TVldTimeStamp Class Reference
Encapsulate the seconds and ns since EPOCH. More...
#include <TVldTimeStamp.hxx>
Public Member Functions | |
| TVldTimeStamp () | |
| Empty ctor (builds current time with nsec field filled as best possible). | |
| TVldTimeStamp (const TVldTimeStamp &source) | |
| Copy. | |
| TVldTimeStamp & | operator= (const TVldTimeStamp &source) |
| Assignment. | |
| TVldTimeStamp (const timespec_t &ts) | |
| Construction from timespec struct. | |
| TVldTimeStamp (const time_t &t, const Int_t nsec) | |
| Construction from time_t and separate nsec. | |
| TVldTimeStamp (UInt_t year, UInt_t month, UInt_t day, UInt_t hour, UInt_t min, UInt_t sec, UInt_t nsec=0, Bool_t isUTC=kTRUE, Int_t secOffset=0) | |
| TVldTimeStamp (UInt_t date, UInt_t time, UInt_t nsec, Bool_t isUTC=kTRUE, Int_t secOffset=0) | |
| TVldTimeStamp (Double_t seconds) | |
| virtual | ~TVldTimeStamp () |
| operator double () const | |
| timespec_t | GetTimeSpec () const |
| Get timestamp as a timespec_t. | |
| time_t | GetSec (void) const |
| Get (integral) seconds after the EPOCH. | |
| Int_t | GetNanoSec (void) const |
| Get nanoseconds after the second. | |
| Double_t | GetSeconds (void) const |
| Get time from the epoch in seconds. | |
| const char * | AsString (Option_t *option="") const |
| void | Copy (TVldTimeStamp &vldts) const |
| Int_t | GetDate (Bool_t inUTC=kTRUE, Int_t secOffset=0, UInt_t *year=0, UInt_t *month=0, UInt_t *day=0) const |
| Int_t | GetTime (Bool_t inUTC=kTRUE, Int_t secOffset=0, UInt_t *hour=0, UInt_t *min=0, UInt_t *sec=0) const |
| void | Add (const TVldTimeStamp &offset) |
| void | Add (Double_t seconds) |
| void | Print (Option_t *option="") const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static TVldTimeStamp | GetBOT () |
| Static method to return the "beginning of time" (start of Unix EPOCH). | |
| static TVldTimeStamp | GetEOT () |
| static TVldTimeStamp | GetNBOT () |
| static Int_t | GetZoneOffset () |
| static time_t | MktimeFromUTC (tm_t *tmstruct) |
| static Bool_t | IsLeapYear (Int_t year) |
| Is the given year a leap year. | |
| static void | DumpTMStruct (const tm_t &tmstruct) |
| Print out the "tm" structure:. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | Set () |
| void | Set (Int_t year, Int_t month, Int_t day, Int_t hour, Int_t min, Int_t sec, Int_t nsec, Bool_t isUTC, Int_t secOffset) |
| void | Set (Int_t date, Int_t time, Int_t nsec, Bool_t isUTC, Int_t secOffset) |
| void | NormalizeNanoSec () |
Private Attributes | |
| Int_t | fSec |
| Int_t | fNanoSec |
Friends | |
| Bool_t | operator== (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| Bool_t | operator!= (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| Bool_t | operator< (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| Bool_t | operator<= (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| Bool_t | operator> (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| Bool_t | operator>= (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
| TVldTimeStamp | operator- (const TVldTimeStamp &lhs, const TVldTimeStamp &rhs) |
Detailed Description
Encapsulate the seconds and ns since EPOCH.
This extends (and isolates) struct timespec
struct timespec { time_t tv_sec; // seconds long tv_nsec; // nanoseconds } time_t seconds is relative to Jan 1, 1970 00:00:00 UTC
Due to ROOT/CINT limitations TVldTimeStamp does not explicitly hold a timespec struct; attempting to do so means the Streamer must be hand written. Instead we have chosen to simply contain similar fields within the private area of this class.
- Note:
- the use of time_t (and its default implementation as a 32 int) implies overflow conditions occurs somewhere around Jan 18, 19:14:07, 2038. If this experiment is still going when it becomes significant someone will have to deal with it.
