Custom plots with mplot: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Stefan Ritt (talk | contribs) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Pagelinks}} | {{Pagelinks}} | ||
= | = Introduction = | ||
Custom pages may contain custom plots, sich as scatter plots, histograms and color plots. This can be achieved by including the <code>mplot.js</code> library and creating a <code><div class="mplot"></code> element. Following example shows the code for a simple page for a scatter plot: | Custom pages may contain custom plots, sich as scatter plots, histograms and color plots. This can be achieved by including the <code>mplot.js</code> library and creating a <code><div class="mplot"></code> element. Following example shows the code for a simple page for a scatter plot: | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Parameter !! Applies to !! Meaning | ! Parameter !! Applies to !! Meaning | ||
|- | |||
| data-type || All plot types || Type of graph, one of "scatter", "histogram", "bar", "colormap". Default is "scatter". | |||
|- | |- | ||
| data-odb-path || All plot types || Path into the ODB where the data for the plot is stored | | data-odb-path || All plot types || Path into the ODB where the data for the plot is stored | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-x || scatter, histogram || ODB path to X data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path) | | data-x || scatter, histogram, bar || ODB path to X data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path). If the ODB array is a array of strings, switch to a category x-axis displaying the string labels | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-y || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path) | | data-y || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-x1 || scatter, histogram || ODB path to X data for the first graph if several graphs are | | data-x1 || scatter, histogram || ODB path to X data for the first graph if several graphs are present (relative to data-odb-path) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-y1 || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the first graph if several graphs are | | data-y1 || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the first graph if several graphs are present (relative to data-odb-path) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-x<n> || scatter, histogram || ODB path to X data for the <n>-th graph | | data-x<n> || scatter, histogram || ODB path to X data for the <n>-th graph. n = [1...16] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-y<n> || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th graph | | data-y<n> || scatter || ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th graph | ||
|- | |||
| data-x<n>-error || scatter || ODB path to X errors for the <n>-th graph | |||
|- | |||
| data-y<n>-error || scatter || ODB path to Y errors for the <n>-th graph | |||
|- | |- | ||
| data-h || histogram || ODB path to Y data for a histogram (relative to data-odb-path) | | data-h || histogram || ODB path to Y data for a histogram (relative to data-odb-path) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-h<n> || histogram || ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th histogram if several | | data-h<n> || histogram || ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th histogram | ||
|- | |||
| data-stats || scatter, histogram, colormap || Show statistics on upper right corner. Set "1" for display, "0" for no display. Default is "1" | |||
|- | |||
| data-label<n> || scatter, histogram || Label for <n>-th graph or histogram | |||
|- | |||
| data-marker<n>-style || scatter || Marker style for <n>-th graph. One of "none", "circle", "square", "diamond", "pentagon", "triangle-up", "triangle-down", "triangle-left", "triangle-right", "cross", "plus" | |||
