Quickstart Linux: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Environment Variables== | ==Environment Variables== | ||
The following Environment variables should to be added to the | The following Environment variables should to be added to the {{File|name=.cshrc}} or {{File|name=.bashrc}} file (depending on your shell) in the {{Filepath|path=$HOME}} directory on the ''experiment host'', so that they will be defined at login. '''Substitute appropriate values for your own setup'''. | ||
<small> | <small> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</small> | </small> | ||
Logout and login again, or source .cshrc (source .bashrc) for the changes to take effect. | Logout and login again, or source {{File|name=.cshrc}} (source {{File|name=.bashrc}}) for the changes to take effect. | ||
;NOTE | ;NOTE | ||
: See [[MIDAS environment variables]] for a list of environment variables used by MIDAS. | : See [[MIDAS environment variables]] for a list of environment variables used by MIDAS. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
The MIDAS package will be installed on the ''experiment host'' in the directory given by MIDASSYS - see [[#Environment Variables]]. | The MIDAS package will be installed on the ''experiment host'' in the directory given by MIDASSYS - see [[#Environment Variables]]. | ||
Install the MIDAS and other package(s) from the MIDAS git repository as follows: | Install the MIDAS and other package(s) from the MIDAS git repository in an xterm as follows: | ||
<small> | <small> | ||
[mhostpc] mkdir $HOME/packages | |||
[mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages | |||
[mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas | |||
[mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/mxml | |||
</small> | </small> | ||
Install the MSCB package '''only''' if you will be using the MSCB system for slow-controls (see [[MSCB Page]]): | Install the MSCB package '''only''' if you will be using the MSCB system for slow-controls (see [[MSCB Page]]): | ||
<small> | <small> | ||
[mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/mscb ## MSCB package | |||
[mhostpc] cd mscb | |||
[mhostpc] make ## Build the MSCB package | |||
[mhostpc] cd ../ | |||
</small> | </small> | ||
The MIDAS Makefile will auto-detect whether MSCB, ROOT, MYSQL, SQLITE, ODBC etc. are available (or have been installed). If you need these features, make sure they are available before building the MIDAS package. | The MIDAS Makefile will auto-detect whether MSCB, ROOT, MYSQL, SQLITE, ODBC etc. are available (or have been installed). If you need these features, make sure they are available before building the MIDAS package. | ||
<small> | <small> | ||
[mhostpc] cd midas | |||
[mhostpc] make ## Build the MIDAS package | |||
[mhostpc] ls -l linux/bin/odbedit ### check that odbedit has been created (do not run it yet) | |||
</small> | </small> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
==ROOTANA Package Installation== | ==ROOTANA Package Installation== | ||
If ROOTANA is needed, | If ROOTANA is needed, | ||
<small> | |||
git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/rootana | [mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages | ||
cd rootana | [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/rootana | ||
make | [mhostpc] cd rootana | ||
[mhostpc] make | |||
</small> | </small> | ||
==ROODY Package Installation== | ==ROODY Package Installation== | ||
If ROODY is needed, | If ROODY is needed, | ||
<small> | |||
git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/roody | [mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages | ||
cd roody | [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/roody | ||
make</small> | [mhostpc] cd roody | ||
[mhostpc] make | |||
</small> | |||
== Create the Experiment file exptab == | == Create the Experiment file exptab == | ||
In this example, the experimental directory is {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}}. Create this directory on the ''experiment host'' (localhost): | In this example, the experimental directory is {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}}. Create this directory on the ''experiment host'' (localhost): | ||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] mkdir $HOME/online | |||
Then create the [[exptab]] file | [mhostpc] cd $HOME/online</small> | ||
Then create the [[exptab]] file {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online/exptab}} containing the three parameters: | |||
# the experiment name | # the experiment name | ||
# location of MIDAS shared memory buffers | # location of MIDAS shared memory buffers | ||
# username | # username | ||
as follows (using parameters for your own experiment): | as follows (using parameters for your own experiment): | ||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] cat > exptab | |||
e777 /home/johnfoo/online johnfoo</small> | e777 /home/johnfoo/online johnfoo</small> | ||
The path of the exptab file is given by MIDAS_EXPTAB - see [[#Environment Variables]]. | The path of the {{File|name=exptab}} file is given by MIDAS_EXPTAB - see [[#Environment Variables]]. | ||
== Create shared memory files == | == Create shared memory files == | ||
At this point you should be able to run [[odbedit]] on the ''experiment host'' (localhost). The first time {{Utility|name=odbedit}} is run, it will create the required .*.SHM files in the MIDAS experiment directory {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}}. These are the saved files for the MIDAS shared memory. | At this point you should be able to run [[odbedit]] on the ''experiment host'' (localhost). The first time {{Utility|name=odbedit}} is run, it will create the required {{File|name=.*.SHM}} files in the MIDAS experiment directory {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}}. These are the saved files for the MIDAS shared memory. | ||
The default directory {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}} will contain the MIDAS messages file ({{File|name=midas.log}}) and | The default directory {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}} will contain the MIDAS messages file ({{File|name=midas.log}}) and | ||
any data files you may create. If you want an alternative location for the data files see [[#Customizing your experiment]]. | any data files you may create. If you want an alternative location for the data files see [[#Customizing your experiment]]. | ||
Run {{Utility|name=odbedit}}, and type {{Odbedit cmd|cmd=ls}} to list the default directories. | |||
<small>odbedit | <small>[mhostpc] odbedit | ||
[local:e777:S]/>ls | [local:e777:S]/>ls | ||
Experiment | Experiment | ||
| Line 131: | Line 136: | ||
== Run the MIDAS logger == | == Run the MIDAS logger == | ||
Start the MIDAS logger [[mlogger]] on the ''experiment host'' (localhost) : | Start the MIDAS logger [[mlogger]] on the ''experiment host'' (localhost) : | ||
<small>mlogger</small> | <small>[mhostpc] mlogger</small> | ||
This should start without error. It is usually run as a daemon, however in this case it is run in a terminal to check for errors. Starting the midas logger [[mlogger]] will automatically create more keys in the {{Odbpath|path=/Logger}} ODB tree. | This should start without error. It is usually run as a daemon, however in this case it is run in a terminal to check for errors. Starting the midas logger [[mlogger]] will automatically create more keys in the {{Odbpath|path=/Logger}} ODB tree. | ||
| Line 140: | Line 145: | ||
Otherwise, the MIDAS Web Server [[mhttpd]] with HTTPS/SSL (Mongoose) will be used. This is the default. | Otherwise, the MIDAS Web Server [[mhttpd]] with HTTPS/SSL (Mongoose) will be used. This is the default. | ||
Start [[mhttpd]] on the ''experiment host'' (localhost) like this: | |||
<small> mhttpd</small> | <small>[mhostpc] mhttpd</small> | ||
