| ID |
Date |
Author |
Topic |
Subject |
|
1695
|
17 Sep 2019 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | New history plot facility | > > On the mhttpd side, please capture the stack trace from the crash
>
> here comes the stack trace (only happens when using safari 12.1.2 macOS 10.14.6):
>
> #10 0x000000000041ce0f in check_digest_auth ...
>
The crash is in check_digest_auth() which checks the mongoose web server password (if not using
password protection from the https proxy i.e. apache httpd).
If so you should see this crash on all pages, not just when you access history pages, yes?
Ok, I just checked, my safari is "Version 12.1.2 (13607.3.10)" and I see no immediate crash, even on
history pages.
But I am macos 10.13.6, maybe that makes a difference.
If you see the safari crash on all pages, then it is not history-specific.
In this case, I would like you to file a bug report on bitbucket "mhttpd crash with safari" and we follow up
on it there.
K.O. |
|
1727
|
18 Oct 2019 |
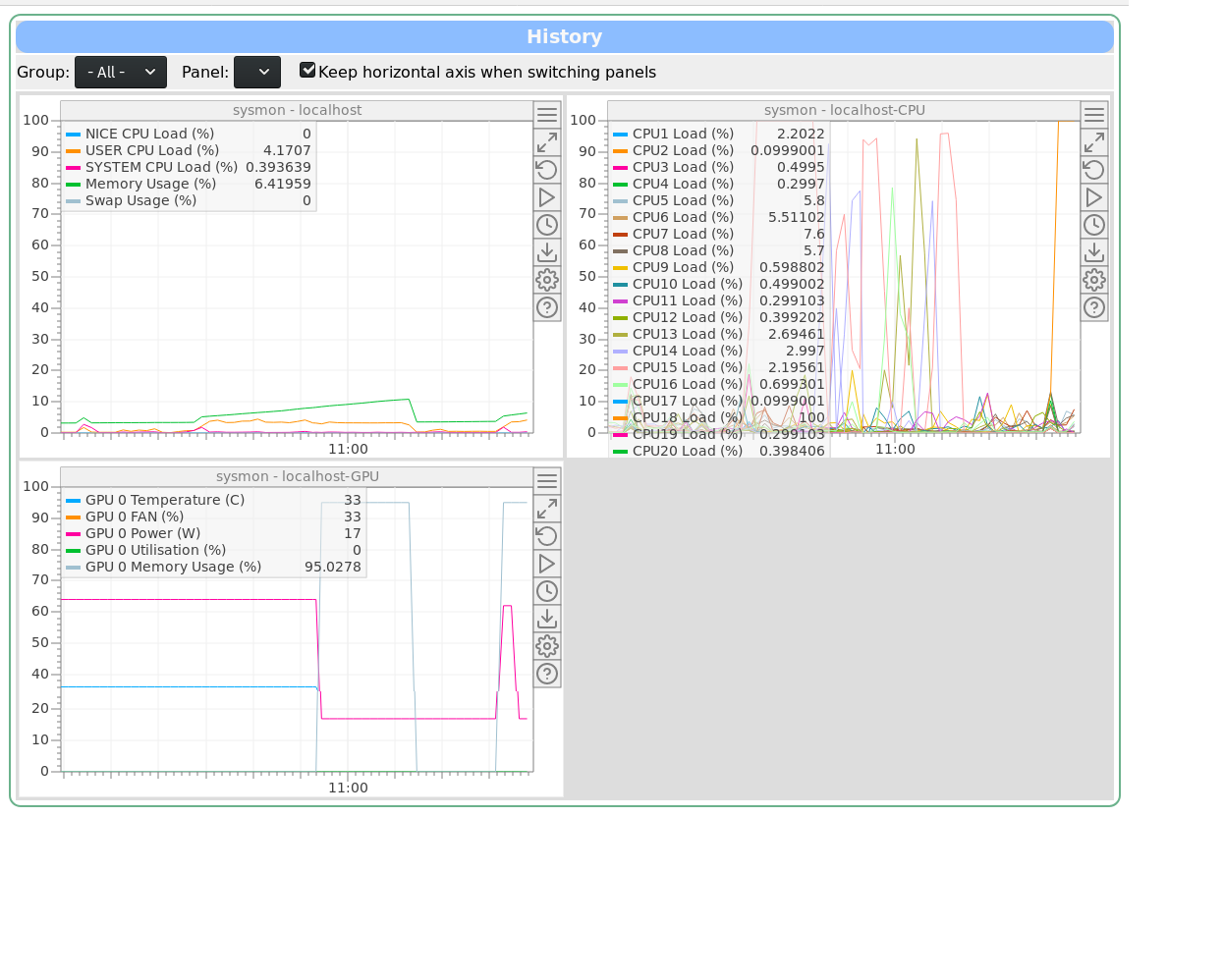
Joseph McKenna | Info | sysmon: New system monitor and performance logging frontend added to MIDAS |
I have written a system monitor tool for MIDAS, that has been merged in the develop branch today: sysmon
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/pull-requests/8/system-monitoring-a-new-frontend-to-log/diff
To use it, simply run the new program
sysmon
on any host that you want to monitor, no configuring required.