|- | |||
| data-line<n>-width || scatter, histogram || Line width in pixel. Zero for no line. | |||
|- | |||
| data-line<n>-style || scatter || Line style. One of "none", "solid", "dashed", "dotted" | |||
|- | |||
| data-bar-width || bar || Width of the bars 0...1. Default is 0.3. At 1 the bars touch each other. | |||
|- | |||
| data-alpha<n> || scatter, histogram || Transparency (alpha) for graph or histogram if several are used. 0 is completely transparent and 1 is opaque. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| data- | | data-zero-color || scatter || Color used for "empty" bins (value < 0.5). Mostly used for 2D histograms to set color of empty bins to white | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-nx || colormap || Number of X bins for a color map. | | data-nx || colormap || Number of X bins for a color map. | ||
| Line 70: | Line 90: | ||
| data-ny || colormap || Number of Y bins for a color map. | | data-ny || colormap || Number of Y bins for a color map. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data- | | data-z || colormap || ODB path to data for a color map (relative to data-odb-path). If data-nx is 3, and data-ny is 4, then data-z must be 12 elements long (one entry for each x,y co-ordinate). Ordering is "loop through all X indices for the lowest Y index before moving to next Y index", e.g. (0,0), (1,0), (2,0), (1,0), (1,1) .... (3,0), (3,1), (3,2). | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-title || All plot types || Title of the graph shown on top | | data-title || All plot types || Title of the graph shown on top | ||
| Line 77: | Line 97: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-y-text || All plot types || Label shown left of the Y-axis | | data-y-text || All plot types || Label shown left of the Y-axis | ||
|- | |||
| data-x-type || scatter || One of "numeric", "datetime", "category". Default is "numeric". "datetime" assumes X data in UNIX time format. "category" expects X data as a string array of text labels in the ODB. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| data-x-min || scatter, histogram || Minimum of the X-axis | | data-x-min || scatter, histogram || Minimum of the X-axis | ||
| Line 93: | Line 115: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| data-z-max || colormap|| Maximum of the Z-axis | | data-z-max || colormap|| Maximum of the Z-axis | ||
|- | |||
| data-z-log || colormap || Use logarithmic Z-axis if "true" | |||
|- | |- | ||
| data-overlay || All plot types || Function which gets called after the graph has been drawn. The function can be used to draw an overlay on the graph. See below for an example. | | data-overlay || All plot types || Function which gets called after the graph has been drawn. The function can be used to draw an overlay on the graph. See below for an example. | ||
|- | |||
| data-event || All plot types || Optional event handler for mouse events. Following parameters are passed to the handler: "event", "this", "ix" and "iy". "event" is the original mouse event, "this" is the reference to the mplot object, and the ix/iy are the colum and row numbers if the plot is a 2D colormap. The event handler can the for example look for "dblclick" events and show information about the current bin. If the event handler returns "true", the framework does not process the mouse event any further. This way one can block the pan/zoom for example. | |||
|- | |||
| data-tooltip || All plot types || Optional user function to create tooltip when hovering over the plot. See below for details. | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 105: | Line 133: | ||
ctx.fillStyle = "red"; | ctx.fillStyle = "red"; | ||
plot.drawTextBox(ctx, "First overlay line\nSecond overlay line", 120, 150); | plot.drawTextBox(ctx, "First overlay line\nSecond overlay line", 120, 150); | ||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