You will get the following messages: | You will get the following messages: | ||
<small>[mhttpd,INFO] ODB subtree /Runinfo corrected successfully | <small>[mhttpd,INFO] ODB subtree /Runinfo corrected successfully | ||
| Line 155: | Line 160: | ||
<small> | <small> | ||
[mhostpc] htdigest -c /home/johnfoo/online/htpasswd.txt Default midas | |||
Adding password for midas in realm Default. | Adding password for midas in realm Default. | ||
New password: | New password: | ||
| Line 163: | Line 168: | ||
Now restart {{Utility|name=mhttpd}} | Now restart {{Utility|name=mhttpd}} | ||
<small> mhttpd | <small>[mhostpc] mhttpd | ||
Mongoose web server will listen on ports "8080r,8443s" **see note | Mongoose web server will listen on ports "8080r,8443s" **see note | ||
Mongoose web server will use SSL certificate file "/home/suz/packages/midas/ssl_cert.pem" | Mongoose web server will use SSL certificate file "/home/suz/packages/midas/ssl_cert.pem" | ||
| Line 177: | Line 182: | ||
You should then see an authentication box asking you for the user name and password. The user name is "midas". Enter the password you just created. The Midas [[Status Page]] should appear with multiple buttons for run control as well as equipment listing (no equipments will be listed as yet) and application listings. Please refer to [[mhttpd]] (the MIDAS Web-based Run Control utility) for further information. You can start and stop runs from the main status page, and use the [[ODB Page]] to access the database (ODB). | You should then see an authentication box asking you for the user name and password. The user name is "midas". Enter the password you just created. The Midas [[Status Page]] should appear with multiple buttons for run control as well as equipment listing (no equipments will be listed as yet) and application listings. Please refer to [[mhttpd]] (the MIDAS Web-based Run Control utility) for further information. You can start and stop runs from the main status page, and use the [[ODB Page]] to access the database (ODB). | ||
; | ; Note | ||
: Default ports of 8080 and 8443 are used by [[mhttpd]]. If these ports are in use on your machine, start | : Default ports of 8080 and 8443 are used by [[mhttpd]]. If these ports are in use on your machine, start <span style="color:darkcyan;font-style:italic">mhttpd</span> with alternative ports, e.g. | ||
<small>mhttpd --https 8448 --http 8089</small> | <small>[mhostpc] mhttpd --https 8448 --http 8089</small> | ||
: or see [[Mhttpd#Usage]] to change the default ports. | : or see [[Mhttpd#Usage]] to change the default ports. | ||
| Line 186: | Line 191: | ||
;NOTE: | ;NOTE: | ||
* If creating a MIDAS experiment with a '''REMOTE''' frontend, '''continue by following the instructions''' [[#Running with one or more REMOTE frontend(s)]]. | * If creating a MIDAS experiment with a '''REMOTE''' frontend, '''continue by following the instructions''' [[#Running with one or more REMOTE frontend(s)]]. | ||
* If all clients are running on the Experiment Host (i.e. '''localhost'''), continue with the following instructions: | * If all clients are running on the Experiment Host (i.e. '''localhost'''), continue with the following instructions: | ||
| Line 197: | Line 201: | ||
On the MIDAS ''experiment host'' (localhost), copy the example to the experiment directory and build it. | On the MIDAS ''experiment host'' (localhost), copy the example to the experiment directory and build it. | ||
cd $HOME/online | <small> | ||
cp $MIDASSYS/examples/experiment/* . | [mhostpc] cd $HOME/online | ||
make | [mhostpc] cp $MIDASSYS/examples/experiment/* . | ||
[mhostpc] make</small> | |||
The analyzer will only build if ROOT has previously been installed. | The analyzer will only build if ROOT has previously been installed. | ||
At this point the frontend and the analyzer should be ready if no errors were generated during the build. Try the frontend and analyzer by starting them in xterms. | At this point the frontend and the analyzer should be ready if no errors were generated during the build. Try the frontend and analyzer by starting them in xterms. | ||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] frontend | |||
[mhostpc] analyzer</small> | |||
=== Equipment ODB tree === | |||
Starting the frontend will automatically create the {{Odbpath|path=/Equipment}} ODB tree and one or more equipments. In this case, the equipments "trigger" and "scaler" have been defined by code in {{File|name=frontend.c}} and created the first time frontend runs. | Starting the frontend will automatically create the {{Odbpath|path=/Equipment}} ODB tree and one or more equipments. In this case, the equipments "trigger" and "scaler" have been defined by code in {{File|name=frontend.c}} and created the first time frontend runs. | ||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] odbedit | |||
[local:e777:S]/>ls /equipment | |||
Trigger | |||
Scaler </small> | |||
View the MIDAS main status web page (by pointing your browser to https://localhost:8443/ or appropriate port if not using the default). | View the MIDAS main status web page (by pointing your browser to https://localhost:8443/ or appropriate port if not using the default). | ||
Observe on the [[Status Page]] that the two Equipments (Trigger, Scaler) have appeared in the Equipment section (Figure 1). | Observe on the [[Status Page]] that the two Equipments (Trigger, Scaler) have appeared in the Equipment section (Figure 1) and are coloured green. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''Click thumbnail to enlarge''' | '''Click thumbnail to enlarge''' | ||
[[File: | [[File:quickstart_status_page.png|thumb|left|Figure 1: web server status page showing example frontend equipments]] | ||
<div style="clear: both"></div> <!-- clear wraparound after thumbnail --> | <div style="clear: both"></div> <!-- clear wraparound after thumbnail --> | ||
Rather than using odbedit, you can view the contents of these equipments by clicking on the ODB button, then on {{Odbpath|path=/Equipment}}, then {{Odbpath|path=Trigger}} or {{Odbpath|path=Scaler}}. See [[ODB Page]] for more information. | Rather than using odbedit, you can view the contents of these equipments by clicking on the ODB button, then on {{Odbpath|path=/Equipment}}, then {{Odbpath|path=Trigger}} or {{Odbpath|path=Scaler}}. See [[ODB Page]] for more information. | ||
=== Start a run === | |||
Start a run by pressing the Start button on the [[Status Page]]. | Start a run by pressing the Start button on the [[Status Page]]. | ||
The Equipment display on the Status Page will now show some event statistics (Figure 2) | |||
'''Click thumbnail to enlarge''' | |||
[[File:sample_frontend_status.png|thumb|left|Figure 2: Equipments shown on Status Page showing event statistics]] | |||
<div style="clear: both"></div> <!-- clear wraparound after thumbnail --> | |||
The frontend will show an event display that will update when a run is started, e.g. | The frontend will show an event display that will update when a run is started, e.g. | ||
| Line 231: | Line 246: | ||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
Trigger OK 13948 99.0 5413.0 0 140 | Trigger OK 13948 99.0 5413.0 0 140 | ||
Scaler OK 15 0.3 15.4 0 15 | |||
The [[Status Page]] will also show events being generated (click the refresh button if necessary). | The [[Status Page]] will also show events being generated (click the refresh button if necessary). | ||
=== Event Dump === | |||
While a run is in progress, the midas application [[mdump]] will provide you an event dump of the collected data from the running frontend, e.g. | While a run is in progress, the midas application [[mdump]] will provide you an event dump of the collected data from the running frontend, e.g. | ||
<small> | |||
- MIDAS revision: Mon Nov 2 11:50:51 2015 -0800 - 3b66779 -- Enter <!> to Exit ------- Midas Dump --- | mhostpc> mdump -l 50 | ||