- Author
- finch
- Version:
- Revision
- 1.2
- Date:
- Date
- 2011/06/09 14:44:29
Contact: R. Hatcher
Created on: Wed Apr 13 17:53:23 2005
Author: R. Hatcher 2000.04.19 R. Hatcher 2000.12.20 -- convert from TDatime to struct timespec
- Id
- TVldTimeStamp.hxx,v 1.2 2011/06/09 14:44:29 finch Exp
Definition at line 62 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
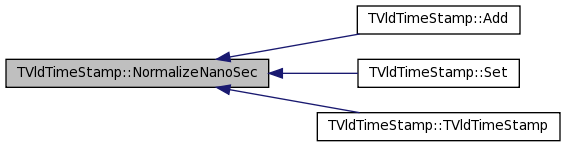
| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | ) |
| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | source | ) | [inline] |
| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | const timespec_t & | ts | ) | [inline] |
Construction from timespec struct.
Definition at line 101 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References NormalizeNanoSec().
00102 : fSec(ts.tv_sec), fNanoSec(ts.tv_nsec) 00103 { NormalizeNanoSec(); }

| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | const time_t & | t, | |
| const Int_t | nsec | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Construction from time_t and separate nsec.
Definition at line 106 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References NormalizeNanoSec().
00107 : fSec(t), fNanoSec(nsec) 00108 { NormalizeNanoSec(); }

| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | UInt_t | year, | |
| UInt_t | month, | |||
| UInt_t | day, | |||
| UInt_t | hour, | |||
| UInt_t | min, | |||
| UInt_t | sec, | |||
| UInt_t | nsec = 0, |
|||
| Bool_t | isUTC = kTRUE, |
|||
| Int_t | secOffset = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create a TVldTimeStamp and set it to the specified year, month, day, time, hour, minute, second and nanosec. If !isUTC then it is assumed to be the standard local time zone.
If local time is PST then one can use
TVldTimeStamp(year,month,day,hour,min,sec,nsec,kFALSE,0);
or
Int_t secOffset = 8*60*60; TVldTimeStamp(year,month,day,hour,min,sec,nsec,kTRUE,8*60*60);
Definition at line 89 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References Set().
00094 : fSec(0), fNanoSec(0) 00095 { 00096 // Create a TVldTimeStamp and set it to the specified year, month, 00097 // day, time, hour, minute, second and nanosec. 00098 // If !isUTC then it is assumed to be the standard local time zone. 00099 // 00100 // If local time is PST then one can use 00101 // TVldTimeStamp(year,month,day,hour,min,sec,nsec,kFALSE,0); 00102 // or 00103 // Int_t secOffset = 8*60*60; 00104 // TVldTimeStamp(year,month,day,hour,min,sec,nsec,kTRUE,8*60*60); 00105 00106 Set(year, month, day, hour, min, sec, nsec, isUTC, secOffset); 00107 }

| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | UInt_t | date, | |
| UInt_t | time, | |||
| UInt_t | nsec, | |||
| Bool_t | isUTC = kTRUE, |
|||
| Int_t | secOffset = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create a TVldTimeStamp and set it to the specified date, time, nanosec. If !isUTC then it is assumed to be the standard local time zone.
Definition at line 110 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References Set().
00112 : fSec(0), fNanoSec(0) 00113 { 00114 // Create a TVldTimeStamp and set it to the specified date, time, nanosec. 00115 // If !isUTC then it is assumed to be the standard local time zone. 00116 00117 Set(date, time, nsec, isUTC, secOffset); 00118 }

| TVldTimeStamp::TVldTimeStamp | ( | Double_t | seconds | ) | [inline] |
Create a TVldTimeStamp using double precision floating point seconds from the EPOCH.
- Warning:
- This will truncate precision to no better than about 1 microsecond. Do not use this constructor for timestamps that are expected to be more precise!
Definition at line 140 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References NormalizeNanoSec().
00141 : fSec((Int_t)seconds), fNanoSec((Int_t)((seconds-fSec)*1.0e9)) 00142 { NormalizeNanoSec(); }

| TVldTimeStamp::~TVldTimeStamp | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 86 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
Member Function Documentation
| void TVldTimeStamp::Add | ( | Double_t | seconds | ) |
Definition at line 296 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, fSec, NormalizeNanoSec(), and SK_DBI_Warn.