= Mouse event function = | |||
The mouse event function can be used to process all types of mouse events. This example shows the current row and column. | |||
<pre> | |||
// This function will be called if you have 'data-event="mevent"' in your plot's div: | |||
function mevent(event, plot, ix, iy) { | |||
if (event.type === "dblclick) { | |||
// Note ix and iy are only set for 2D plots; for 1D plots they are undefined | |||
console.log(ix + " / " + iy); | |||
return true; // don't process the event any further | |||
} | |||
return false; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
= User-defined tooltip function = | |||
Using the '''data-tooltip="func"''' function, the user might define a custom tooltip generation. The function is called when the mouse hovers over the plot, and passed the current plot object. It then can return a sting for the tooltip to be displayed. Here is an example: | |||
<pre> | |||
// This function will be called if you have a 'data-tooltip="usertooltip"' in your plot's div: | |||
function usertooltip(plotGraph) { | |||
let text = "X=" + plotGraph.marker.x + " Y=" + plotGraph.marker.y; | |||
if (plotGraph.param.plot[0].type === "colormap") | |||
text += " Z=" + plotGraph.marker.z; | |||
return text; | |||
} | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 163: | Line 223: | ||
}, | }, | ||
" | "plots": [ | ||
{ | { | ||
"type": "scatter", | "type": "scatter", | ||
| Line 219: | Line 279: | ||
let y = x.map(x => x*x); // create y array with y_i = x_i^2 | let y = x.map(x => x*x); // create y array with y_i = x_i^2 | ||
p.setData(0, x, y); | p.setData(0, x, y); | ||
</pre> | |||
To create a plot directly from JavaScript code without a <code><div class="mplot" ...></code> HTML element, directly use the MPlotGraph() constructor as | |||
<pre> | |||
let plot = new MPlotGraph(document.getElementById("plotId")); | |||
plot.setData(0, x, y) | |||
</pre> | |||
A set of parameters can be passed to the constructor. This allows to create plots other than a scatter plot with different parameters such as: | |||
<pre> | |||
// create colormap plot with parameters | |||
let param = { | |||
type = "colormap"; | |||
showZScale: true, | |||
nx: 32, | |||
ny: 32, | |||
xMin : -20, | |||
xMax: 20, | |||
yMin: -10, | |||
yMax: 10 | |||
}; | |||
let plot = new MPlotGraph(document.getElementById("plotId"), param); | |||
// create some dummy data | |||
let size = 32; | |||
let z = Array.from({length: size*size}); | |||
for (let y=0 ; y<size ; y++) | |||
for (let x=0 ; x<size ; x++) { | |||
z[y*size + x] = 10 * Math.exp(-(x-size/2)*(x-size/2) / size) * | |||
Math.exp(-(y-size/2)*(y-size/2) / size ); | |||
} | |||
// display dummy data | |||
plot.setData(0, z) | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:03, 21 December 2025
Introduction
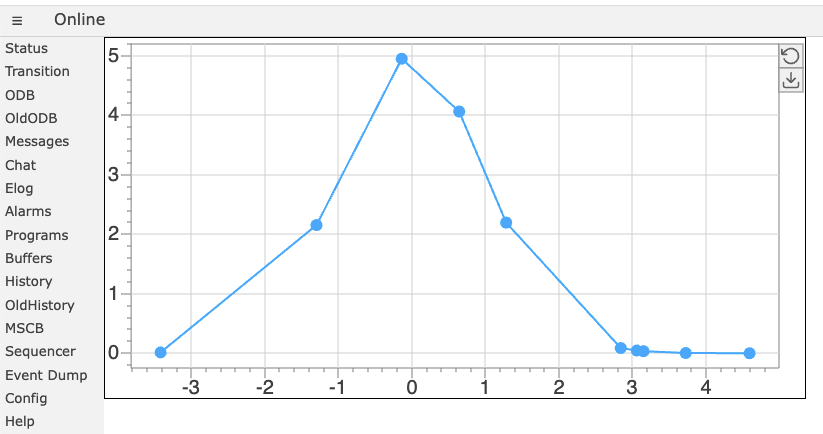
Custom pages may contain custom plots, sich as scatter plots, histograms and color plots. This can be achieved by including the mplot.js library and creating a <div class="mplot"> element. Following example shows the code for a simple page for a scatter plot:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="midas.css">
<script src="controls.js"></script>
<script src="midas.js"></script>
<script src="mhttpd.js"></script>
<script src="mplot.js"></script>
<title>myPage</title>
</head>
<body class="mcss" onload="mhttpd_init('myPage');mplot_init()">
<div id="mheader"></div>
<div id="msidenav"></div>
<div id="mmain">
<div class="mplot" style="height: 360px;width: 700px;"
data-odb-path="/Path/To/Data"
data-x="X" data-y="Y">
</div>
</div>
And here is the resulting page:
The data is stored in the ODB under the X-array /Path/To/Data/X and the Y-array under /Path/To/Data/Y as two float arrays of the same size.