------------------------ Event# 1 ------------------------ | <span style="color:whitesmoke">blank</span> | ||
Evid:0001- Mask:0000- Serial:0- Time:0x567a0c5d- Dsize:40/0x28 | - MIDAS revision: Mon Nov 2 11:50:51 2015 -0800 - 3b66779 -- Enter <!> to Exit ------- Midas Dump --- | ||
#banks:2 - Bank list:-ADC0TDC0- | ------------------------ Event# 1 ------------------------ | ||
Evid:0001- Mask:0000- Serial:0- Time:0x567a0c5d- Dsize:40/0x28 | |||
Bank:ADC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 | #banks:2 - Bank list:-ADC0TDC0- | ||
<span style="color:whitesmoke">blank</span> | |||
Bank:ADC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 | |||
1-> 0x0167 0x03c6 0x0069 0x0073 | 1-> 0x0167 0x03c6 0x0069 0x0073 | ||
<span style="color:whitesmoke">blank</span> | |||
Bank:TDC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 | Bank:TDC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 | ||
1-> 0x0051 0x00ff 0x004a 0x00ec | 1-> 0x0051 0x00ff 0x004a 0x00ec | ||
</small> | |||
For further data processing/analysis, either the midas analyzer or the rootana can used for data display as well. | For further data processing/analysis, either the midas analyzer or the rootana can used for data display as well. | ||
=== Create a start_daq script (localhost) === | === Create a start_daq script (localhost) === | ||
It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called a start_daq script. Create $HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh on the ''experiment host'' as follows (supply the mhttpd ports if default is not used): | It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called for convenience a "start_daq" script (any name can be used). Create {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh}} on the ''experiment host'' as follows (supply the [[mhttpd]] ports if default is not used): | ||
<small>#!/bin/sh | <small>#!/bin/sh | ||
| Line 258: | Line 276: | ||
odbedit -c clean | odbedit -c clean | ||
# start mhttpd on default port. (Mongoose https version) | # start mhttpd on default port. (Mongoose https version) | ||
mhttpd -D # optionally restrict access to localhost and | mhttpd -D # you can optionally restrict access to localhost and other specified hosts - see [[mhttpd]] | ||
xterm -e ./frontend & | xterm -e ./frontend & | ||
xterm -e ./analyzer & | xterm -e ./analyzer & | ||
| Line 265: | Line 283: | ||
Before running this script, you will need to shutdown any running clients: | Before running this script, you will need to shutdown any running clients: | ||
<small>mhostpc> odbedit -c "sh all"</small> | |||
or you can use the mhttpd [[ | or you can use the {{Utility|name=mhttpd}} [[Programs Page]] to shut them down. | ||
The script will start them as daemons. | The script will start them as daemons. | ||
By running the script start_daq.sh, several MIDAS applications will be started in sequence: | By running the script start_daq.sh, several MIDAS applications will be started in sequence: | ||
# Cleanup previous MIDAS application (if any). | |||
# Start the MIDAS web server [mhttpd] | |||
# Start the frontend application in its own xterm (for debugging purpose). | |||
# Start the analyzer application in its own xterm (for debugging purpose). | |||
# Start the MIDAS Data logger [mlogger] | |||
<small>[mhostpc] sh ./start_daq</small> | |||
Later, you may wish to modify the script to restart missing clients only, and write a script kill_daq.sh to shutdown all clients. | |||
== Running with one or more REMOTE frontends == | |||
These instructions assume you have already followed the instructions to setup an experiment running on the MIDAS experiment host (localhost), i.e. you have setup the MIDAS Environment variables, downloaded MIDAS packages, setup the [[mhttpd]] password and have {{Utility|name=mhttpd}} running successfully. | |||
== Running with one or more REMOTE | |||
These instructions assume you have already followed the instructions to setup an experiment running on the MIDAS experiment host (localhost), i.e. you have setup the MIDAS Environment variables, downloaded MIDAS packages, setup the [[mhttpd]] password and have | |||
In the case of '''remote''' frontend(s), the remote cpu(s) typically have access to some or all of the hardware. They might be VMIC cpus running in VME crates for example, connected to the MIDAS Host via Ethernet. They read data from the hardware and send it back to the MIDAS ''experiment host'' to be logged and analyzed. | In the case of '''remote''' frontend(s), the remote cpu(s) typically have access to some or all of the hardware. They might be VMIC cpus running in VME crates for example, connected to the MIDAS Host via Ethernet. They read data from the hardware and send it back to the MIDAS ''experiment host'' to be logged and analyzed. | ||
These instructions assume that there is one | === Experimental setup (remote) === | ||
These instructions assume that the MIDAS ''experiment host'' computer is 64-bit (if not see [[#Build 32-bit MIDAS libraries|note below]]), and there is one ''remote host'', a 32-bit machine named "rlxhost". | |||
It is | The ''remote host'' mounts the {{Filepath|path=/home}} disk of the ''experiment host'', so that it '''has access to the MIDAS packages''', the {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online}} directory and shares the .cshrc (or .bashrc) script. It is convenient to set up ssh keys (use ssh-keygen) so that the ''remote host'' can be accessed without supplying the password from the ''experiment host''. | ||
If your setup is different, you will have to make changes as appropriate. | |||
If | |||
=== Build 32-bit MIDAS libraries === | === Build 32-bit MIDAS libraries === | ||
If | NOTE | ||
<p style="margin-left:40px;margin-right:40px;"> | |||
If the MIDAS ''experiment host'' computer is 32-bit (i.e. the same as the ''remote host''), which is a simpler setup, you will have built the 32-bit MIDAS libraries already, and can skip the rest of this section. Note however, that in the .cshrc file in the [[#Modify .cshrc (.bashrc) for remote host|following section]] you will not need the lines starting "# select 64-bit or 32-bit MIDAS and ROOT". The PATH should contain <span style="color:#214200; font-weight:normal; font-style:italic">$MIDASSYS/linux/bin</span> on both experiment host and remote host. This will point to the 32-bit MIDAS libraries. | |||
------------------------------ | |||
</p> | |||
<br> | |||
Assuming the MIDAS host computer is 64-bit, you will have already built the 64-bit MIDAS libraries. | |||
In this case, if the remote frontend is 32-bit, you will need to build the 32-bit MIDAS libraries on the 64-bit machine, i.e. | |||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] cd /home/packages/midas | |||
[mhostpc] make linux32 ### build the 32-bit MIDAS libraries on 64-bit machine | |||
[mhostpc] ls -l linux-m32/bin/odbedit ### check that the 32-bit odbedit has been created </small> | |||
Do not run {{Utility|name=odbedit}} yet on the ''remote host''! | |||
=== Modify .cshrc (.bashrc) for remote host === | |||
Add the following to the {{File|name=.cshrc}} (modified appropriately if using {{File|name=.bashrc}}). When running with a REMOTE Host, the application [[mserver]] will be started (using a particular port) on the MIDAS ''experiment host'' machine only. Note that the environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is defined on the remote machine(s) but NOT on the ''experiment host''. | |||
<small> | |||
=== Modify .cshrc (. | |||
Add the following to the .cshrc (modified appropriately | |||
# setenv MIDAS_HOST mhostpc # substitute your experiment host name | # setenv MIDAS_HOST mhostpc # substitute your experiment host name | ||
# setenv REMOTE_HOST rlxhost | # setenv REMOTE_HOST rlxhost # substitute your remote host name | ||
# setup the MIDAS mserver host | # setup the MIDAS mserver host | ||
# | # | ||
| Line 313: | Line 335: | ||