The program is a frontend for MIDAS, there is no need for configuration, as upon initialisation it builds a history display for you. Simply run one instance per machine you want to monitor. By default, it only logs once per 10 seconds.
The equipment name is derived from the hostname, so multiple instances can be run across multiple machines without conflict. A new history display will be created for each host.
sysmon uses the /proc pseudo-filesystem, so unfortunately only linux is supported. It does however work with multiple architectures, so x86 and ARM processors are supported.
If the build machine has NVIDIA drivers installed, there is an additional version of sysmon that gets built: sysmon-nvidia. This will log the GPU temperature and usage, as well as CPU, memory and swap. A host should only run either sysmon or sysmon-nvidia
elog:1727/1 shows the History Display generated by sysmon-nvidia. sysmon would only generate the first two displays (sysmon/localhost and sysmon/localhost-CPU) |
| Attachment 1: sysmon-gpu.png
|
|
|
1746
|
03 Dec 2019 |
Joseph McKenna | Info | mfe.c: MIDAS frontend's 'Equipment name' can embed hostname, determined at run-time | A little advertised feature of the modifications needed support the msysmon program is
that MIDAS equipment names can support the injecting of the hostname of the system
running the frontend at runtime (register_equipment(void)).
https://midas.triumf.ca/MidasWiki/index.php/Equipment_List_Parameters#Equipment_Name
A special string ${HOSTNAME} can be put in any position in the equipment name. It will
be replaced with the hostname of the computer running the frontend at run-time. Note,
the frontend_name string will be trimmed down to 32 characters.
Example usage: msysmon
EQUIPMENT equipment[] = {
{ "${HOSTNAME}_msysmon", /* equipment name */ {
EVID_MONITOR, 0, /* event ID, trigger mask */
"SYSTEM", /* event buffer */
EQ_PERIODIC, /* equipment type */
0, /* event source */
"MIDAS", /* format */
TRUE, /* enabled */
RO_ALWAYS, /* Read when running */
10000, /* poll every so milliseconds */
0, /* stop run after this event limit */
0, /* number of sub events */
1, /* history period */
"", "", ""
},
read_system_load,/* readout routine */
},
{ "" }
}; |
|
1748
|
06 Dec 2019 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | c++11 for RHEL/SL/CentOS-6 | > The default el6 (RHEL/SL/CentOS-6) compiler is gcc-4.4.7, it does not support c++11, not even a little bit.
The previously posted instructions are incomplete - one cannot cross-compile 32-bit executables (i.e. for running on 32-bit VME
processors) because 64-bit packages are missing 4 files for the 32-bit C++ standard library (libstdc++_nonshared.a).
After a bit of searching I found the missing files, i.e. here:
https://copr-be.cloud.fedoraproject.org/results/mayeut/devtoolset-8/epel-6-i386/01045166-devtoolset-8-gcc/
There are 2 options:
a) install the 32-bit development package:
rpm -vh --install https://ladd00.triumf.ca/~olchansk/devtoolset-8/devtoolset-8-libstdc++-devel-8.3.1-3.1.el6.i686.rpm
b) install just the 4 missing files from here:
https://ladd00.triumf.ca/~olchansk/devtoolset-8/i686-redhat-linux/8/
into
/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/8/
After doing this, "make linux32" builds. (requires latest midas-2019-09 for minor Makefile fixes)
K.O.
