RPI3: Difference between revisions
| (86 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Raspberry Pi3 = | = Raspberry Pi3 = | ||
= Links = | |||
* | * https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspios_full_armhf/release_notes.txt | ||
= On-board hardware = | |||
* AAA | * AAA | ||
= Serial console = | |||
there is no useful serial console | there is no useful serial console | ||
= Benchmarks = | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
= Original boot files with the CentOS 7.1 userland = | |||
NOTE: CentOS-7 userland is now obsolete. use Raspbian userland instead! | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 119: | Line 121: | ||
[root@armdaq05 ~]# | [root@armdaq05 ~]# | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
= Create bootable SD card = | |||
Original boot files are in daqstore:/daq/daqstore/olchansk/daq/RPI3: | |||
<pre> | |||
rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+ | |||
rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+ | |||
</pre> | |||
* use 32GB micro-SD flash | |||
* connect to USB-to-SD flash adapter, plug into linux computer | |||
* login as root | |||
* identify the /dev/sdXXX device corresponding to target media: use "fdisk -l", look for a 32GB disk with a single MS-DOS partition | |||
* ensure the partitions of /dev/sdXXX are not mounted, use "df -kl" and umount /dev/sdXXX1, etc. | |||
* run "fdisk /dev/sdXXX" | |||
* create MSDOS partition table: command "o" | |||
* create first partition 64Mbytes: command "n", primary "p", first sector "<enter>", last sector: "+64M" | |||
* set partition type "C": command "t", partition 1 is selected automatically, hex code "c" | |||
* mark bootable: command "a", partition 1 is selected automatically | |||
* confirm correct layout: command "p" | |||
<pre> | |||
Disk /dev/sde: 31.1 GB, 31104958464 bytes, 60751872 sectors | |||
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System | |||
/dev/sde1 * 2048 133119 65536 c W95 FAT32 (LBA) | |||
</pre> | |||
* save new partition table: command "w", there should be no messages other than "syncing disks" | |||
* mkfs.msdos /dev/sdXXX1 | |||
* mkdir -p /mnt/tmp | |||
* mount /dev/sdXXX1 /mnt/tmp, cd /mnt/tmp | |||
* rsync -av /daq/daqstore/olchansk/daq/RPI3/rpi3-boot-XXX/ . | |||
* sync | |||
* select boot method: | |||
** cp cmdline-mmcblk.txt cmdline.txt ### to boot from SD flash | |||
** cp cmdline-nfsroot.txt cmdline.txt ### to boot from network (dhcp and nfsroot) | |||
* sync | |||
* cd /; umount /mnt/tmp | |||
* eject /dev/sdXXX | |||
* try to boot from the SD flash - on HDMI video, should see Linux kernel boot all the way to a panic on failure to mount rootfs. | |||
= cmdline.txt = | |||
cmdlinux.txt provides the linux kernel command line parameters. | |||
* rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+/cmdline-mmcblk.txt - boot from SD card | |||
<pre> | |||
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait | |||
</pre> | |||
* rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+/cmdline-nfsroot.txt - boot from NFS | |||
<pre> | |||
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs elevator=deadline panic=60 | |||
</pre> | |||
* rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+/cmdline-mmcblk.txt - boot form SD card | |||
<pre> | |||
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 root=PARTUUID=641f3e0d-02 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait quiet splash plymouth.ignore-serial-consoles | |||
</pre> | |||
* rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+/cmdline-nfsroot.txt - boot from NFS | |||
<pre> | |||
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 elevator=deadline ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs panic=60 | |||
</pre> | |||
= Create bootable CentOS7 SD card = | |||
NOTE: CentOS-7 userland is now obsolete. Use Rapsbian userland instead!!! | |||
* use a 32 GB micro-SD flash card | |||
* go through the steps to create a bootable SD flash card (see above) | |||
* connect and identify /dev/sdXXX same as above | |||
* ensure all partitions are unmounted, same as above | |||
* create second partion of maximum size: | |||
* fdisk /dev/sdXXX | |||
* command "n", "p", enter, enter | |||
* command "p" to see the layout: | |||
<pre> | |||
Disk /dev/sde: 31.1 GB, 31104958464 bytes, 60751872 sectors | |||
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System | |||
/dev/sde1 * 2048 133119 65536 c W95 FAT32 (LBA) | |||
/dev/sde2 133120 60751871 30309376 83 Linux | |||
</pre> | |||
* command "w" to save the changes | |||
* if it complains about "Device or resource busy": | |||
** eject /dev/sdXXX | |||
** remove it from usb adapter | |||
** connect to usb adapter and identify device again, same as above | |||
* ls -l /dev/sdXXX* to see there are two partitions "1" and "2" | |||
* mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdXXX2 | |||
* mkdir -p /mnt/tmp | |||
* mount /dev/sdXXX2 /mnt/tmp, cd /mnt/tmp | |||
* rsync -av /ladd/data0/backup.os/armdaq06/ . | |||
* e2label /dev/sdXXX2 el7 | |||
* sync | |||
* cd /; umount /mnt/tmp | |||
* eject /dev/sdXXX | |||
* try to boot, should boot all the way to the login prompt. | |||