breaksw | breaksw | ||
default: | default: | ||
setenv MIDAS_SERVER_HOST $MIDAS_HOST.triumf.ca:1175 ## for remote host, define as hostname + domain name + default mserver port | setenv MIDAS_SERVER_HOST $MIDAS_HOST.triumf.ca:1175 ## for remote host, define MIDAS_SERVER_HOST | ||
## as hostname + domain name + default mserver port | |||
## port must match that of [[mserver]] used in start_daq.sh | ## port must match that of [[mserver]] used in start_daq.sh | ||
endsw | endsw | ||
| Line 331: | Line 354: | ||
setenv PATH .:$HOME/online/bin:$HOME/packages/roody/bin:$ROOTSYS/bin:$PATH | setenv PATH .:$HOME/online/bin:$HOME/packages/roody/bin:$ROOTSYS/bin:$PATH | ||
# | # | ||
</small> | |||
After executing {{File|name=.cshrc}} (or {{File|name=.bashrc}}) or logging out, on the MIDAS host (mhostpc) make sure environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is NOT defined | |||
<small>[mhostpc] echo $MIDAS_SERVER_HOST | |||
[mhostpc] MIDAS_SERVER_HOST: Undefined variable.</small> | |||
and on the '''''remote host''''', make sure MIDAS_SERVER_HOST IS defined: | |||
<span style="color:green; font-size:80%">[rlxhost] echo $MIDAS_SERVER_HOST | |||
[rlxhost] MIDAS_SERVER_HOST</span> | |||
Also on the ''remote host'', make sure that the correct (32-bit) {{Utility|name=odbedit}} will be used (do not run it yet!) | |||
<span style="color:green; font-size:80%">[rlxhost] which odbedit | |||
/home/johnfoo/packages/midas/linux-m32/bin/odbedit</span> | |||
Also on the | |||
[ | |||
/home/johnfoo/packages/midas/linux-m32/bin/odbedit | |||
=== Grant REMOTE host access permission === | === Grant REMOTE host access permission === | ||
Give permission for the remote host(s) to access the experiment | Give permission for the remote host(s) to access the experiment by following the instructions to [[Security#MIDAS programs on remote machines|allow MIDAS programs on remote machines]]. If the MIDAS web server [[mhttpd]] is running, use [[ODB Page]] to edit the ODB keys listed, otherwise use [[odbedit]] on the ''experiment host'' machine. | ||
=== Start mserver on MIDAS Experiment Host === | === Start mserver on MIDAS Experiment Host === | ||
The application [[mserver]] is not required when running an experiment on localhost only, but it '''IS required''' for access from a REMOTE frontend. | The application [[mserver]] is not required when running an experiment on the ''experiment host'' (localhost) only, but it '''IS required''' for access from a '''REMOTE''' frontend. | ||
Start [[mserver]] on MIDAS host (default port 1175) or use the "-p" option for a different port. | Start [[mserver]] on MIDAS host (default port 1175) or use the "-p" option for a different port. | ||
The port must match the port defined for MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in .cshrc (or . | The port must match the port defined for environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in {{File|name=.cshrc}} (or {{File|name=.bashrc}}) [[#Modify .cshrc (.bashrc) for remote host|above]]. | ||
[ | <small>[mhostpc] mserver -D</small> | ||
The environment variables on the REMOTE host should be: | The environment variables on the REMOTE host should be: | ||
[ | <span style="color:green; font-size:80%"> | ||
[rlxhost] printenv | grep MIDAS | |||
MIDASSYS=/home/e777/packages/midas | |||
MIDAS_EXPT_NAME=e777 | |||
MIDAS_SERVER_HOST=mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175</span> | |||
(a different port may be used - see above) | (a different port may be used - see above) | ||
=== Check access to ODB from REMOTE host === | === Check access to ODB from REMOTE host === | ||
Run {{Utility|name=odbedit}} on the remote host to check access to ODB. | Run {{Utility|name=odbedit}} on the remote host to check access to ODB. | ||
[ | <span style="color:green; font-size:80%">[rlxhost] odbedit | ||
[mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175:e777:Stopped]/>ls | [mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175:e777:Stopped]/>ls </span> | ||
If it does not work correctly, check that | If it does not work correctly, check that | ||
* MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is defined on REMOTE host with same port as [[mserver]] | * MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is defined on REMOTE host with same port as [[mserver]] | ||
* | * <span style="color:darkcyan;font-style:italic">mserver</span> is running on MIDAS host with the correct port | ||
* MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is NOT defined on MIDAS host | * MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is NOT defined on MIDAS host | ||
* remote access permission to REMOTE host has been granted as described above. | * remote access permission to REMOTE host has been granted as described above. | ||
| Line 381: | Line 405: | ||
To avoid confusion, create a different subdirectory for the frontend, e.g. | To avoid confusion, create a different subdirectory for the frontend, e.g. | ||
[ | <span style="color:green; font-size:80%">[rlxhost] mkdir $HOME/online/fe_32</span> | ||
Copy the Makefile and frontend code from the same example to this directory. | Copy the Makefile and frontend code from the same example to this directory. | ||
Modify the Makefile as needed, and only build the frontend. | Modify the Makefile as needed, and only build the frontend. | ||
Once built, start the frontend in an xterm on the REMOTE host. | Once built, start the frontend in an xterm on the REMOTE host. | ||
[ | <span style="color:green; font-size:80%">[rlxhost] $HOME/online/fe_32/frontend</span> | ||
Check that it connects successfully to the experiment and the Equipments appear on the [[Status Page]] as described under [[#Frontend and analyzer (localhost)]]. The Equipment Status (Figure 1) should show that the Equipments are now running on the remote cpu, i.e. "SampleFrontend@rlxhost.triumf.ca" rather than "Sample Frontend@localhost". | Check that it connects successfully to the experiment and the Equipments appear on the [[Status Page]] as described under [[#Frontend and analyzer (localhost)]]. The Equipment Status (Figure 1) should show that the Equipments are now running on the remote cpu, i.e. "SampleFrontend@rlxhost.triumf.ca" rather than "Sample Frontend@localhost". | ||
=== Run the Analyzer === | === Run the Analyzer === | ||
Start the analyzer in an xterm on the MIDAS ''experiment host'' | Start the analyzer in an xterm on the MIDAS ''experiment host'' | ||
[johnfoo@mhostpc e777] $HOME/online/analyzer | <small>[johnfoo@mhostpc e777] $HOME/online/analyzer</small> | ||
Continue by starting a run and dumping the data as described under [[#Frontend and analyzer (localhost)]]. | Continue by starting a run and dumping the data as described under [[#Frontend and analyzer (localhost)]]. | ||
=== Create experiment startup script === | === Create experiment startup script === | ||
It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called a start_daq script. Create $HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh | It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called for convenience a "start_daq" script (any name can be used). Create {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh}} on the ''experiment host'' as follows, (supply the [[mhttpd]] ports if default is not used) : | ||
<small> | |||
#!/bin/sh | #!/bin/sh | ||
# start_daq.sh | # start_daq.sh | ||
| Line 402: | Line 427: | ||
# | # | ||
switch (`hostname`) | switch (`hostname`) | ||
case $MIDAS_HOST*: | case $MIDAS_HOST*: ## MIDAS_HOST is assigned in .cshrc (.bashrc) | ||
echo "Good, we are on $MIDAS_HOST" | echo "Good, we are on $MIDAS_HOST" | ||
breaksw | breaksw | ||
case $REMOTE_HOST*: | case $REMOTE_HOST*: ## REMOTE_HOST is assigned in .cshrc (.bashrc) | ||