00297 { 00298 // Add 'seconds' as a delta time 00299 00300 fSec += (Int_t) seconds; 00301 fNanoSec += (Int_t) (fmod(seconds,1.0) * 1e9); 00302 NormalizeNanoSec(); 00303 if(seconds > 1e6) 00304 SK_DBI_Warn( "VldTimeStamp moved by offset " << seconds <<" which is too large to maintain ns accuracy." << " "); 00305 }

| void TVldTimeStamp::Add | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | offset | ) |
Definition at line 286 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, fSec, and NormalizeNanoSec().
00287 { 00288 // Add "offset" as a delta time. 00289 00290 fSec += offset.fSec; 00291 fNanoSec += offset.fNanoSec; 00292 NormalizeNanoSec(); 00293 00294 }

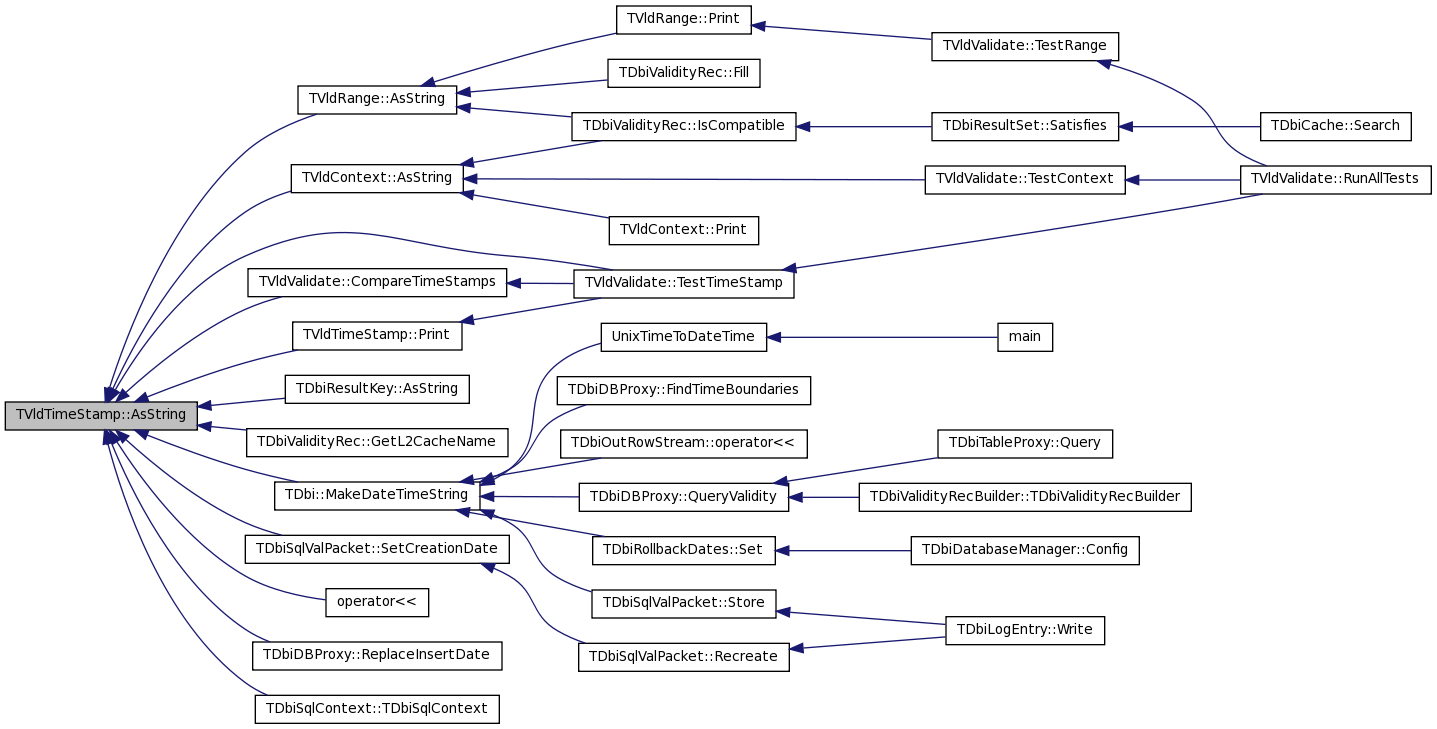
| const char * TVldTimeStamp::AsString | ( | Option_t * | option = "" |
) | const |
Return the date & time as a string.
Result is pointer to a statically allocated string. User should copy this into their own buffer before calling this method again. This is somewhat mitigated by use of a circular buffer of strings.