= Create bootable Raspbian SD card = | |||
Two ways: | |||
* download and "dd" the Raspbian OS image (then customize it per Raspbian and Ubuntu instructions) | |||
* clone an already customized Raspbian image | |||
To clone a customized image: | |||
* use a 32 GB micro-SD flash card | |||
* make it bootable (see instructions above, select cmdlinux-mmcblk.txt) | |||
* add the Raspbian userland (follow CentOS-7 instructions above, but rsync Raspbian image instead of CentOS-7 image) | |||
= Network-boot Raspbian = | |||
Prepare the boot server in the usual way: | |||
* setup dhcpd or dnsmasq to serve the IP address and the NFS-Root mount path for the userland image | |||
* tftp is not used, is not needed | |||
* setup NFS server to permit mounting the userland image. in /etc/exports have this: | |||
<pre> | |||
/nfsroot @xxx_netgroup(rw,no_root_squash,async) | |||
</pre> | |||
* do not forget to enable dhcpd/dmsmasq and NFS to start on boot | |||
* do not forget to run "exportfs -rv" and "systemctl restart dhcpd" after making any changes | |||
Prepare a bootable SD card | |||
* use SD card of any size (8 GB or bigger) | |||
* follow instructions to make it bootable | |||
* select cmdline-nfsroot.txt | |||
<pre> | |||
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs panic=60 | |||
</pre> | |||
Install bootable SD card into RPi, power up, and observe: | |||
* RPi boots linux kernel | |||
* linux kernel starts | |||
* makes DHCP request, receives answer | |||
* RPi pings | |||
* RPi mounts the NFS-Root filesystem as specified by DHCP | |||
* RPi OS boots normally | |||
* there is a login prompt | |||
* from boot server, RPi pings and ssh'es. | |||
= Setup Python i2c tools = | |||
NOTE: DO NOT DO THIS! | |||
<pre> | |||
su - root | |||
yum install python-setuptools.noarch | |||
yum install python-cffi | |||
yum install python-devel | |||
cd git | |||
git clone https://github.com/bivab/smbus-cffi.git | |||
cd smbus-cffi | |||
python setup.py install | |||
</pre> | |||
= Enable i2c drivers = | |||
NOTE: DO NOT DO THIS! | |||
<pre> | |||
(already done) edit boot config.txt, uncomment "dtparam=i2c_arm=on" and "dtparam=i2c1=on", reboot | |||
echo modprobe i2c-dev >> /etc/rc.local | |||
echo modprobe i2c_bcm2708 >> /etc/rc.local | |||
ls -l /dev/i2c* | |||
i2cdetect -l | |||
i2cdetect 1 | |||
echo chmod a+wr /dev/i2c* >> /etc/rc.local | |||
reboot, run i2cdetect again. | |||
</pre> | |||
= Script for creating boot files = | |||
~olchansk/git/scripts/clone/boot_rpi3.perl | |||
= Boot modes = | |||
See https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/hardware/raspberrypi/bootmodes/msd.md and https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/hardware/raspberrypi/bootmodes/bootflow_2711.md | |||
* RPi2, RPi3B - SD flash is the default. USB mass storage boot is disabled, but can be enabled. | |||
* RPi3B+ - default boot order: SD flash, USB boot | |||
* RPi4B - boots from internal SPI EEPROM (see recovery.bin). continues booting from SD flash. network boot (DHCP+TFTP), firmware 2020-xx-yy. (how to enable?). usb mass storage boot (not available as of 2020-apr-21). | |||
= Raspbian OS = | |||
Recommended RaspberryPi OS is "Raspbian". | |||
== Rapsbian images and kernel versions == | |||
* 2016-09-23-raspbian-jessie-lite : Linux version 4.4.21+ | |||
* 2020-05-27-raspios-buster-lite-armhf : Linux version 4.19.118-v8+ | |||
* 2021-01-11-raspios-buster-armhf-lite : ??? | |||
* 2021-03-04-raspios-buster-armhf-lite : Linux version 5.10.17-v7+ | |||
== Raspbian boot from SD card == | |||
* download here https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/ | |||
* unzip, dd to a 32GB SD flash card | |||
* insert card into RPi3, power up, it will boot into login prompt | |||
* default user: pi, password: raspbian, login change default password, install ssh keys for user pi and user root. | |||
* change default keyboard layout from UK (with the pound key): vi /etc/default/keyboard, set XKBLAYOUT="us" | |||
* change default locale from UK to "C" (en_US.UTF8 does not seem to be available): vi /etc/default/locale, set LANG=C.UTF-8 | |||
* enable ssh server: apt-get install openssh-server, systemctl enable sshd.service, systemctl start sshd.service | |||
* reboot: shutdown -r now | |||
* RJ45 ethernet network will autoconfigure by DHCP, ssh pi@... and root@... should work | |||
* login as root, install missing packages: | |||
** apt-get update | |||
** apt-get install git emacs xemacs21 cmake | |||
* install additional packages as needed as listed here: https://daq.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian and here: https://daq.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Ubuntu | |||
= Backport python3-yaml to Debian Buster = | |||
Debian Bullseye ships pyYAML 5.3.1, it is relatively easy to build the package for Debian Buster. | |||
1. Downlowd | |||
http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/pyyaml/pyyaml_5.3.1.orig.tar.gz | |||
and | |||
http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/pyyaml/pyyaml_5.3.1-1.debian.tar.xz | |||
from https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-yaml (under "Download Source Package"). Note the bullseye in the URL. | |||