echo "start_daq script should be executed on $MIDAS_HOST" | echo "start_daq script should be executed on $MIDAS_HOST" | ||
endsw | endsw | ||
| Line 411: | Line 436: | ||
odbedit -c clean | odbedit -c clean | ||
# start mhttpd on default port (Mongoose https version) | # start mhttpd on default port (Mongoose https version) | ||
mhttpd -D # optionally restrict access to localhost | mhttpd -D # you can optionally restrict access to localhost and/or other specified hosts - see [[mhttpd]] | ||
# start mserver on default port (use argument -p to use a different port) | # start mserver on default port (use argument -p to use a different port) | ||
mserver -D # start mserver on default port (1175) or a different port using -p option - see [[mserver]] | mserver -D # start mserver on default port (1175) or a different port using -p option - see [[mserver]] | ||
# the port must match that of MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in .cshrc (. | # the port must match that of MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in .cshrc (.bashrc) - see above | ||
# access must be specifically allowed - see [[#Grant REMOTE host access permission||above]] | # access must be specifically allowed - see [[#Grant REMOTE host access permission||above]] | ||
xterm -e ./analyzer & | xterm -e ./analyzer & | ||
| Line 421: | Line 446: | ||
mlogger -D | mlogger -D | ||
#end file | #end file | ||
</small> | |||
Note that command to start the frontend on the remote host is commented out. It can be uncommented once the start_frontend script is written and tested. | |||
Shut down any clients that are running already by running odbedit on the MIDAS ''experiment host'' and execute the new startup script start_daq.sh (make it executable if desired) | |||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] odbedit | |||
Shut down any clients that are running already by running odbedit on the MIDAS | [local:e777:S]/>sh all | ||
[mhostpc] start_daq.sh </small> | |||
and check that {{Utility|name=odbedit}} still works on the ''REMOTE host'' | |||
<span style="color:green; font-size:80%"> | |||
[rlxhost] odbedit | |||
[mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175:e777:Stopped]/>ls </span> | |||
Later, you may wish to modify the script to restart missing clients only, and write a script kill_daq.sh to shutdown all clients. | |||
=== Create start_frontend script === | === Create start_frontend script === | ||
The startup file start_daq.sh invoked a file start_frontend to start the remote frontend. This line was commented out (see above). | The startup file start_daq.sh invoked a file start_frontend to start the remote frontend. This line was commented out (see [[#Create experiment startup script|above]]). Once the frontend is working, create a script to start the frontend (e.g. file {{Filepath|path=$HOME/online/bin/start_frontend}}). | ||
<small> | |||
#!/bin/tcsh | #!/bin/tcsh | ||
# Script to start frontend running on $REMOTE_HOST | # Script to start frontend running on $REMOTE_HOST | ||
| Line 446: | Line 473: | ||
echo "Frontend task has been started" | echo "Frontend task has been started" | ||
exit | exit | ||
</small> | |||
Check that this script works by running it on the REMOTE host | Check that this script works by running it on the REMOTE host. If successful, | ||
run the commented command in an xterm on the ''experiment host'' | |||
<small>[mhostpc] ssh $REMOTE_HOST $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend -O >& $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend.log & </small> | |||
This command relies on password-less access set up with SSH keys (see [[#Experimental setup (remote)]]). | |||
If successful, uncomment line in {{File|name=start_daq.sh}}, and run the script to check that it can start the remote client(s) from the MIDAS ''experiment host'' (first shutting down all running clients) : | |||
<small> | |||
[mhostpc] odbedit -c "sh all" | |||
[mhostpc] ./start_daq.sh </small> | |||
| Line 482: | Line 514: | ||
=== set up history system === | === set up history system === | ||
See [[History System]] and [[History Page]] | See [[History System]] and [[History Page]] | ||
=== write scripts which run at start and end of run === | |||
See [[/Programs ODB tree#Execute on start run]] and [[/Programs ODB tree#Execute on stop run]] | |||
=== set up the Sequencer === | === set up the Sequencer === | ||
The [[Sequencer Page#Sequencer]] can be used to run a sequence of runs, changing parameters as needed. | The [[Sequencer Page#Sequencer]] can be used to run a sequence of runs, changing parameters as needed. | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 6 January 2016
Introduction
This quickstart shows you how to install the MIDAS packages on a linux box and create a MIDAS experiment. The linux box will be called the MIDAS experiment host.
Installation
Log on to the Experiment Host and decide on a name for the MIDAS experiment (the experiment name). In these instructions, the MIDAS packages and experiment will be installed under the username "johnfoo". The ODB and other shared memory buffers for the MIDAS experiment will reside on the experiment host (localhost). MIDAS and the other required packages will be installed under directory $HOME/packages. The MIDAS experiment directory will be $HOME/online and the MIDAS experiment name will be "e777". The name of the experiment host will be "mhostpc".
- NOTE
- The user should substitute directory paths for the MIDAS packages and experiment directory as required, and names for experiment host, username, experiment name appropriate to his/her own setup.
Experimental setup
These instructions describe setting up an experiment that will run ONLY on the MIDAS experiment host computer (i.e. localhost only). In this case, the MIDAS experiment host has access to any hardware required, and all frontends, logger, analyzer etc. run on the one computer.
Modifications to run an experiment with additional frontend(s) running remotely (i.e. on remote cpu(s)) will also be described. Follow the instructions for setting up a localhost-only experiment until indicated.
In both cases, the main MIDAS applications (e.g. mlogger, mhttpd) run on the MIDAS experiment host.
Environment Variables
The following Environment variables should to be added to the .cshrc or .bashrc file (depending on your shell) in the $HOME directory on the experiment host, so that they will be defined at login. Substitute appropriate values for your own setup.
| csh | bash | comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| setenv LANG C | export LANG=C | ||
| setenv GIT_EDITOR "emacs -nw" | export GIT_EDITOR="emacs -nw" | ||
| setenv MIDASSYS $HOME/packages/midas | export MIDASSYS=$HOME/packages/midas | Base directory of the MIDAS package | |
| setenv ROOTSYS $HOME/packages/root | export ROOTSYS=$HOME/packages/root | setup ROOTSYS only if using ROOT | |
| setenv MIDAS_EXPTAB $HOME/online/exptab | export MIDAS_EXPTAB=$HOME/online/exptab | MIDAS experiment table | |
| setenv MIDAS_EXPT_NAME e777 | export MIDAS_EXPT_NAME=e777 | MIDAS experiment name | |
| setenv PATH .:$MIDASSYS/linux/bin:$PATH | export PATH=$PATH:$MIDASSYS/linux/bin | path | |
| setenv PATH .:$HOME/online/bin:$ROOTSYS/bin:$PATH | export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/online/bin:$ROOTSYS/bin | if using ROOT |
Logout and login again, or source .cshrc (source .bashrc) for the changes to take effect.
- NOTE
- See MIDAS environment variables for a list of environment variables used by MIDAS.
ROOT Package Installation
For full MIDAS operation, ROOT is needed for the data logging and analysis packages. It needed to build the example analyzer in this Quickstart. However, ROOT is not essential to run MIDAS. If ROOT is NOT installed, the environment variable ROOTSYS should be undefined.
