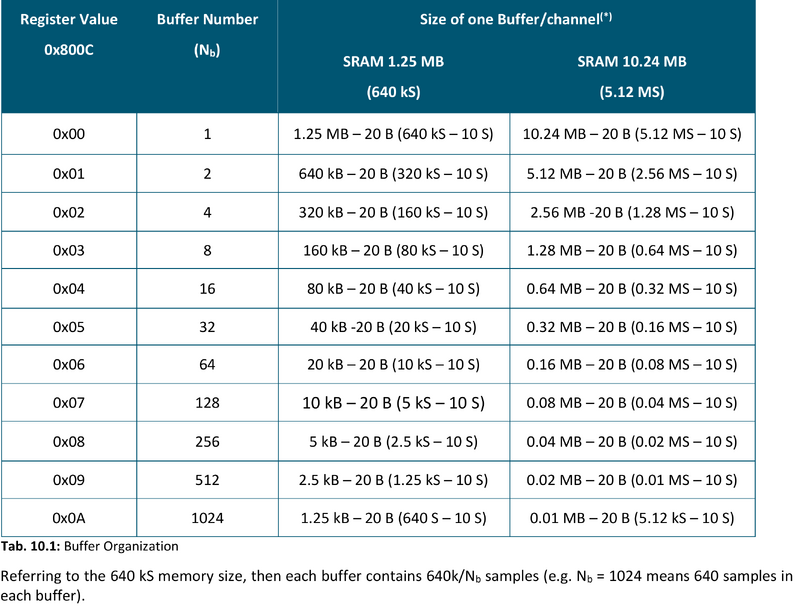
Buffer Organization
Post-Trigger Setting
The number of post‐trigger samples is the number of further samples that are written by the FPGA in the channel memory, when a trigger occurs, before to freeze the buffer. The number of post trigger samples is:
Npost = PostTriggerValue*N + ConstantLatency
where:
Npost = number of post trigger samples.
PostTriggerValue = value to be set.
N = 4 (for 730) is the coefficient to be multiplied by the PostTriggerValue.
ConstantLatency = constant number of samples added due to the latency associated to the trigger processing logic in the ROC FPGA. The value of this constant depends on the trigger source used and can change between different firmware revisions.
Channel Enable Mask
[15:0] Channel Enable Mask. Bit n can enable/disable channel n to participate in the event readout. Options are: 0 = disabled; 1 = enabled. NOTE: bits[15:8] are reserved
[31:16] Reserved.