Optional parameters
Several options are possible to modify the plot. Following table gives an overview of the various parameters:
| Parameter | Applies to | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| data-type | All plot types | Type of graph, one of "scatter", "histogram", "bar", "colormap". Default is "scatter". |
| data-odb-path | All plot types | Path into the ODB where the data for the plot is stored |
| data-x | scatter, histogram, bar | ODB path to X data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path). If the ODB array is a array of strings, switch to a category x-axis displaying the string labels |
| data-y | scatter | ODB path to Y data for the first graph (relative to data-odb-path) |
| data-x1 | scatter, histogram | ODB path to X data for the first graph if several graphs are present (relative to data-odb-path) |
| data-y1 | scatter | ODB path to Y data for the first graph if several graphs are present (relative to data-odb-path) |
| data-x<n> | scatter, histogram | ODB path to X data for the <n>-th graph. n = [1...16] |
| data-y<n> | scatter | ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th graph |
| data-x<n>-error | scatter | ODB path to X errors for the <n>-th graph |
| data-y<n>-error | scatter | ODB path to Y errors for the <n>-th graph |
| data-h | histogram | ODB path to Y data for a histogram (relative to data-odb-path) |
| data-h<n> | histogram | ODB path to Y data for the <n>-th histogram |
| data-stats | scatter, histogram, colormap | Show statistics on upper right corner. Set "1" for display, "0" for no display. Default is "1" |
| data-label<n> | scatter, histogram | Label for <n>-th graph or histogram |
| data-marker<n>-style | scatter | Marker style for <n>-th graph. One of "none", "circle", "square", "diamond", "pentagon", "triangle-up", "triangle-down", "triangle-left", "triangle-right", "cross", "plus" |
| data-line<n>-width | scatter, histogram | Line width in pixel. Zero for no line. |
| data-line<n>-style | scatter | Line style. One of "none", "solid", "dashed", "dotted" |
| data-bar-width | bar | Width of the bars 0...1. Default is 0.3. At 1 the bars touch each other. |
| data-alpha<n> | scatter, histogram | Transparency (alpha) for graph or histogram if several are used. 0 is completely transparent and 1 is opaque. |
| data-zero-color | scatter | Color used for "empty" bins (value < 0.5). Mostly used for 2D histograms to set color of empty bins to white |
| data-nx | colormap | Number of X bins for a color map. |
| data-ny | colormap | Number of Y bins for a color map. |
| data-z | colormap | ODB path to data for a color map (relative to data-odb-path). If data-nx is 3, and data-ny is 4, then data-z must be 12 elements long (one entry for each x,y co-ordinate). Ordering is "loop through all X indices for the lowest Y index before moving to next Y index", e.g. (0,0), (1,0), (2,0), (1,0), (1,1) .... (3,0), (3,1), (3,2). |
| data-title | All plot types | Title of the graph shown on top |
| data-x-text | All plot types | Label shown below the X-axis |
| data-y-text | All plot types | Label shown left of the Y-axis |
| data-x-type | scatter | One of "numeric", "datetime", "category". Default is "numeric". "datetime" assumes X data in UNIX time format. "category" expects X data as a string array of text labels in the ODB. |
| data-x-min | scatter, histogram | Minimum of the X-axis |
| data-x-max | scatter, histogram | Maximum of the X-axis |
| data-x-log | scatter, histogram | Use logarithmic X-axis if "true" |
| data-y-min | scatter, histogram | Minimum of the Y-axis |
| data-y-max | scatter, histogram | Maximum of the Y-axis |
| data-y-log | scatter, histogram | Use logarithmic Y-axis if "true" |
| data-z-min | colormap | Minimum of the Z-axis (color axis for color maps) |
| data-z-max | colormap | Maximum of the Z-axis |
| data-z-log | colormap | Use logarithmic Z-axis if "true" |
| data-overlay | All plot types | Function which gets called after the graph has been drawn. The function can be used to draw an overlay on the graph. See below for an example. |
| data-event | All plot types | Optional event handler for mouse events. Following parameters are passed to the handler: "event", "this", "ix" and "iy". "event" is the original mouse event, "this" is the reference to the mplot object, and the ix/iy are the colum and row numbers if the plot is a 2D colormap. The event handler can the for example look for "dblclick" events and show information about the current bin. If the event handler returns "true", the framework does not process the mouse event any further. This way one can block the pan/zoom for example. |
| data-tooltip | All plot types | Optional user function to create tooltip when hovering over the plot. See below for details. |
Overlay function
The overlay function can be used to draw text or graphics on top of the graph. Following function puts a label at the graph:
function overlay(plot, ctx) {
ctx.fillStyle = "red";
plot.drawTextBox(ctx, "First overlay line\nSecond overlay line", 120, 150);
}
Mouse event function
The mouse event function can be used to process all types of mouse events. This example shows the current row and column.