If ROOT is needed, see Install ROOT.
MIDAS Package Installation
The MIDAS package will be installed on the experiment host in the directory given by MIDASSYS - see #Environment Variables.
Install the MIDAS and other package(s) from the MIDAS git repository in an xterm as follows:
[mhostpc] mkdir $HOME/packages [mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/mxml
Install the MSCB package only if you will be using the MSCB system for slow-controls (see MSCB Page):
[mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/mscb ## MSCB package [mhostpc] cd mscb [mhostpc] make ## Build the MSCB package [mhostpc] cd ../
The MIDAS Makefile will auto-detect whether MSCB, ROOT, MYSQL, SQLITE, ODBC etc. are available (or have been installed). If you need these features, make sure they are available before building the MIDAS package.
[mhostpc] cd midas [mhostpc] make ## Build the MIDAS package [mhostpc] ls -l linux/bin/odbedit ### check that odbedit has been created (do not run it yet)
In case of problems see
ROOTANA Package Installation
If ROOTANA is needed,
[mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/rootana [mhostpc] cd rootana [mhostpc] make
ROODY Package Installation
If ROODY is needed,
[mhostpc] cd $HOME/packages [mhostpc] git clone https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/roody [mhostpc] cd roody [mhostpc] make
Create the Experiment file exptab
In this example, the experimental directory is $HOME/online. Create this directory on the experiment host (localhost):
[mhostpc] mkdir $HOME/online [mhostpc] cd $HOME/online
Then create the exptab file $HOME/online/exptab containing the three parameters:
- the experiment name
- location of MIDAS shared memory buffers
- username
as follows (using parameters for your own experiment):
[mhostpc] cat > exptab e777 /home/johnfoo/online johnfoo
The path of the exptab file is given by MIDAS_EXPTAB - see #Environment Variables.
At this point you should be able to run odbedit on the experiment host (localhost). The first time odbedit is run, it will create the required .*.SHM files in the MIDAS experiment directory $HOME/online. These are the saved files for the MIDAS shared memory.
The default directory $HOME/online will contain the MIDAS messages file ( midas.log) and any data files you may create. If you want an alternative location for the data files see #Customizing your experiment.
Run odbedit, and type odbedit command ls to list the default directories.
[mhostpc] odbedit [local:e777:S]/>ls Experiment System Programs Logger Runinfo Alarms
Run the MIDAS logger
Start the MIDAS logger mlogger on the experiment host (localhost) :
[mhostpc] mlogger
This should start without error. It is usually run as a daemon, however in this case it is run in a terminal to check for errors. Starting the midas logger mlogger will automatically create more keys in the /Logger ODB tree.
Run the MIDAS Web Server
If you are running behind a firewall or plan to set up an HTTPS/SSL proxy, follow the instructions mhttpd using an HTTPS/SSL proxy.
Otherwise, the MIDAS Web Server mhttpd with HTTPS/SSL (Mongoose) will be used. This is the default. Start mhttpd on the experiment host (localhost) like this:
[mhostpc] mhttpd
You will get the following messages:
[mhttpd,INFO] ODB subtree /Runinfo corrected successfully Mongoose web server will listen on ports "8080r,8443s" Mongoose web server will use SSL certificate file "/home/johnfoo/packages/midas/ssl_cert.pem" [mhttpd,ERROR] [mhttpd.cxx:17633:mongoose,ERROR] mongoose web server cannot find password file "/home/johnfoo/online/htpasswd.txt" [mhttpd,ERROR] [mhttpd.cxx:17634:mongoose,ERROR] please create password file: htdigest -c /home/johnfoo/online/htpasswd.txt Default midas could not start the mongoose web server, see messages and midas.log, bye!
For testing, use the SSL certificate file provided in the MIDAS package (unless your site provides one, or you wish to create your own SSL certificate for added security.
However, you do need to create a password file by following the above instructions. You will be asked to type in a password
[mhostpc] htdigest -c /home/johnfoo/online/htpasswd.txt Default midas Adding password for midas in realm Default. New password: Re-type new password:
It is a good idea to set the password file htpasswd.txt readable and writable by owner only.
Now restart mhttpd
[mhostpc] mhttpd Mongoose web server will listen on ports "8080r,8443s" **see note Mongoose web server will use SSL certificate file "/home/suz/packages/midas/ssl_cert.pem" Mongoose web server will use authentication realm "Default", password file "./htpasswd.txt"
Now point a web browser running on the same host computer (localhost) to https://localhost:8443 If the web browser is running on a different computer, go to URL of the form
https://mhostpc.triumf.ca:8443 (substitute your host machine name and domain for "mhostpc.triumf.ca")
If you are using the default SSL certificate you will probably get a message: "This Connection is Untrusted". Click "I understand the risks" and add an exception. This is because the test certificate is self-signed. Then confirm an exception.
You should then see an authentication box asking you for the user name and password. The user name is "midas". Enter the password you just created. The Midas Status Page should appear with multiple buttons for run control as well as equipment listing (no equipments will be listed as yet) and application listings. Please refer to mhttpd (the MIDAS Web-based Run Control utility) for further information. You can start and stop runs from the main status page, and use the ODB Page to access the database (ODB).
- Note
- Default ports of 8080 and 8443 are used by mhttpd. If these ports are in use on your machine, start mhttpd with alternative ports, e.g.
[mhostpc] mhttpd --https 8448 --http 8089
- or see Mhttpd#Usage to change the default ports.
Clients run on Localhost only
- NOTE
- If creating a MIDAS experiment with a REMOTE frontend, continue by following the instructions #Running with one or more REMOTE frontend(s).
- If all clients are running on the Experiment Host (i.e. localhost), continue with the following instructions:
Frontend and analyzer (localhost)
There are several examples of Frontend user code ( frontend.c) in the MIDAS package available under $MIDASSYS/examples/. Choose a suitable example from this directory that you can later modify for your own particular setup (e.g. for a slow control, choose the ../slowcont/ example).
A frontend is a program that usually reads data from the hardware and sends it to a buffer to be logged and analyzed. You can find documentation about the frontend structure under Frontend Application, Frontend Operation and Frontend user code.
The example chosen here is from $MIDASSYS/examples/experiment/. It does not need any hardware and produces simulated events.
On the MIDAS experiment host (localhost), copy the example to the experiment directory and build it.
[mhostpc] cd $HOME/online
[mhostpc] cp $MIDASSYS/examples/experiment/* .
[mhostpc] make
The analyzer will only build if ROOT has previously been installed. At this point the frontend and the analyzer should be ready if no errors were generated during the build. Try the frontend and analyzer by starting them in xterms.
[mhostpc] frontend
[mhostpc] analyzer
Equipment ODB tree
Starting the frontend will automatically create the /Equipment ODB tree and one or more equipments. In this case, the equipments "trigger" and "scaler" have been defined by code in frontend.c and created the first time frontend runs.
[mhostpc] odbedit
[local:e777:S]/>ls /equipment
Trigger
Scaler
View the MIDAS main status web page (by pointing your browser to https://localhost:8443/ or appropriate port if not using the default).
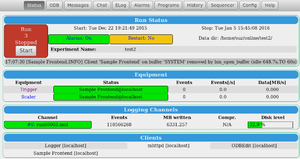
Observe on the Status Page that the two Equipments (Trigger, Scaler) have appeared in the Equipment section (Figure 1) and are coloured green.