2. Unpack pyyaml_5.3.1.orig.tar.gz and, inside the PyYAML-5.3.1 directory, pyyaml_5.3.1-1.debian.tar.xz. | |||
3. Install some dependencies needed for the build: | |||
sudo apt install python3-all-dev python3-all-dbg libyaml-dev cython cython-dbg python-all-dev python-all-dbg | |||
sudo apt install dpkg-dev | |||
4. Build the package (on the target architecture) | |||
sudo dpkg-buildpackage -us -uc -nc | |||
= Openbox X Session = | |||
Have a look in /etc/xdg/openbox | |||
= Custom Raspbian Images = | |||
The official tool used raspberrypi.org is available here: https://github.com/RPi-Distro/pi-gen | |||
It is working out of the box with Debian bullseye. The tool is built around [https://wiki.debian.org/Debootstrap debootstrap], all packages are pulled from http://archive.raspbian.org/ (not the official debian repos!). | |||
The user has to provide a config file named "config" in the root directory. For instance: | |||
<pre> | |||
IMG_NAME=MVM_GUI_TRIUMF | |||
RELEASE=buster | |||
DEPLOY_ZIP=0 | |||
USE_QEMU=0 | |||
LOCALE_DEFAULT=C.UTF-8 | |||
TARGET_HOSTNAME=mvm_gui | |||
KEYBOARD_KEYMAP=us | |||
KEYBOARD_LAYOUT="English (US)" | |||
TIMEZONE_DEFAULT="America/Vancouver" | |||
FIRST_USER_NAME="mvm" | |||
FIRST_USER_PASS="gui" | |||
ENABLE_SSH=0 | |||
STAGE_LIST="stage0 stage1 stage2 stage3 stage4" | |||
</pre> | |||
To build the image, simply run ./build.sh and wait. | |||
== MVM example == | |||
Let's build an image tailored to the MVM GUI. The assumes the user is running Debian bullseye. | |||
=== Optional Step: Setup a Local APT Cache === | |||
A local cache speeds-up things if you have to (re)build multiple images. | |||
The procedure supposes that you have docker and docker-compose installed on the build machine. | |||
In the root directory, run | |||
<pre> | |||
apt install docker-compose ### Ubuntu LTS 18.04 | |||
docker-compose up -d | |||
</pre> | |||
Add the line | |||
APT_PROXY=http://172.17.0.1:3142 | |||
to the config file | |||
=== Main Procedure === | |||
Install dependencies (Debian): | |||
<pre> | |||
sudo apt install coreutils quilt parted qemu-user-static debootstrap zerofree zip \ | |||
dosfstools bsdtar libcap2-bin grep rsync xz-utils file git curl bc | |||
</pre> | |||
Install dependancies (Ubuntu LTS 18.04) | |||
<pre> | |||
ssh root@... | |||
apt-get install quilt qemu-user-static debootstrap zerofree bsdtar curl | |||
</pre> | |||
Clone the TRIUMF repo: | |||
<pre> | |||
https://gitlab.triumf.ca/mvmdev/GUIAutoBuild --single-branch slim-raspbian-buster | |||
</pre> | |||
Run: | |||
<pre> | |||
LANG=C.UTF-8 ./build.sh | |||
</pre> | |||
Wait ... the images will be saved in the deploy directory. | |||
= GPIO = | |||
== wiringpi == | |||
* apt-get install wiringpi | |||
* gpio readall | |||
* gpio mode 24 output | |||
* gpio write 24 1 | |||
* gpio write 24 0 | |||
== pinctrl == | |||
<pre> | |||
root@dlpi:~# pinctrl get 18 | |||
18: ip pd | lo // GPIO18 = input | |||
root@dlpi:~# pinctrl set 18 op dh ### drives 3.3V | |||
root@dlpi:~# pinctrl set 18 op dl ### drives 0V | |||
</pre> | |||
= SPI = | |||
* if there is no /dev/spidev0.0 and /dev/spidev0.1, edit /boot/config.txt, uncomment dtparam=spi=on, reboot | |||
* CS pins are: | |||
** CE0 is J8 pin 24 (GPIO8) is /dev/spidev0,0 | |||
** CE1 is J8 pin 26 (GPIO7) is /dev/spidev0,1 | |||
* https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/Documentation/spi/spidev.rst | |||
* https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54923582/spi-ioc-messagen-on-raspberry-pi-3 | |||
* https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v4.14/driver-api/spi.html#c.spi_message | |||
= I2C = | |||
* if there is no /dev/i2c*: | |||
** mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /boot | |||
** edit /boot/config.txt, uncomment "dtparam=i2c_arm=on" | |||
** run "echo i2c_dev >> /etc/modules-load.d/i2c_dev.conf" | |||
** umount /boot | |||
** reboot | |||
** after reboot check that i2c_dev and i2c_bcm2835 modules are loaded: | |||
<pre> | |||
root@lvdb04:~# lsmod | grep i2c | |||
i2c_dev 20480 0 | |||
i2c_bcm2835 16384 0 | |||
root@lvdb04:~# | |||
</pre> | |||
* if no permission to open /dev/i2c*: | |||
** edit /etc/group, add your user to group "i2c", for example: | |||
<pre> | |||
root@lvdb04:~# grep i2c /etc/group | |||
i2c:x:998:pi,agdaq | |||
root@lvdb04:~# | |||
</pre> | |||
** logout, login again (/etc/group is applied at login time) | |||
* apt-get install python-smbus i2c-tools | |||
* i2cdetect -y 1 ### found device at address 0x70: | |||
<pre> | |||
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | |||
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
70: 70 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | |||
</pre> | |||
= PWM = | |||
We will enable PWM output on GPIO 18. | |||
* add to /boot/firmware/config.txt, reboot | |||
<pre> | |||
dtoverlay=pwm,pin=18,func=2 | |||
</pre> | |||
* driver should now exist: | |||
<pre> | |||
root@dlpi:~# ls -l /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/ | |||
total 0 | |||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 device -> ../../../fe20c000.pwm | |||