// This function will be called if you have 'data-event="mevent"' in your plot's div:
function mevent(event, plot, ix, iy) {
if (event.type === "dblclick) {
// Note ix and iy are only set for 2D plots; for 1D plots they are undefined
console.log(ix + " / " + iy);
return true; // don't process the event any further
}
return false;
}
User-defined tooltip function
Using the data-tooltip="func" function, the user might define a custom tooltip generation. The function is called when the mouse hovers over the plot, and passed the current plot object. It then can return a sting for the tooltip to be displayed. Here is an example:
// This function will be called if you have a 'data-tooltip="usertooltip"' in your plot's div:
function usertooltip(plotGraph) {
let text = "X=" + plotGraph.marker.x + " Y=" + plotGraph.marker.y;
if (plotGraph.param.plot[0].type === "colormap")
text += " Z=" + plotGraph.marker.z;
return text;
}
JSON parameter set
Instead of defining all parameters with data-xxx tags, the parameters might be defined inside the <div> tag using JSON encoding. Following text gives a complete example of all parameters:
<div class="mplot" style="height: 400px;width: 700px;">
{
"showMenuButtons": true,
"color": {
"background": "#FFFFFF",
"axis": "#808080",
"grid": "#D0D0D0",
"label": "#404040"
},
"title": {
"color": "#404040",
"backgroundColor": "#808080",
"textSize": 20,
"text": "Customized scatter plot"
},
"legend": {
"show": true,
"color": "#D0D0D0",
"backgroundColor": "#FFFFFF",
"textColor": "#404040",
"textSize": 16
},
"xAxis": {
"log": false,
"min": -10,
"max": 10,
"grid": true,
"textSize": 10,
"title": {
"text": "x [mm]",
"textSize" : 14
}
},
"yAxis": {
"log": false,
"min": -10,
"max": 10,
"grid": true,
"textSize": 10,
"title": {
"text": "Scaler [Hz]",
"textSize" : 10
}
},
"plots": [
{
"type": "scatter",
"getFromODB": true,
"odbPath": "/System/Tmp/Plot",
"x": "X2",
"y": "Y2",
"label": "High threshold",
"marker": {
"draw": true,
"lineColor": 3,
"fillColor": 3,
"style": "cross",
"size": 10,
"lineWidth": 2
},
"line": {
"draw": false,
"fill": true,
"color": 0,
"style": "solid",
"width": 1
}
}
]