Option "l" returns it in local zone format (can be applied to default or compact format).
Default format is RFC822 compliant: "Mon, 02 Jan 2001 18:11:12 +0000 (GMT) +999999999 nsec" "Mon, 02 Jan 2001 10:11:12 -0800 (PST) +999999999 nsec"
Option "c" compact is (almost) ISO 8601 compliant: "2001-01-02 18:11:12.9999999999Z" "2001-01-02 10:11:12.9999999999-0800" if PST * uses "-" as date separator as specified in ISO 8601 * uses "." rather than preferred "," for decimal separator * -HHMM is the difference between local and UTC (if behind, + if ahead). The "-HHMM" is replaced with "Z" if given as UTC. To be strictly conforming it should use "T" instead of the blank separating the date and time.
Option "2" returns as {sec,nsec} integers.
Option "s" returns "2001-01-02 18:11:12" with an implied UTC, overrides "l" option.
Internally uses a circular list of buffers to avoid problems using AsString multiple times in a single statement.
Definition at line 121 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, and fSec.
Referenced by TVldRange::AsString(), TVldContext::AsString(), TDbiResultKey::AsString(), TVldValidate::CompareTimeStamps(), TDbiValidityRec::GetL2CacheName(), TDbi::MakeDateTimeString(), operator<<(), Print(), TDbiDBProxy::ReplaceInsertDate(), TDbiSqlValPacket::SetCreationDate(), TDbiSqlContext::TDbiSqlContext(), and TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().
00122 { 00123 // Return the date & time as a string. 00124 // 00125 // Result is pointer to a statically allocated string. 00126 // User should copy this into their own buffer before calling 00127 // this method again. This is somewhat mitigated 00128 // by use of a circular buffer of strings. 00129 // 00130 // Option "l" returns it in local zone format 00131 // (can be applied to default or compact format). 00132 // 00133 // Default format is RFC822 compliant: 00134 // "Mon, 02 Jan 2001 18:11:12 +0000 (GMT) +999999999 nsec" 00135 // "Mon, 02 Jan 2001 10:11:12 -0800 (PST) +999999999 nsec" 00136 // 00137 // Option "c" compact is (almost) ISO 8601 compliant: 00138 // "2001-01-02 18:11:12.9999999999Z" 00139 // "2001-01-02 10:11:12.9999999999-0800" if PST 00140 // * uses "-" as date separator as specified in ISO 8601 00141 // * uses "." rather than preferred "," for decimal separator 00142 // * -HHMM is the difference between local and UTC (if behind, + if ahead). 00143 // The "-HHMM" is replaced with "Z" if given as UTC. 00144 // To be strictly conforming it should use "T" instead of the 00145 // blank separating the date and time. 00146 // 00147 // Option "2" returns as {sec,nsec} integers. 00148 // 00149 // Option "s" returns "2001-01-02 18:11:12" with an implied UTC, 00150 // overrides "l" option. 00151 00152 // Internally uses a circular list of buffers to avoid problems 00153 // using AsString multiple times in a single statement. 00154 00155 const int nbuffers = 8; // # of buffers 00156 00157 static char formatted[nbuffers][64]; // strftime fields substituted 00158 static char formatted2[nbuffers][64]; // nanosec field substituted 00159 static int ibuffer = nbuffers; 00160 ibuffer = (ibuffer+1)%nbuffers; // each call moves to next buffer 00161 00162 TString opt = option; 00163 opt.ToLower(); 00164 00165 if (opt.Contains("2")) { 00166 // return string formatted as integer {sec,nsec} 00167 sprintf(formatted[ibuffer], "{%d,%d}", fSec, fNanoSec); 00168 return formatted[ibuffer]; 00169 } 00170 00171 #ifdef linux 00172 // under linux %z is the hour offset and %Z is the timezone name 00173 const char *RFC822 = "%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S %z (%Z) +#9ld nsec"; 00174 const char *ISO8601 = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.#9.9ld%z"; 00175 const char *ISO8601Z = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.#9.9ldZ"; 00176 #else 00177 // otherwise only %Z is guarenteed to be defind 00178 const char *RFC822 = "%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S %Z +#9ld nsec"; 00179 const char *ISO8601 = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.