>
> Do this to install newer c++ compilers and build MIDAS with c++11:
>
> ssh root@sl6machine
> # yum install centos-release-scl-rh
> # yum install devtoolset-8
> # yum install cmake3
> # scl -l
> devtoolset-8
> ...
>
> $ ssh user@sl6machine
> $ scl enable devtoolset-8 bash
> $ gcc -v
> COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/lto-wrapper
> gcc version 8.3.1 20190311 (Red Hat 8.3.1-3) (GCC)
> $ cd git/midas
> $ make cclean
> $ make cmake3
> $ ls -l bin/odbedit
>
> K.O. |
|
1758
|
12 Jan 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | midas on centos-8 status | I now have a centos-8 computer and I tried midas on it:
- the develop and midas-2019-09 branches build, mhttpd runs
- there are compiler warnings about use of strncpy() that need to be looked into, but see https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50198319/gcc-8-wstringop-truncation-what-is-
the-good-practice
- mhttpd built-in https support does not seem to work (see the other forum thread)
- apache httpd proxy for https can be made to work, but there are problems with certbot.
K.O. |
|
1764
|
13 Jan 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | How to convert C midas frontends to C++, CAEN libraries | Big thanks to Peter Kunz - specifically when using the CAEN libraries:
>
> After upgrading to the lastes MIDAS version I got the DAQ frontend of my application running by
> changing all compiler directives from cc to g++ and using
>
> #include "mfe.h"
>
> extern HNDLE hDB
>
> extern "C" {
> #include <CAENComm.h>
> }
>
> With these changes everything seems to work fine.
>
K.O.
> > To convert a MIDAS frontend to C++ follow this checklist:
>
> Pierre A.-A. reminded me that include files for CAEN libraries have to
> use "extern C" brackets:
>
> some 3rd party libraries (CAEN, etc) are written in C (or require C linkage),
> if their include files are not C++ compatible (do not have "extern C" brackets
> for all exported symbols), the experiment frontend code must say something like this:
>
> extern "C" {
> #include "3rd-party-c-library.h"
> }
>
> Note: "#ifdef cplusplus" is not needed because we already know we are C++, not C.
>
> K.O. |
|
1769
|
13 Jan 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | status of self-signed https certificates | Now firefox returns the same error. version 72.0.1.
> daqlabpc.triumf.ca has a security policy called HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), which means that Firefox can only connect to it securely. You canít add an exception to visit this site.
> Error code: MOZILLA_PKIX_ERROR_SELF_SIGNED_CERT
I think the problem is with HSTS. I enabled HSTS (in mhttpd and in apache httpd) because
SSLlabs encourage it and because my reading of it's description at
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Strict-Transport-Security
makes it sound like a good idea without any downsides.
However, the actual HSTS RFC says something completely different:
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6797
"The aim is to prevent click-through insecurity and address other potential threats".
To me this explains what I see. In contrast to the description at developer.mozilla.org,
firefox (and google chrome) disable "click-through" exceptions for "I do not like this https certificate",
and there is no way to connect to self-signed https.
Bottom line, either use certbot to get blessed https certificate or no https for you.
K.O.
> > > > In the mean time, we continue to recommend that mhttpd should be used behind a password protected https proxy (i.e. apache
> > > > httpd, etc).
>
> There we go. google-chrome 74 refuses to connect to mhttpd configured with a self-signed certificate generated per instructions printed by mhttpd.
>
> Here is the full error text (there is no button to "let me connect to it anyway"):
>
> Your connection is not private
> Attackers might be trying to steal your information from musr03.triumf.ca (for example, passwords, messages, or credit cards). Learn more
> NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
>
> Help improve Safe Browsing by sending some system information and page content to Google. Privacy policy
> musr03.triumf.ca normally uses encryption to protect your information. When Google Chrome tried to connect to musr03.triumf.ca this time, the website sent back unusual and incorrect credentials. This may happen when an
> attacker is trying to pretend to be musr03.triumf.ca, or a Wi-Fi sign-in screen has interrupted the connection. Your information is still secure because Google Chrome stopped the connection before any data was exchanged.