Click thumbnail to enlarge
Rather than using odbedit, you can view the contents of these equipments by clicking on the ODB button, then on /Equipment, then Trigger or Scaler. See ODB Page for more information.
Start a run
Start a run by pressing the Start button on the Status Page. The Equipment display on the Status Page will now show some event statistics (Figure 2) Click thumbnail to enlarge
The frontend will show an event display that will update when a run is started, e.g.
Sample Frontend connected to <local>. Press "!" to exit 18:48:2546:08 ========================================================================== Run status: Running Run number 2 |/ / =========================================================================== Equipment Status Events Events/sec Rate[B/s] ODB->FE FE->OD --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Trigger OK 13948 99.0 5413.0 0 140 Scaler OK 15 0.3 15.4 0 15
The Status Page will also show events being generated (click the refresh button if necessary).
Event Dump
While a run is in progress, the midas application mdump will provide you an event dump of the collected data from the running frontend, e.g.
mhostpc> mdump -l 50 blank - MIDAS revision: Mon Nov 2 11:50:51 2015 -0800 - 3b66779 -- Enter <!> to Exit ------- Midas Dump --- ------------------------ Event# 1 ------------------------ Evid:0001- Mask:0000- Serial:0- Time:0x567a0c5d- Dsize:40/0x28 #banks:2 - Bank list:-ADC0TDC0- blank Bank:ADC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 1-> 0x0167 0x03c6 0x0069 0x0073 blank Bank:TDC0 Length: 8(I*1)/2(I*4)/4(Type) Type:Unsigned Integer*2 1-> 0x0051 0x00ff 0x004a 0x00ec
For further data processing/analysis, either the midas analyzer or the rootana can used for data display as well.
Create a start_daq script (localhost)
It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called for convenience a "start_daq" script (any name can be used). Create $HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh on the experiment host as follows (supply the mhttpd ports if default is not used):
#!/bin/sh # start_daq.sh cd $HOME/online odbedit -c clean # start mhttpd on default port. (Mongoose https version) mhttpd -D # you can optionally restrict access to localhost and other specified hosts - see mhttpd xterm -e ./frontend & xterm -e ./analyzer & mlogger -D #end file
Before running this script, you will need to shutdown any running clients:
mhostpc> odbedit -c "sh all"
or you can use the mhttpd Programs Page to shut them down.
The script will start them as daemons. By running the script start_daq.sh, several MIDAS applications will be started in sequence:
- Cleanup previous MIDAS application (if any).
- Start the MIDAS web server [mhttpd]
- Start the frontend application in its own xterm (for debugging purpose).
- Start the analyzer application in its own xterm (for debugging purpose).
- Start the MIDAS Data logger [mlogger]
[mhostpc] sh ./start_daq
Later, you may wish to modify the script to restart missing clients only, and write a script kill_daq.sh to shutdown all clients.
Running with one or more REMOTE frontends
These instructions assume you have already followed the instructions to setup an experiment running on the MIDAS experiment host (localhost), i.e. you have setup the MIDAS Environment variables, downloaded MIDAS packages, setup the mhttpd password and have mhttpd running successfully.
In the case of remote frontend(s), the remote cpu(s) typically have access to some or all of the hardware. They might be VMIC cpus running in VME crates for example, connected to the MIDAS Host via Ethernet. They read data from the hardware and send it back to the MIDAS experiment host to be logged and analyzed.
Experimental setup (remote)
These instructions assume that the MIDAS experiment host computer is 64-bit (if not see note below), and there is one remote host, a 32-bit machine named "rlxhost".
The remote host mounts the /home disk of the experiment host, so that it has access to the MIDAS packages, the $HOME/online directory and shares the .cshrc (or .bashrc) script. It is convenient to set up ssh keys (use ssh-keygen) so that the remote host can be accessed without supplying the password from the experiment host.
If your setup is different, you will have to make changes as appropriate.
Build 32-bit MIDAS libraries
NOTE
If the MIDAS experiment host computer is 32-bit (i.e. the same as the remote host), which is a simpler setup, you will have built the 32-bit MIDAS libraries already, and can skip the rest of this section. Note however, that in the .cshrc file in the following section you will not need the lines starting "# select 64-bit or 32-bit MIDAS and ROOT". The PATH should contain $MIDASSYS/linux/bin on both experiment host and remote host. This will point to the 32-bit MIDAS libraries.
Assuming the MIDAS host computer is 64-bit, you will have already built the 64-bit MIDAS libraries.
In this case, if the remote frontend is 32-bit, you will need to build the 32-bit MIDAS libraries on the 64-bit machine, i.e.
[mhostpc] cd /home/packages/midas [mhostpc] make linux32 ### build the 32-bit MIDAS libraries on 64-bit machine [mhostpc] ls -l linux-m32/bin/odbedit ### check that the 32-bit odbedit has been created
Do not run odbedit yet on the remote host!
Modify .cshrc (.bashrc) for remote host
Add the following to the .cshrc (modified appropriately if using .bashrc). When running with a REMOTE Host, the application mserver will be started (using a particular port) on the MIDAS experiment host machine only. Note that the environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is defined on the remote machine(s) but NOT on the experiment host.
# setenv MIDAS_HOST mhostpc # substitute your experiment host name
# setenv REMOTE_HOST rlxhost # substitute your remote host name
# setup the MIDAS mserver host
#
switch (`hostname`)
case $MIDAS_HOST*:
unsetenv MIDAS_SERVER_HOST ## MIDAS_SERVER_HOST not defined
breaksw
default:
setenv MIDAS_SERVER_HOST $MIDAS_HOST.triumf.ca:1175 ## for remote host, define MIDAS_SERVER_HOST
## as hostname + domain name + default mserver port
## port must match that of mserver used in start_daq.sh
endsw
#
# select 64-bit or 32-bit MIDAS and ROOT
#
switch (`uname -i`)
case i386:
setenv ROOTSYS /triumfcs/trshare/olchansk/root/root_v5.28.00_SL55_32 ## or appropriate path
setenv PATH .:$MIDASSYS/linux-m32/bin:$PATH
breaksw
default:
setenv ROOTSYS $HOME/packages/root
setenv PATH .:$MIDASSYS/linux/bin:$PATH
endsw
#
setenv PATH .:$HOME/online/bin:$HOME/packages/roody/bin:$ROOTSYS/bin:$PATH
#
After executing .cshrc (or .bashrc) or logging out, on the MIDAS host (mhostpc) make sure environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is NOT defined
[mhostpc] echo $MIDAS_SERVER_HOST [mhostpc] MIDAS_SERVER_HOST: Undefined variable.
and on the remote host, make sure MIDAS_SERVER_HOST IS defined:
[rlxhost] echo $MIDAS_SERVER_HOST
[rlxhost] MIDAS_SERVER_HOST
Also on the remote host, make sure that the correct (32-bit) odbedit will be used (do not run it yet!)
[rlxhost] which odbedit
/home/johnfoo/packages/midas/linux-m32/bin/odbedit
Grant REMOTE host access permission
Give permission for the remote host(s) to access the experiment by following the instructions to allow MIDAS programs on remote machines. If the MIDAS web server mhttpd is running, use ODB Page to edit the ODB keys listed, otherwise use odbedit on the experiment host machine.