--w--w---- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 export | |||
-r--r--r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 npwm | |||
drwxrwxr-x 2 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 power | |||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 subsystem -> ../../../../../../class/pwm | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 uevent | |||
--w--w---- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 unexport | |||
root@dlpi:~# | |||
</pre> | |||
* create pwm0 | |||
<pre> | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 0 >> /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export | |||
root@dlpi:~# ls -l /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/ | |||
total 0 | |||
-r--r--r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 capture | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 duty_cycle | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 enable | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 period | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 polarity | |||
drwxrwxr-x 2 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:38 power | |||
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 uevent | |||
</pre> | |||
* output something: | |||
<pre> | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 240000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/period | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 120000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/enable | |||
</pre> | |||
* on the scope: | |||
<pre> | |||
square wave, period 240 us, on time 120 us | |||
</pre> | |||
* on the RPi4, go faster: | |||
<pre> | |||
period granularity is 20 ns, smallest is value 40 (40 ns) | |||
duty_cycle granularity is 20 ns, smallest is value 20 (19.6 ns) | |||
fastest waveform is: | |||
period 40, duty_cycle 10 -> on time 19.6 ns, period 40 ns | |||
</pre> | |||
* settinggs for DLDB pulser, 50 kHz, ~10 ns apparent pulse width | |||
<pre> | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 1000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle | |||
root@dlpi:~# echo 20000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/period | |||
</pre> | |||
= WiFi and Bluetooth = | |||
The WiFi and Bluetooth interfaces can be disabled in the boot/config.txt. As a side effect, the [http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0183g/index.html PL011] UART is re-routed to the GPIOs 14 and 15. By default, the UART is used by the BT modem. | |||
One has to disable the BT modem initialization service to avoid conflicts. | |||
<pre> | |||
systemctl disable hciuart | |||
</pre> | |||
Note: there is a second "MiniUART" aviabale on the Rpi, but its fonctionally are very limited. See https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/uart.md | |||
<pre> | |||
# Disables the Bluetooth device (also restores UART0/ttyAMA0 to GPIOs 14 and 15). | |||
dtoverlay=disable-bt | |||
dtoverlay=disable-wifi | |||
</pre> | |||
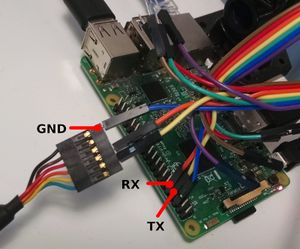
= RS232 = | |||
The Rpi3 has two serial interfaces (https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/uart.md). Levels are *3.3V*. | |||
[[File:Rpi3 rs232 3 3v.jpg|thumb|Rpi3 RS233 3.3V wiring with a standard TTL-232R to USB serial cable (FTDI chip)]] | |||
= Update RPi firmware = | |||
Please go here: | |||
https://daq00.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian#install_RPi4_from_scratch | |||
!!! check that SD card is mounted as /boot/firmware !!! | |||
<pre> | |||
apt update | |||
apt upgrade ### install latest eeprom | |||
rpi-eeprom-update -a | |||
</pre> | |||
= RPi4 boot from network = | |||
Please go here: | |||
https://daq00.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian#install_RPi4_from_scratch | |||
* run raspi-config, in advanced options, set boot order to network-first | |||
* reboot | |||
* check that the change took | |||
<pre> | |||
root@magpi03:~# vcgencmd bootloader_config | |||
[all] | |||
BOOT_UART=0 | |||
WAKE_ON_GPIO=1 | |||
POWER_OFF_ON_HALT=0 | |||
[all] | |||
BOOT_ORDER=0xf21 | |||
</pre> | |||
* shutdown, power off the RPi4 | |||
* remove SD card | |||
* power up | |||
* tail -100f /var/log/syslog | |||
* observe RPi4 does DHCP and requests files from /tftpboot/SERIALNUMBER/ | |||
* give it files it want, copy the from the SD card /boot/firmware | |||
* copy all of /boot/firmware/overlays to /tftpboot/... | |||
* symlink kernel8.img and initramfs8 to files in /nfsroot/ | |||
* should have this: | |||
<pre> | |||
root@haicudaq01:~# ls -l /tftpboot/c914e0e6/ | |||
total 1732 | |||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 56112 Nov 26 15:43 bcm2711-rpi-4-b.dtb | |||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 70 Nov 26 15:43 cmdline.txt | |||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1245 Nov 26 15:40 config.txt | |||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5456 Nov 26 15:42 fixup4.dat | |||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 27 Nov 26 15:47 initramfs8 -> /nfsroot/magpi03/initrd.img | |||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 Nov 26 15:47 kernel8.img -> /nfsroot/magpi03/vmlinuz | |||