}
</div>
The parameter list does not have to be complete. Any existing parameter in this list is combined with the internal default parameter set. The colors might be either a direct color like "red" or "#FF0000", or an index to the list of 16 internal colors, which have to be chosen to be as far apart as possible in color space.
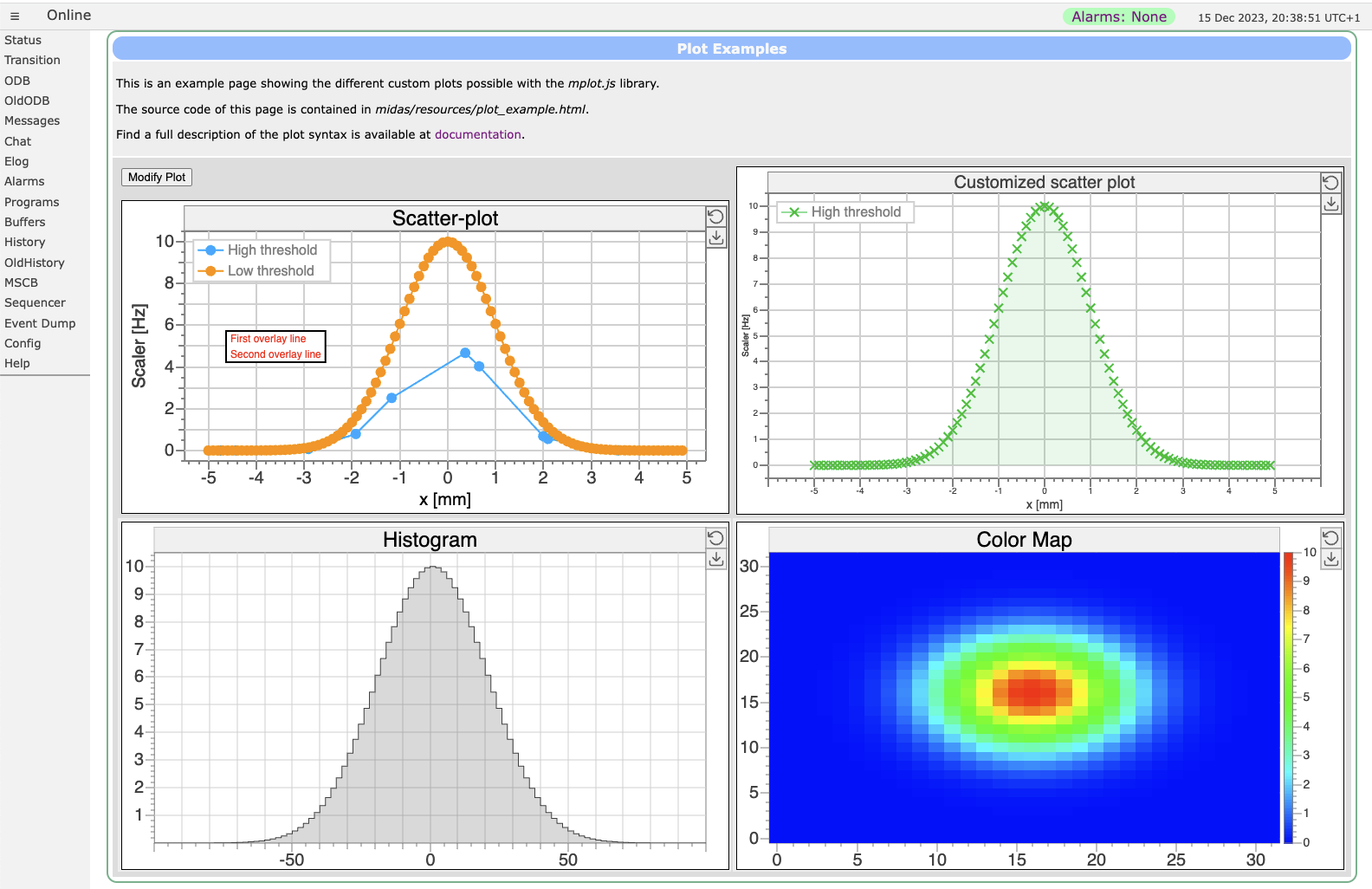
More examples
More plot examples are contained in the plot_example.html file in the midas/resource/ directory which produces following page:
Setting parameters and data programmatically
To set the parameters of a plot via JavaScript code, simply access the plot object and modify its parameters like
let p = document.getElementById("MyPlot").mpg; // obtain plot from ID
p.param.title.text = "Different titel"; // change plot title
p.param.plot[0].line.color = 2; // change line color of first plot to index 2
To change the data of the plot, use the function setData(index, x, y) for scatter plots or setData(index, h) for histograms like
let p = document.getElementById("MyPlot").mpg; // obtain plot from ID
let x = Array.from({length: 20}, (_, i) => i); // create x array with 20 elements 0,1,2,...19
let y = x.map(x => x*x); // create y array with y_i = x_i^2
p.setData(0, x, y);
To create a plot directly from JavaScript code without a <div class="mplot" ...> HTML element, directly use the MPlotGraph() constructor as
let plot = new MPlotGraph(document.getElementById("plotId"));
plot.setData(0, x, y)
A set of parameters can be passed to the constructor. This allows to create plots other than a scatter plot with different parameters such as:
// create colormap plot with parameters
let param = {
type = "colormap";
showZScale: true,
nx: 32,
ny: 32,
xMin : -20,
xMax: 20,
yMin: -10,
yMax: 10
};
let plot = new MPlotGraph(document.getElementById("plotId"), param);
// create some dummy data
let size = 32;
let z = Array.from({length: size*size});
for (let y=0 ; y<size ; y++)
for (let x=0 ; x<size ; x++) {
z[y*size + x] = 10 * Math.exp(-(x-size/2)*(x-size/2) / size) *
Math.exp(-(y-size/2)*(y-size/2) / size );
}
// display dummy data
plot.setData(0, z)