Start mserver on MIDAS Experiment Host
The application mserver is not required when running an experiment on the experiment host (localhost) only, but it IS required for access from a REMOTE frontend. Start mserver on MIDAS host (default port 1175) or use the "-p" option for a different port. The port must match the port defined for environment variable MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in .cshrc (or .bashrc) above.
[mhostpc] mserver -D
The environment variables on the REMOTE host should be:
[rlxhost] printenv | grep MIDAS
MIDASSYS=/home/e777/packages/midas
MIDAS_EXPT_NAME=e777
MIDAS_SERVER_HOST=mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175
(a different port may be used - see above)
Check access to ODB from REMOTE host
Run odbedit on the remote host to check access to ODB.
[rlxhost] odbedit
[mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175:e777:Stopped]/>ls
If it does not work correctly, check that
- MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is defined on REMOTE host with same port as mserver
- mserver is running on MIDAS host with the correct port
- MIDAS_SERVER_HOST is NOT defined on MIDAS host
- remote access permission to REMOTE host has been granted as described above.
Build the analyzer on the MIDAS Experiment Host
The analyzer will be built and run on the MIDAS experiment host machine. Select an example from $MIDASSYS/examples/ (see #Frontend and analyzer (localhost)) and copy it to $HOME/online on the MIDAS host machine. Since we are assuming a 64-bit MIDAS host and a 32-bit remote host, edit the example Makefile so only the analyzer will be built.
Build the frontend (32bit) for REMOTE host
The frontend runs on a 32-bit remote host in this example. It therefore must either
- be built 32-bit on the 64-bit MIDAS host with the "-m32" flag
- or built on the REMOTE host
and in either case the 32-bit MIDAS libraries used for linking.
To avoid confusion, create a different subdirectory for the frontend, e.g.
[rlxhost] mkdir $HOME/online/fe_32
Copy the Makefile and frontend code from the same example to this directory. Modify the Makefile as needed, and only build the frontend.
Once built, start the frontend in an xterm on the REMOTE host.
[rlxhost] $HOME/online/fe_32/frontend
Check that it connects successfully to the experiment and the Equipments appear on the Status Page as described under #Frontend and analyzer (localhost). The Equipment Status (Figure 1) should show that the Equipments are now running on the remote cpu, i.e. "SampleFrontend@rlxhost.triumf.ca" rather than "Sample Frontend@localhost".
Run the Analyzer
Start the analyzer in an xterm on the MIDAS experiment host
[johnfoo@mhostpc e777] $HOME/online/analyzer
Continue by starting a run and dumping the data as described under #Frontend and analyzer (localhost).
Create experiment startup script
It is useful to create a script that will automatically start all the required clients for the experiment. This is called for convenience a "start_daq" script (any name can be used). Create $HOME/online/bin/start_daq.sh on the experiment host as follows, (supply the mhttpd ports if default is not used) :
#!/bin/sh
# start_daq.sh
cd $HOME/online
#
switch (`hostname`)
case $MIDAS_HOST*: ## MIDAS_HOST is assigned in .cshrc (.bashrc)
echo "Good, we are on $MIDAS_HOST"
breaksw
case $REMOTE_HOST*: ## REMOTE_HOST is assigned in .cshrc (.bashrc)
echo "start_daq script should be executed on $MIDAS_HOST"
endsw
#
odbedit -c clean
# start mhttpd on default port (Mongoose https version)
mhttpd -D # you can optionally restrict access to localhost and/or other specified hosts - see mhttpd
# start mserver on default port (use argument -p to use a different port)
mserver -D # start mserver on default port (1175) or a different port using -p option - see mserver
# the port must match that of MIDAS_SERVER_HOST in .cshrc (.bashrc) - see above
# access must be specifically allowed - see |above
xterm -e ./analyzer &
## start frontend on remote host
#ssh $REMOTE_HOST $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend -O >& $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend.log &
mlogger -D
#end file
Note that command to start the frontend on the remote host is commented out. It can be uncommented once the start_frontend script is written and tested.
Shut down any clients that are running already by running odbedit on the MIDAS experiment host and execute the new startup script start_daq.sh (make it executable if desired)
[mhostpc] odbedit [local:e777:S]/>sh all [mhostpc] start_daq.sh
and check that odbedit still works on the REMOTE host
[rlxhost] odbedit
[mhostpc.triumf.ca:1175:e777:Stopped]/>ls
Later, you may wish to modify the script to restart missing clients only, and write a script kill_daq.sh to shutdown all clients.
Create start_frontend script
The startup file start_daq.sh invoked a file start_frontend to start the remote frontend. This line was commented out (see above). Once the frontend is working, create a script to start the frontend (e.g. file $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend).
#!/bin/tcsh # Script to start frontend running on $REMOTE_HOST # # This script runs on the REMOTE HOST # echo "starting frontend for experiment $MIDAS_EXPT_NAME " xterm -geometry 150x50+800+0 -fg white -bg blue -title "Frontend" -e "$HOME/online/fe_32/frontend" & echo "Frontend task has been started" exit
Check that this script works by running it on the REMOTE host. If successful, run the commented command in an xterm on the experiment host
[mhostpc] ssh $REMOTE_HOST $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend -O >& $HOME/online/bin/start_frontend.log &
This command relies on password-less access set up with SSH keys (see #Experimental setup (remote)). If successful, uncomment line in start_daq.sh, and run the script to check that it can start the remote client(s) from the MIDAS experiment host (first shutting down all running clients) :
[mhostpc] odbedit -c "sh all" [mhostpc] ./start_daq.sh
Customize MIDAS for your experiment
Here are some of the more common operations users can do to customize their experiments according to their own preferences:
Write frontend(s) to read out and control your hardware
Modify the example frontend and Makefile (from $MIDASSYS/examples/) you have already copied and built so it accesses your hardware.
The example Frontend.c is an example of Frontend user code. You can find documentation about the frontend structure under Frontend Application, Frontend Operation and Frontend user code. You may need to set up some Event Notification (Hot-Link)s in the frontend. The MIDAS package includes device drivers for some of the more common hardware. See MIDAS Driver Library for more information.
Modify analyzer(s) for your data
Modify the example analyzer code as necessary to analyze the data from your frontends.
Slow Controls
Control your slow-controls equipment with slow-control frontend(s) optionally using the MSCB system.
Create kill_daq script
Optionally create a script similar to start_daq.sh to shutdown the experiment
Data logger
Set up the data logger mlogger to log data to a storage device. Many options are available - see Data Logging, mlogger and /Logger ODB tree for instructions.
Lazy logger
Set up the lazylogger for archiving data for storage.
create edit-on-start parameters
allow programs to be restarted from the Programs Page
See mhttpd Programs Page and /Programs ODB tree
set up the alarm system
See Alarm System and Alarm Page
See mhttpd Status Page#page_switch_buttons
set up history system
See History System and History Page
write scripts which run at start and end of run
See /Programs ODB tree#Execute on start run and /Programs ODB tree#Execute on stop run
set up the Sequencer
The Sequencer Page#Sequencer can be used to run a sequence of runs, changing parameters as needed.
set up the Electronic logbook (Elog)
See Elog for details
write a webserver Custom page
To better control and monitor your experiment, you may want to write a Custom Page.