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 339 Oct 22 06:05 overlays | |||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2259296 Nov 26 15:37 start4.elf | |||
root@haicudaq01:~# | |||
</pre> | |||
* cycle power on the RPi4, it should boot from the network (SD card removed) | |||
* not so fast. it did not boot all the way, ssh does not work. | |||
* go to /nfsroot/magpi03/etc/fstab, edit /boot/firmware to have "nofail" otherwise boot will stall at mounting the removed SD card: | |||
<pre> | |||
/dev/mmcblk0p1 /boot/firmware vfat defaults,nofail 0 2 | |||
</pre> | |||
* cycle power on RPi4 again, now it should boot all the way to ssh | |||
* ssh magpi03 | |||
* disable swap (swap to NFS does not/cannot work) | |||
<pre> | |||
systemctl stop dphys-swapfile | |||
systemctl disable dphys-swapfile | |||
rm /var/swap | |||
</pre> | |||
* done | |||
= End = | |||
Latest revision as of 00:46, 27 March 2025
Raspberry Pi3
Links
On-board hardware
- AAA
Serial console
there is no useful serial console
Benchmarks
[root@armdaq05 ~]# uname -a Linux armdaq05.triumf.ca 4.4.21-v7+ #911 SMP Thu Sep 15 14:22:38 BST 2016 armv7l armv7l armv7l GNU/Linux [root@armdaq05 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 4 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 38.40 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 1 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 4 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 38.40 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 2 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 4 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 38.40 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 processor : 3 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 4 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 38.40 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd03 CPU revision : 4 Hardware : BCM2709 Revision : a22082 Serial : 00000000852ec765 [root@armdaq05 ~]#
[root@armdaq05 ~]# ./memcpy_arm memcpy 1 KiBytes: 710 MB/sec memcpy 2 KiBytes: 1037 MB/sec memcpy 4 KiBytes: 1340 MB/sec memcpy 8 KiBytes: 1572 MB/sec memcpy 16 KiBytes: 1703 MB/sec memcpy 32 KiBytes: 2010 MB/sec memcpy 64 KiBytes: 1780 MB/sec memcpy 128 KiBytes: 1808 MB/sec memcpy 256 KiBytes: 1421 MB/sec memcpy 512 KiBytes: 971 MB/sec memcpy 1024 KiBytes: 862 MB/sec memcpy 2048 KiBytes: 824 MB/sec memcpy 4096 KiBytes: 862 MB/sec memcpy 8192 KiBytes: 817 MB/sec memcpy 16384 KiBytes: 797 MB/sec memcpy 32768 KiBytes: 767 MB/sec memcpy 65536 KiBytes: 765 MB/sec memcpy 131072 KiBytes: 766 MB/sec [root@armdaq05 ~]#
Original boot files with the CentOS 7.1 userland
NOTE: CentOS-7 userland is now obsolete. use Raspbian userland instead!
[root@armdaq05 ~]# blkid
/dev/mmcblk0p1: SEC_TYPE="msdos" LABEL="boot" UUID="70F7-FA1D" TYPE="vfat"
/dev/mmcblk0p2: LABEL="el7" UUID="0ca625c5-8db1-4f78-a9fd-e6cce04f399e" TYPE="ext4"
/dev/mmcblk0: PTTYPE="dos"
[root@armdaq05 ~]#
[root@armdaq05 ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/mmcblk0: 31.4 GB, 31439454208 bytes, 61405184 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x5a7089a1
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/mmcblk0p1 8192 137215 64512 c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
/dev/mmcblk0p2 137216 2713599 1288192 83 Linux
[root@armdaq05 ~]#
[root@armdaq05 ~]# df -kl
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/root 1235136 1029272 125072 90% /
devtmpfs 469536 0 469536 0% /dev
tmpfs 473868 0 473868 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 473868 29964 443904 7% /run
tmpfs 473868 0 473868 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
tmpfs 94776 0 94776 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mmcblk0p1 64456 21192 43264 33% /mnt/tmp
[root@armdaq05 ~]#
Create bootable SD card
Original boot files are in daqstore:/daq/daqstore/olchansk/daq/RPI3:
rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+ rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+
- use 32GB micro-SD flash
- connect to USB-to-SD flash adapter, plug into linux computer
- login as root
- identify the /dev/sdXXX device corresponding to target media: use "fdisk -l", look for a 32GB disk with a single MS-DOS partition
- ensure the partitions of /dev/sdXXX are not mounted, use "df -kl" and umount /dev/sdXXX1, etc.
- run "fdisk /dev/sdXXX"
- create MSDOS partition table: command "o"
- create first partition 64Mbytes: command "n", primary "p", first sector "<enter>", last sector: "+64M"
- set partition type "C": command "t", partition 1 is selected automatically, hex code "c"
- mark bootable: command "a", partition 1 is selected automatically
- confirm correct layout: command "p"
Disk /dev/sde: 31.1 GB, 31104958464 bytes, 60751872 sectors Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sde1 * 2048 133119 65536 c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
- save new partition table: command "w", there should be no messages other than "syncing disks"
- mkfs.msdos /dev/sdXXX1
- mkdir -p /mnt/tmp
- mount /dev/sdXXX1 /mnt/tmp, cd /mnt/tmp
- rsync -av /daq/daqstore/olchansk/daq/RPI3/rpi3-boot-XXX/ .