>
> You cannot visit musr03.triumf.ca right now because the website uses HSTS. Network errors and attacks are usually temporary, so this page will probably work later. |
|
1799
|
29 Jan 2020 |
Pintaudi Giorgio | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Hello!
As you know, the generic MIDAS frontend has a class driver, device driver, bus driver
structure. Assuming a slow device frontend, its class driver should have a routine of type INT idle (EQUIPMENT * pequipment) This routine is called with a rate controlled by the
"/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common/Event limit" parameter.
The idle routine usually reads one channel of the frontend and stores the results
in the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables" ODB folder.
My question is: it is possible to force (from the code) the frontend to call the idle routine at a
certain point. This is because I need to update the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables"
variables inside the "begin_of_run" routine, at a very specific time.
One dirty solution would be to increase a lot the reading rate ... but I need this
increased reading rate only during the run start while I need a low reading rate
during the run. So the question: is it possible to increase and decrease the reading
rate (event limit) of a frontend without stopping and restarting it?
If you need more info, please let me know.
Thank you
Giorgio |
|
1802
|
02 Feb 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Hi, Giorgio - I think you encountered a fundamental problem with what to do at the begin of
run. There are two ways of thinking about it.
Some experiments want to start the run as quickly as possible, so they do not want
begin_of_run() to do too much stuff.
Other experiments want to record all the current settings and conditions before starting a
run, their begin_of_run() will read all the slow controls, interrogate all the power supplies,
read all the voltages, temperatures, pressures, etc. By necessity this will slow down the
starting of the run quite significantly.
The best I understand the midas class driver structure, it is more geared for the first case -
fast starting of runs.
The thinking behind this choice considers the nature of most slow control data in typical
physics experiments:
- if the data does not change quickly (say, room temperature, atmospheric pressure, etc),
and you read it say every 1 minute, then you do not need to read it again at begin run time -
the 1 minute old measurement is still good enough - nothing changed much since then
- if the opposite is true, the data changes wildly (i.e. detector high voltage current goes up
and down in response to the quickly changing beam current), measuring it at the start of
the run does us no good - by the time the first event comes around, it has already changed
completely.
Hopefully Stefan can help you with your specific problem, he has better understanding of
the midas class drivers.
K.O.
[quote="Pintaudi Giorgio"]Hello!
As you know, the generic MIDAS frontend has a class driver, device driver, bus driver
structure. Assuming a slow device frontend, its class driver should have a routine of type
[CODE]INT idle (EQUIPMENT * pequipment)[/CODE]
This routine is called with a rate controlled by the
"[I]/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common/Event limit[/I]" parameter.
The idle routine usually reads one channel of the frontend and stores the results
in the "[I]/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables[/I]" ODB folder.
[B]My question is: it is possible to force (from the code) the frontend to call the idle routine
at a
certain point. This is because I need to update the "[I]/Equipment/<frontend
name>/Variables[/I]"
variables inside the "[I]begin_of_run[/I]" routine, at a very specific time.[/B]
One dirty solution would be to increase a lot the reading rate ... but I need this
increased reading rate only during the run start while I need a low reading rate
during the run. So the question: is it possible to increase and decrease the reading
rate (event limit) of a frontend without stopping and restarting it?
If you need more info, please let me know.
Thank you
Giorgio[/quote] |
|
1805
|
02 Feb 2020 |
Pintaudi Giorgio | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Dear Konstantin,
thank you very much for the explanation. I already have an idea of how to solve my problem by bypassing the class driver altogether or by slightly modifying the mfe.cxx frontend.
But either way is not very elegant. If there was a way to do what I need easily and without writing much code, I would obviously choose that.
So let us wait for Stefan opinion!
Thanks again
Giorgio
| Quote: | > Hi, Giorgio - I think you encountered a fundamental problem with what to do at the begin of
> run. There are two ways of thinking about it.
>
> Some experiments want to start the run as quickly as possible, so they do not want
> begin_of_run() to do too much stuff.
>
> Other experiments want to record all the current settings and conditions before starting a
> run, their begin_of_run() will read all the slow controls, interrogate all the power supplies,
> read all the voltages, temperatures, pressures, etc. By necessity this will slow down the
> starting of the run quite significantly.
>
> The best I understand the midas class driver structure, it is more geared for the first case -
> fast starting of runs.
