MIDAS Event Construction: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==MIDAS event construction== The MIDAS Event Structure is a variable length event format. It uses banks as subsets of an eve...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Midas Data Types]] | [[Midas Data Types]] | ||
==Creation of MIDAS banks== | |||
[[MIDAS Event Structure #MIDAS Data Bank |MIDAS banks]] may be created in the [[Frontend Operation#Frontend]] user readout code with calls to the MIDAS library. | |||
The following routines are available in the MIDAS package : | |||
- | * ''bk_init()'' Initializes a bank structure in an event. | ||
* ''bk_init32()'' Initializes a bank structure in an event. '''bk_init32()''' can be used to reduce the size of very large banks, where the data will fit into a 32-bit word | |||
* ''bk_create()'' Creates a bank with a given name (exactly four characters) | |||
* ''bk_close()'' Closes a bank previously opened with bk_create(). | |||
* ''bk_locate()'' Locates a bank within an event by its name. | |||
* ''bk_iterate()'' Returns bank and data pointers to each bank in the event. | |||
* ''bk_list()'' Constructs a string with all the banks' names in the event. | |||
* ''bk_size()'' Returns the size in bytes of all banks including the bank headers in an event. | |||
=== Example === | |||
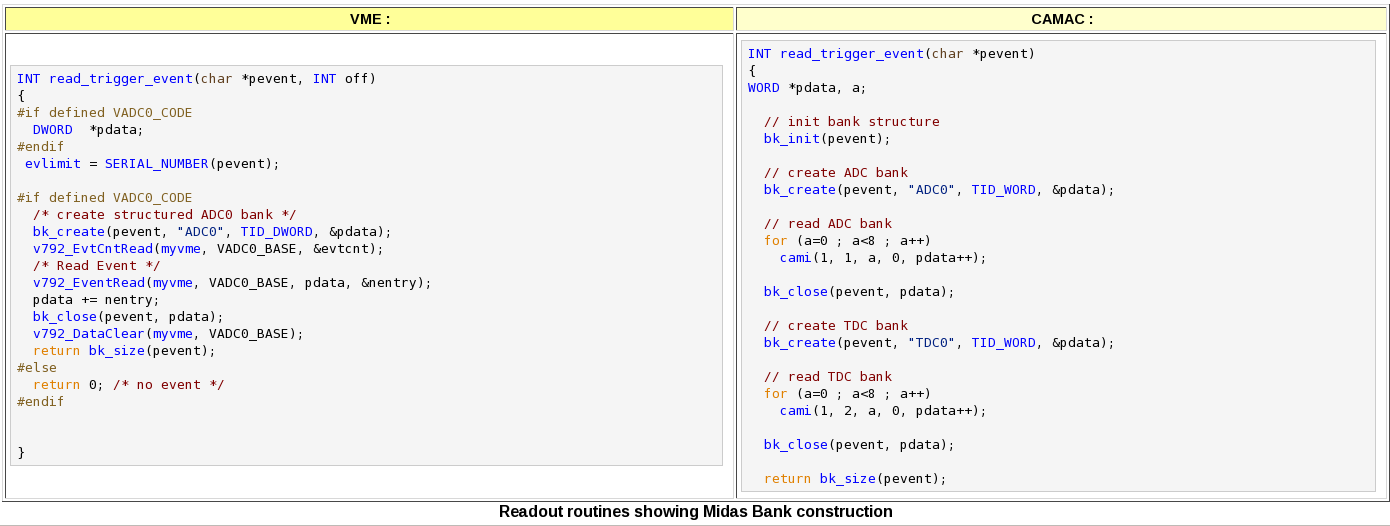
Examples showing the creation of MIDAS banks for VME and CAMAC hardware are shown below. | |||
The VME example reads out a VME ADC module into one MIDAS bank. In the CAMAC example the event will contain two banks: one for the ADC data and one for the TDC data. | |||
[[File:Example1.png]] | |||
Revision as of 01:24, 24 October 2013
MIDAS event construction
The MIDAS Event Structure is a variable length event format. It uses banks as subsets of an event.
Usually a bank contains an array of values that logically belong together. For example, an experiment can generate an ADC bank, a TDC bank and a bank with trigger information. The length of a bank can vary from one event to another due to zero suppression from the hardware. Besides the variable data length support of the bank structure, another main advantage is the possibility for the analyzer to add more (calculated) banks during the analysis process to the event in process. After the first analysis stage, the event can contain in addition to the the raw ADC bank, a bank with calibrated ADC values called CADC for example. In this CADC bank the raw ADC values could be offset or gain-corrected.
Creation of MIDAS banks
MIDAS banks may be created in the Frontend Operation#Frontend user readout code with calls to the MIDAS library. The following routines are available in the MIDAS package :
- bk_init() Initializes a bank structure in an event.
- bk_init32() Initializes a bank structure in an event. bk_init32() can be used to reduce the size of very large banks, where the data will fit into a 32-bit word
- bk_create() Creates a bank with a given name (exactly four characters)
- bk_close() Closes a bank previously opened with bk_create().
- bk_locate() Locates a bank within an event by its name.
- bk_iterate() Returns bank and data pointers to each bank in the event.
- bk_list() Constructs a string with all the banks' names in the event.
- bk_size() Returns the size in bytes of all banks including the bank headers in an event.
Example
Examples showing the creation of MIDAS banks for VME and CAMAC hardware are shown below.
The VME example reads out a VME ADC module into one MIDAS bank. In the CAMAC example the event will contain two banks: one for the ADC data and one for the TDC data.