- sync
- select boot method:
- cp cmdline-mmcblk.txt cmdline.txt ### to boot from SD flash
- cp cmdline-nfsroot.txt cmdline.txt ### to boot from network (dhcp and nfsroot)
- sync
- cd /; umount /mnt/tmp
- eject /dev/sdXXX
- try to boot from the SD flash - on HDMI video, should see Linux kernel boot all the way to a panic on failure to mount rootfs.
cmdline.txt
cmdlinux.txt provides the linux kernel command line parameters.
- rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+/cmdline-mmcblk.txt - boot from SD card
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait
- rpi3-boot-4.4.21-v7+/cmdline-nfsroot.txt - boot from NFS
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs elevator=deadline panic=60
- rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+/cmdline-mmcblk.txt - boot form SD card
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 root=PARTUUID=641f3e0d-02 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait quiet splash plymouth.ignore-serial-consoles
- rpi3-boot-5.10.17-v7+/cmdline-nfsroot.txt - boot from NFS
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 elevator=deadline ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs panic=60
Create bootable CentOS7 SD card
NOTE: CentOS-7 userland is now obsolete. Use Rapsbian userland instead!!!
- use a 32 GB micro-SD flash card
- go through the steps to create a bootable SD flash card (see above)
- connect and identify /dev/sdXXX same as above
- ensure all partitions are unmounted, same as above
- create second partion of maximum size:
- fdisk /dev/sdXXX
- command "n", "p", enter, enter
- command "p" to see the layout:
Disk /dev/sde: 31.1 GB, 31104958464 bytes, 60751872 sectors Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sde1 * 2048 133119 65536 c W95 FAT32 (LBA) /dev/sde2 133120 60751871 30309376 83 Linux
- command "w" to save the changes
- if it complains about "Device or resource busy":
- eject /dev/sdXXX
- remove it from usb adapter
- connect to usb adapter and identify device again, same as above
- ls -l /dev/sdXXX* to see there are two partitions "1" and "2"
- mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdXXX2
- mkdir -p /mnt/tmp
- mount /dev/sdXXX2 /mnt/tmp, cd /mnt/tmp
- rsync -av /ladd/data0/backup.os/armdaq06/ .
- e2label /dev/sdXXX2 el7
- sync
- cd /; umount /mnt/tmp
- eject /dev/sdXXX
- try to boot, should boot all the way to the login prompt.
Create bootable Raspbian SD card
Two ways:
- download and "dd" the Raspbian OS image (then customize it per Raspbian and Ubuntu instructions)
- clone an already customized Raspbian image
To clone a customized image:
- use a 32 GB micro-SD flash card
- make it bootable (see instructions above, select cmdlinux-mmcblk.txt)
- add the Raspbian userland (follow CentOS-7 instructions above, but rsync Raspbian image instead of CentOS-7 image)
Network-boot Raspbian
Prepare the boot server in the usual way:
- setup dhcpd or dnsmasq to serve the IP address and the NFS-Root mount path for the userland image
- tftp is not used, is not needed
- setup NFS server to permit mounting the userland image. in /etc/exports have this:
/nfsroot @xxx_netgroup(rw,no_root_squash,async)
- do not forget to enable dhcpd/dmsmasq and NFS to start on boot
- do not forget to run "exportfs -rv" and "systemctl restart dhcpd" after making any changes
Prepare a bootable SD card
- use SD card of any size (8 GB or bigger)
- follow instructions to make it bootable
- select cmdline-nfsroot.txt
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 ip=dhcp rw root=/dev/nfs panic=60
Install bootable SD card into RPi, power up, and observe:
- RPi boots linux kernel
- linux kernel starts
- makes DHCP request, receives answer
- RPi pings
- RPi mounts the NFS-Root filesystem as specified by DHCP
- RPi OS boots normally
- there is a login prompt
- from boot server, RPi pings and ssh'es.
Setup Python i2c tools
NOTE: DO NOT DO THIS!
su - root yum install python-setuptools.noarch yum install python-cffi yum install python-devel cd git git clone https://github.com/bivab/smbus-cffi.git cd smbus-cffi python setup.py install
Enable i2c drivers
NOTE: DO NOT DO THIS!
(already done) edit boot config.txt, uncomment "dtparam=i2c_arm=on" and "dtparam=i2c1=on", reboot echo modprobe i2c-dev >> /etc/rc.local echo modprobe i2c_bcm2708 >> /etc/rc.local ls -l /dev/i2c* i2cdetect -l i2cdetect 1 echo chmod a+wr /dev/i2c* >> /etc/rc.local reboot, run i2cdetect again.
Script for creating boot files
~olchansk/git/scripts/clone/boot_rpi3.perl
Boot modes
See https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/hardware/raspberrypi/bootmodes/msd.md and https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/hardware/raspberrypi/bootmodes/bootflow_2711.md
- RPi2, RPi3B - SD flash is the default. USB mass storage boot is disabled, but can be enabled.
- RPi3B+ - default boot order: SD flash, USB boot
- RPi4B - boots from internal SPI EEPROM (see recovery.bin). continues booting from SD flash. network boot (DHCP+TFTP), firmware 2020-xx-yy. (how to enable?). usb mass storage boot (not available as of 2020-apr-21).
Raspbian OS
Recommended RaspberryPi OS is "Raspbian".