>
> The thinking behind this choice considers the nature of most slow control data in typical
> physics experiments:
> - if the data does not change quickly (say, room temperature, atmospheric pressure, etc),
> and you read it say every 1 minute, then you do not need to read it again at begin run time -
> the 1 minute old measurement is still good enough - nothing changed much since then
> - if the opposite is true, the data changes wildly (i.e. detector high voltage current goes up
> and down in response to the quickly changing beam current), measuring it at the start of
> the run does us no good - by the time the first event comes around, it has already changed
> completely.
>
> Hopefully Stefan can help you with your specific problem, he has better understanding of
> the midas class drivers.
>
>
> K.O. |
|
|
1806
|
03 Feb 2020 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | It is important to note that slow control readout and sending of midas events are two separate things. Readout is done as fast as possible, even multi-threaded if selected. On fast devices this can be 100 Hz readout rate and even more. This data is stored in an internal buffer. When one of the values changes by more than the update threshold, then the ODB gets updated. The midas events are composed from this internal buffer when a new event has to be sent. This is typically periodic (like every 10 seconds or so), or during run transitions. If you specify this in the equipment list with the RO_xxx flags. If you want an event at the begin-of-run, just add there RO_BOR. It should be noted however that this then creates and event during BOR from the last values in the internal buffer, which - depending on the readout speed - can be a few ms "old". I would recommend that you test the readout speed of your variables and then check if this delay is acceptable.
Best,
Stefan
| Pintaudi Giorgio wrote: | Hello!
As you know, the generic MIDAS frontend has a class driver, device driver, bus driver
structure. Assuming a slow device frontend, its class driver should have a routine of type INT idle (EQUIPMENT * pequipment) This routine is called with a rate controlled by the
"/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common/Event limit" parameter.
The idle routine usually reads one channel of the frontend and stores the results
in the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables" ODB folder.
My question is: it is possible to force (from the code) the frontend to call the idle routine at a
certain point. This is because I need to update the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables"
variables inside the "begin_of_run" routine, at a very specific time.
One dirty solution would be to increase a lot the reading rate ... but I need this
increased reading rate only during the run start while I need a low reading rate
during the run. So the question: is it possible to increase and decrease the reading
rate (event limit) of a frontend without stopping and restarting it?
If you need more info, please let me know.
Thank you
Giorgio |
|
|
1808
|
04 Feb 2020 |
Pintaudi Giorgio | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Dear Stefan,
thank you very much for the clarification. I knew about the DF_XXX flags and I am making good use of them in all my frontends. Anyway, what I really needed was to change the readout rate depending on the run status (in particular DF_RUNNING or DF_TRANSITION).
Moreover, currently, I am not using the MIDAS events framework at all. For the real DAQ, we have our way of acquiring and saving the raw data using the Pyrame software. For the slow control devices, we just use the information that MIDAS automatically saves in the history files .hst (very handy). But I am going to use the MIDAS events at some point in the future, so your explanation is very welcome.
However, I was able to solve my problem by slightly modifying the mfe.cxx file in this way:
@@ -411,6 +411,17 @@ static INT register_equipment(void)
ss_sleep(3000);
return 0;
}
+#ifdef WAGASCI_OPEN_ODB_HOTLINK
+ status = db_open_record(hDB, hKey, eq_info, sizeof(EQUIPMENT), MODE_READ,
+ nullptr, nullptr);
+ if (status != DB_SUCCESS) {
+ printf("ERROR: Cannot open hotlink with equipment record \"%s\", db_open_record() status %d\n",
+ str, status);
+ cm_disconnect_experiment();
+ ss_sleep(3000);
+ return 0;
+ }
+#endif
} else if (status == DB_STRUCT_MISMATCH) {
cm_msg(MINFO, "register_equipment", "Correcting \"%s\", db_check_record() status %d", str, status);
db_create_record(hDB, 0, str, EQUIPMENT_COMMON_STR);
I was quite surprised that I could get things done by just opening a hotlink to the EQUIPMENT eq_info struct. That way I can change dynamically the readout rate (the rate at which the idle routine of a slow device frontend is called is tuned by the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common/Event Limit" variable). I change this variable temporarily during a transition to increase the reading rate. I have done some testing and it seems to have no collateral effect.