Rapsbian images and kernel versions
- 2016-09-23-raspbian-jessie-lite : Linux version 4.4.21+
- 2020-05-27-raspios-buster-lite-armhf : Linux version 4.19.118-v8+
- 2021-01-11-raspios-buster-armhf-lite : ???
- 2021-03-04-raspios-buster-armhf-lite : Linux version 5.10.17-v7+
Raspbian boot from SD card
- download here https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/
- unzip, dd to a 32GB SD flash card
- insert card into RPi3, power up, it will boot into login prompt
- default user: pi, password: raspbian, login change default password, install ssh keys for user pi and user root.
- change default keyboard layout from UK (with the pound key): vi /etc/default/keyboard, set XKBLAYOUT="us"
- change default locale from UK to "C" (en_US.UTF8 does not seem to be available): vi /etc/default/locale, set LANG=C.UTF-8
- enable ssh server: apt-get install openssh-server, systemctl enable sshd.service, systemctl start sshd.service
- reboot: shutdown -r now
- RJ45 ethernet network will autoconfigure by DHCP, ssh pi@... and root@... should work
- login as root, install missing packages:
- apt-get update
- apt-get install git emacs xemacs21 cmake
- install additional packages as needed as listed here: https://daq.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian and here: https://daq.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Ubuntu
Backport python3-yaml to Debian Buster
Debian Bullseye ships pyYAML 5.3.1, it is relatively easy to build the package for Debian Buster.
1. Downlowd
http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/pyyaml/pyyaml_5.3.1.orig.tar.gz
and
http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/pyyaml/pyyaml_5.3.1-1.debian.tar.xz
from https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-yaml (under "Download Source Package"). Note the bullseye in the URL.
2. Unpack pyyaml_5.3.1.orig.tar.gz and, inside the PyYAML-5.3.1 directory, pyyaml_5.3.1-1.debian.tar.xz.
3. Install some dependencies needed for the build:
sudo apt install python3-all-dev python3-all-dbg libyaml-dev cython cython-dbg python-all-dev python-all-dbg
sudo apt install dpkg-dev
4. Build the package (on the target architecture)
sudo dpkg-buildpackage -us -uc -nc
Openbox X Session
Have a look in /etc/xdg/openbox
Custom Raspbian Images
The official tool used raspberrypi.org is available here: https://github.com/RPi-Distro/pi-gen
It is working out of the box with Debian bullseye. The tool is built around debootstrap, all packages are pulled from http://archive.raspbian.org/ (not the official debian repos!).
The user has to provide a config file named "config" in the root directory. For instance:
IMG_NAME=MVM_GUI_TRIUMF RELEASE=buster DEPLOY_ZIP=0 USE_QEMU=0 LOCALE_DEFAULT=C.UTF-8 TARGET_HOSTNAME=mvm_gui KEYBOARD_KEYMAP=us KEYBOARD_LAYOUT="English (US)" TIMEZONE_DEFAULT="America/Vancouver" FIRST_USER_NAME="mvm" FIRST_USER_PASS="gui" ENABLE_SSH=0 STAGE_LIST="stage0 stage1 stage2 stage3 stage4"
To build the image, simply run ./build.sh and wait.
MVM example
Let's build an image tailored to the MVM GUI. The assumes the user is running Debian bullseye.
Optional Step: Setup a Local APT Cache
A local cache speeds-up things if you have to (re)build multiple images. The procedure supposes that you have docker and docker-compose installed on the build machine.
In the root directory, run
apt install docker-compose ### Ubuntu LTS 18.04 docker-compose up -d
Add the line
APT_PROXY=http://172.17.0.1:3142
to the config file
Main Procedure
Install dependencies (Debian):
sudo apt install coreutils quilt parted qemu-user-static debootstrap zerofree zip \ dosfstools bsdtar libcap2-bin grep rsync xz-utils file git curl bc
Install dependancies (Ubuntu LTS 18.04)
ssh root@... apt-get install quilt qemu-user-static debootstrap zerofree bsdtar curl
Clone the TRIUMF repo:
https://gitlab.triumf.ca/mvmdev/GUIAutoBuild --single-branch slim-raspbian-buster
Run:
LANG=C.UTF-8 ./build.sh
Wait ... the images will be saved in the deploy directory.
GPIO
wiringpi
- apt-get install wiringpi
- gpio readall
- gpio mode 24 output
- gpio write 24 1
- gpio write 24 0
pinctrl
root@dlpi:~# pinctrl get 18 18: ip pd | lo // GPIO18 = input root@dlpi:~# pinctrl set 18 op dh ### drives 3.3V root@dlpi:~# pinctrl set 18 op dl ### drives 0V
SPI
- if there is no /dev/spidev0.0 and /dev/spidev0.1, edit /boot/config.txt, uncomment dtparam=spi=on, reboot
- CS pins are:
- CE0 is J8 pin 24 (GPIO8) is /dev/spidev0,0
- CE1 is J8 pin 26 (GPIO7) is /dev/spidev0,1
- https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/Documentation/spi/spidev.rst
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54923582/spi-ioc-messagen-on-raspberry-pi-3
- https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v4.14/driver-api/spi.html#c.spi_message
I2C
- if there is no /dev/i2c*:
- mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /boot
- edit /boot/config.txt, uncomment "dtparam=i2c_arm=on"
- run "echo i2c_dev >> /etc/modules-load.d/i2c_dev.conf"
- umount /boot
- reboot
- after reboot check that i2c_dev and i2c_bcm2835 modules are loaded:
root@lvdb04:~# lsmod | grep i2c i2c_dev 20480 0 i2c_bcm2835 16384 0 root@lvdb04:~#
- if no permission to open /dev/i2c*:
- edit /etc/group, add your user to group "i2c", for example:
root@lvdb04:~# grep i2c /etc/group i2c:x:998:pi,agdaq root@lvdb04:~#
- logout, login again (/etc/group is applied at login time)
- apt-get install python-smbus i2c-tools
- i2cdetect -y 1 ### found device at address 0x70:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 70: 70 -- -- -- -- -- -- --
PWM
We will enable PWM output on GPIO 18.