There is only one caveat.
- Every change to the equipment "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common" is instantaneously applied (and might crash the frontend?)
Just to give you an example of a situation where all of this might be useful, think about the ramping-up of the high voltage applied to APD or MPPC. When ramping up from 0 to X volts, you want to read out the voltage and current frequently (let's say once every second) to check for overcurrent and stuff. But as soon as the voltage is up and stable you do not need to monitor it every second and a reading every minute might be more than enough. In our case, the HV power supplies are connected through a serial bus (a nightmare to get it working) and once in a while, we have a transitory connection error. If we kept the reading rate very high continuously the log would be flooded with these innocuous errors (but every new shifter would panic every time he/she notices them). Anyway, this is just an example.
| Stefan Ritt wrote: | It is important to note that slow control readout and sending of midas events are two separate things. Readout is done as fast as possible, even multi-threaded if selected. On fast devices this can be 100 Hz readout rate and even more. This data is stored in an internal buffer. When one of the values changes by more than the update threshold, then the ODB gets updated. The midas events are composed from this internal buffer when a new event has to be sent. This is typically periodic (like every 10 seconds or so), or during run transitions. If you specify this in the equipment list with the RO_xxx flags. If you want an event at the begin-of-run, just add there RO_BOR. It should be noted however that this then creates and event during BOR from the last values in the internal buffer, which - depending on the readout speed - can be a few ms "old". I would recommend that you test the readout speed of your variables and then check if this delay is acceptable.
Best,
Stefan
| Pintaudi Giorgio wrote: | Hello!
As you know, the generic MIDAS frontend has a class driver, device driver, bus driver
structure. Assuming a slow device frontend, its class driver should have a routine of type INT idle (EQUIPMENT * pequipment) This routine is called with a rate controlled by the
"/Equipment/<frontend name>/Common/Event limit" parameter.
The idle routine usually reads one channel of the frontend and stores the results
in the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables" ODB folder.
My question is: it is possible to force (from the code) the frontend to call the idle routine at a
certain point. This is because I need to update the "/Equipment/<frontend name>/Variables"
variables inside the "begin_of_run" routine, at a very specific time.
One dirty solution would be to increase a lot the reading rate ... but I need this
increased reading rate only during the run start while I need a low reading rate
during the run. So the question: is it possible to increase and decrease the reading
rate (event limit) of a frontend without stopping and restarting it?
If you need more info, please let me know.
Thank you
Giorgio |
|
|
|
1811
|
07 Feb 2020 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Dear Giorgio,
ok, now I'm slowly getting your point.
Dynamically changing the slow control readout rate is possible with your modification, but I consider this badd practice.
You mentioned the case of your HV over a quirky serial line. I had the same some years ago. Rather than reducing the readout rate to reduce the number of errors, I modified my device driver. If the connection is broken, the driver tries silently to reconnect. Only if the reconnect fails for more than a given period (like 1 min), then an error is produced. Otherwise the driver reads as fast as possible. Imagine you have some instabilities in your HV, which only last for a few seconds. If you read only once per minute, you might miss that. We worked hard to make the slow control system multi-threaded, so a slow many-times-retrying-to-reconnect driver does not slow any other equipment. On the other hand, if the re-connect fails for a minute, then you know that your HV unit really has a problem the shifter should follow up.
Best,
Stefan |
|
1812
|
07 Feb 2020 |
Pintaudi Giorgio | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | Dear Stefan,
Thank you for the advice. I will try to modify the driver as you say. As for the dynamical change of readout rate, basically you are telling me that is not achievable without dirty hacks like mine and it is better to find a way to avoid it.
Best regards
Giorgio
| Stefan Ritt wrote: | Dear Giorgio,
ok, now I'm slowly getting your point.
Dynamically changing the slow control readout rate is possible with your modification, but I consider this badd practice.
You mentioned the case of your HV over a quirky serial line. I had the same some years ago. Rather than reducing the readout rate to reduce the number of errors, I modified my device driver. If the connection is broken, the driver tries silently to reconnect. Only if the reconnect fails for more than a given period (like 1 min), then an error is produced. Otherwise the driver reads as fast as possible. Imagine you have some instabilities in your HV, which only last for a few seconds. If you read only once per minute, you might miss that. We worked hard to make the slow control system multi-threaded, so a slow many-times-retrying-to-reconnect driver does not slow any other equipment. On the other hand, if the re-connect fails for a minute, then you know that your HV unit really has a problem the shifter should follow up.
Best,
Stefan |
|
|
1813
|
09 Feb 2020 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | You dirty hacks will probably work, but what you REALLY want is to read out your HV always as fast as possible, not only during run transitions or ramping. We had a case where a detector produced electrostatic discharges which only lasted for a second or so, and we were happy to detect this in spikes in the HV current. With measurements of only one per minute we would not have realized that so quicky.
Stefan
| Pintaudi Giorgio wrote: | Dear Stefan,
Thank you for the advice. I will try to modify the driver as you say. As for the dynamical change of readout rate, basically you are telling me that is not achievable without dirty hacks like mine and it is better to find a way to avoid it.
|
|
|
1816
|
10 Feb 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | > We had a case where a detector produced electrostatic discharges which only lasted for a second or so
> and we were happy to detect this in spikes in the HV current. With measurements of only one per minute
> we would not have realized that so quicky.
For the T2K/ND280 TPC we implemented something similar. The TPC uses MicroMegas detector which sparks during
normal operation. We asked Wiener/ISEG to implement a "spark counting mode" for us (and they did). In this mode,
high voltage over-current (a micromegas spark) sets a special flag (does not trip the high voltage). Our midas frontend
reads this flag at rate about 1/min, if flag is set, clears it, increments the software spark counter, reads the flag again,
if the flag is still set (failed to clear), it means this was not a normal spark but a high voltage breakdown
and the offending channel is shut down. I believe this mode is still part of the ISEG normal firmware.
Because the Wiener/ISEG interface uses SNMP to "read all data in one operation", the MIDAS "device driver" structure
was not useful, the readout was a simple loop, the readout frequency was easy to control, and indeed,
we read the high voltage with increased frequency during ramping. This was easy to implement because we
did not have to fight the MIDAS "device driver" framework.
If you want a similar solution, talk to the device, interpret the data, record values to odb and history, generate
midas events - all without hand holding from (arm wrestling with the rest of) midas - I recommend
the new tmfe.h/tmfe.cxx c++ frontend - see the two examples in midas/progs/fetest_tmfe.cxx
and fetest_tmfe_thread.cxx (single-threaded and multi-threaded).
K.O. |
|
1821
|
12 Feb 2020 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | Force triggering of idle routine of a frontend | I had a look again at the issue. If you sett the event limit to zero in the EQUIPMENT list, then the idle() routine of your class driver is called as often as possible. Typically with 100 Hz. It's then up to you what to do in the class driver. The hv_idle() routine of the HV class driver shipped in the distribution for example read a channel more often if it has been changed recently. Look at the lines
/* additionally read channel recently updated if not multithreaded */
if (!(hv_info->driver[hv_info->last_channel]->flags & DF_MULTITHREAD)) {
act_time = ss_millitime();
act = (hv_info->last_channel_updated + 1) % hv_info->num_channels;
while (!(act_time - hv_info->last_change[act] < 10000)) {
act = (act + 1) % hv_info->num_channels;
if (act == hv_info->last_channel_updated) {
/* non found, so return */
return status;
}
}
/* updated channel found, so read it additionally */
status = hv_read(pequipment, act);
hv_info->last_channel_updated = act;
}
You can do similar things there like if you are ramping. On an end-of-run, the class drivers cd_xx_read() routine is called from the framework, which in turn sends a full midas event down the stream, but getting the current slow control values from its local cache, not from the actual device (otherwise stopping a run could be very slow). So if you want all values at the end of the run with good precision, you have to read them DURING the run as fast as possible. That's why I posted my comment about fixing dropped serial connections automatically and reading as fast as possible.