- add to /boot/firmware/config.txt, reboot
dtoverlay=pwm,pin=18,func=2
- driver should now exist:
root@dlpi:~# ls -l /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/ total 0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 device -> ../../../fe20c000.pwm --w--w---- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 export -r--r--r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 npwm drwxrwxr-x 2 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 power lrwxrwxrwx 1 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:33 subsystem -> ../../../../../../class/pwm -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 uevent --w--w---- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:33 unexport root@dlpi:~#
- create pwm0
root@dlpi:~# echo 0 >> /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export root@dlpi:~# ls -l /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/ total 0 -r--r--r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 capture -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 duty_cycle -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 enable -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 period -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 polarity drwxrwxr-x 2 root gpio 0 Feb 24 03:38 power -rw-rw-r-- 1 root gpio 4096 Feb 24 03:38 uevent
- output something:
root@dlpi:~# echo 240000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/period root@dlpi:~# echo 120000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle root@dlpi:~# echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/enable
- on the scope:
square wave, period 240 us, on time 120 us
- on the RPi4, go faster:
period granularity is 20 ns, smallest is value 40 (40 ns) duty_cycle granularity is 20 ns, smallest is value 20 (19.6 ns) fastest waveform is: period 40, duty_cycle 10 -> on time 19.6 ns, period 40 ns
- settinggs for DLDB pulser, 50 kHz, ~10 ns apparent pulse width
root@dlpi:~# echo 1000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle root@dlpi:~# echo 20000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm0/period
WiFi and Bluetooth
The WiFi and Bluetooth interfaces can be disabled in the boot/config.txt. As a side effect, the PL011 UART is re-routed to the GPIOs 14 and 15. By default, the UART is used by the BT modem.
One has to disable the BT modem initialization service to avoid conflicts.
systemctl disable hciuart
Note: there is a second "MiniUART" aviabale on the Rpi, but its fonctionally are very limited. See https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/uart.md
# Disables the Bluetooth device (also restores UART0/ttyAMA0 to GPIOs 14 and 15). dtoverlay=disable-bt dtoverlay=disable-wifi
RS232
The Rpi3 has two serial interfaces (https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/uart.md). Levels are *3.3V*.
Update RPi firmware
Please go here: https://daq00.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian#install_RPi4_from_scratch
!!! check that SD card is mounted as /boot/firmware !!!
apt update apt upgrade ### install latest eeprom rpi-eeprom-update -a
RPi4 boot from network
Please go here: https://daq00.triumf.ca/DaqWiki/index.php/Raspbian#install_RPi4_from_scratch
- run raspi-config, in advanced options, set boot order to network-first
- reboot
- check that the change took
root@magpi03:~# vcgencmd bootloader_config [all] BOOT_UART=0 WAKE_ON_GPIO=1 POWER_OFF_ON_HALT=0 [all] BOOT_ORDER=0xf21
- shutdown, power off the RPi4
- remove SD card
- power up
- tail -100f /var/log/syslog
- observe RPi4 does DHCP and requests files from /tftpboot/SERIALNUMBER/
- give it files it want, copy the from the SD card /boot/firmware
- copy all of /boot/firmware/overlays to /tftpboot/...
- symlink kernel8.img and initramfs8 to files in /nfsroot/
- should have this:
root@haicudaq01:~# ls -l /tftpboot/c914e0e6/ total 1732 -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 56112 Nov 26 15:43 bcm2711-rpi-4-b.dtb -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 70 Nov 26 15:43 cmdline.txt -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1245 Nov 26 15:40 config.txt -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5456 Nov 26 15:42 fixup4.dat lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 27 Nov 26 15:47 initramfs8 -> /nfsroot/magpi03/initrd.img lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 Nov 26 15:47 kernel8.img -> /nfsroot/magpi03/vmlinuz drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 339 Oct 22 06:05 overlays -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2259296 Nov 26 15:37 start4.elf root@haicudaq01:~#
- cycle power on the RPi4, it should boot from the network (SD card removed)
- not so fast. it did not boot all the way, ssh does not work.
- go to /nfsroot/magpi03/etc/fstab, edit /boot/firmware to have "nofail" otherwise boot will stall at mounting the removed SD card:
/dev/mmcblk0p1 /boot/firmware vfat defaults,nofail 0 2
- cycle power on RPi4 again, now it should boot all the way to ssh
- ssh magpi03
- disable swap (swap to NFS does not/cannot work)
systemctl stop dphys-swapfile systemctl disable dphys-swapfile rm /var/swap
- done