Stefan
| Pintaudi Giorgio wrote: | Dear Stefan,
Thank you for the advice. I will try to modify the driver as you say. As for the dynamical change of readout rate, basically you are telling me that is not achievable without dirty hacks like mine and it is better to find a way to avoid it.
|
|
|
1851
|
10 Mar 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | MIDAS vs JSROOT web pages | Just FYI, I am looking at the ROOT web programming component JSROOT and I notice that the RPC mechanism quite different from the JSON-
RPC I implemented for MIDAS.
https://github.com/root-project/jsroot/blob/master/docs/HttpServer.md (explanation of JSROOT RPC and server side machinery)
https://github.com/root-project/jsroot/blob/master/docs/JSROOT.md (explanation of JSROOT javascript library)
Then I looked at the dates:
MIDAS mjsonrpc was done at the end of 2013
JSROOT main development started at the end of 2014.
The web server component in both projects is (almost) the same - vanilla mongoose in mhttpd
and civetweb, a fork of an older version of mongoose, in ROOT/JSROOT.
The web server in both projects is partially multithreaded:
- ROOT THttpServer/TCivetWeb uses multiple threads to handle the network connections and some file access,
but interaction with ROOT is done in the main thread of ROOT. (The main thread must periodically call ProcessRequests()).
- mhttpd uses a single thread to multiplex the network connections (it is a change from old mongoose/civetweb to current mongoose 6.16),
but all requests are farmed to a pool of threads and execute in parallel (unless not thread-safe, i.e. accessing history files).
Both implementations suffer from "head of queue" blocking, a "slow" request i.e. a slow file read, will
delay subsequent quick requests, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Head-of-line_blocking#In_HTTP
Solution for this problem is to use HTTP/2 when it becomes supported in mongoose/civetweb/apache httpd (in el7).
It will be interesting to see which on of the two systems works better for building "user facing" web pages... especially
hybrid pages that have to pull data both from midas (using mjsonrpc) and from online ROOT analyzers (using jsroot).
K.O. |
|
1852
|
16 Mar 2020 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | MIDAS will use C++11 | > After much discussion, and following the MIDAS workshop at TRIUMF, we made the decision to use C++11 in MIDAS.
>
> There are many benefits, and only one drawback - no c++11 compilers in the default OS install on older computers (i.e.
> RHEL/SL/CentOS before el7). (the same applies to our use of cmake).
>
It turns out that support for the c++11 "regex" feature is missing on el7 (CentOS-7, our most common platform at TRIUMF).
According to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12530406/is-gcc-4-8-or-earlier-buggy-about-regular-expressions
gcc 4.9.0 is the first one to implement c++11 regular expressions. el7 comes with gcc-4.8.5 and I confirm
that examples of using std::regex_replace() do not compile. I was looking to use std::regex_replace to implement URL rewriting
in the reverse proxy code in mhttpd.
I do not need this feature immediately, but I am surprised that such a thing can happen, thought others should know.
K.O. |
|
1853
|
16 Mar 2020 |
Pintaudi Giorgio | Info | MIDAS will use C++11 | About the boost library, that is exactly
what I did for a project of mine (the
calibration software for the WAGASCI
experiment). It turned out not so easy to
mantain because different Linux distros
package different versions of boost.
The reason I went down the "c++11 plus
boost" road is that the official T2K OS
is CentOS7 as well.
Looking back I think that using c++17 and
requiring a more recent version of the
compiler is much easier to maintain than
the combo c++11 + boost. In CentOS is
just a matter of installing a recent
devtool package ...
Another solution might be too repackage
boost into MIDAS so you have full control
of the environment.
> > After much discussion, and following
the MIDAS workshop at TRIUMF, we made the
decision to use C++11 in MIDAS.
> >
> > There are many benefits, and only one
drawback - no c++11 compilers in the
default OS install on older computers
(i.e.
> > RHEL/SL/CentOS before el7). (the same
applies to our use of cmake).
> >
>
> It turns out that support for the c++11
"regex" feature is missing on el7
(CentOS-7, our most common platform at
TRIUMF).
>
> According to
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12530
406/is-gcc-4-8-or-earlier-buggy-about-
regular-expressions
> gcc 4.9.0 is the first one to implement
c++11 regular expressions. el7 comes with
gcc-4.8.5 and I confirm
> that examples of using
std::regex_replace() do not compile. I
was looking to use std::regex_replace to
implement URL rewriting
> in the reverse proxy code in mhttpd.
>
> I do not need this feature immediately,
but I am surprised that such a thing can
happen, thought others should know.
>
> K.O. |
|