#9.9ld%Z"; 00180 const char *ISO8601Z = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.#9.9ldZ"; 00181 #endif 00182 const char *SQL = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"; 00183 00184 Bool_t asLocal = opt.Contains("l"); 00185 Bool_t asSQL = opt.Contains("s"); 00186 if (asSQL) asLocal = kFALSE; 00187 00188 const char *format = RFC822; 00189 if (opt.Contains("c")) { 00190 format = ISO8601; 00191 if (!asLocal) format = ISO8601Z; 00192 } 00193 if (asSQL) format = SQL; 00194 00195 struct tm *ptm; 00196 time_t seconds = (time_t) fSec; // deal with possible mismatch of types 00197 // of fSec and the time_t required 00198 // by functions 00199 00200 // get the components into a tm struct 00201 ptm = (asLocal) ? localtime(&seconds) : gmtime(&seconds); 00202 00203 // format all but the nsec field 00204 // size_t length = 00205 strftime(formatted[ibuffer], sizeof(formatted[ibuffer]), format, ptm); 00206 00207 if (asSQL) return formatted[ibuffer]; 00208 00209 // hack in the nsec part 00210 char *ptr = strrchr(formatted[ibuffer], '#'); 00211 if (ptr) *ptr = '%'; // substitute % for # 00212 sprintf(formatted2[ibuffer], formatted[ibuffer], fNanoSec); 00213 00214 return formatted2[ibuffer]; 00215 }
| void TVldTimeStamp::Copy | ( | TVldTimeStamp & | vldts | ) | const |
| void TVldTimeStamp::DumpTMStruct | ( | const tm_t & | tmstruct | ) | [static] |
Print out the "tm" structure:.
Definition at line 568 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
00569 { 00570 // Print out the "tm" structure: 00571 // tmstruct.tm_year = year; // years since 1900 00572 // tmstruct.tm_mon = month-1; // months since Jan [0,11] 00573 // tmstruct.tm_mday = day; // day of the month [1,31] 00574 // tmstruct.tm_hour = hour; // hours since midnight [0,23] 00575 // tmstruct.tm_min = min; // minutes after the hour [0,59] 00576 // tmstruct.tm_sec = sec; // seconds after the minute [0,59] 00577 // tmstruct.tm_wday // day of week [0,6] 00578 // tmstruct.tm_yday // days in year [0,365] 00579 // tmstruct.tm_isdst // DST [-1/0/1] (unknown,false,true) 00580 00581 printf(" tm { year %4d, mon %2d, day %2d,\n", 00582 tmstruct.tm_year, 00583 tmstruct.tm_mon, 00584 tmstruct.tm_mday); 00585 printf(" hour %2d, min %2d, sec %2d,\n", 00586 tmstruct.tm_hour, 00587 tmstruct.tm_min, 00588 tmstruct.tm_sec); 00589 printf(" wday %2d, yday %3d, isdst %2d", 00590 tmstruct.tm_wday, 00591 tmstruct.tm_yday, 00592 tmstruct.tm_isdst); 00593 #ifdef linux 00594 //#ifdef __GNUC__ 00595 // special GCC extras 00596 printf(",\n tm_gmtoff %7ld, tm_zone \"%s\"", 00597 #ifdef __USE_BSD 00598 tmstruct.tm_gmtoff,tmstruct.tm_zone); 00599 #else 00600 tmstruct.__tm_gmtoff,tmstruct.__tm_zone); 00601 #endif 00602 #endif 00603 printf("}\n"); 00604 }
| TVldTimeStamp TVldTimeStamp::GetBOT | ( | ) | [static] |
Static method to return the "beginning of time" (start of Unix EPOCH).
Definition at line 64 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References TVldTimeStamp().
00065 { 00066 return TVldTimeStamp((time_t)0,0); 00067 }

| Int_t TVldTimeStamp::GetDate | ( | Bool_t | inUTC = kTRUE, |
|
| Int_t | secOffset = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | year = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | month = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | day = 0 | |||
| ) | const |
Return date in form of 19971224 (i.e. 24/12/1997), if non-zero pointers supplied for year, month, day fill those as well
Definition at line 228 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fSec.
Referenced by TDbi::MakeTimeStamp(), and TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().
00230 { 00231 // Return date in form of 19971224 (i.e. 24/12/1997), 00232 // if non-zero pointers supplied for year, month, day fill those as well 00233 00234 time_t atime = fSec + secOffset; 00235 struct tm *ptm = (inUTC) ? gmtime(&atime) : localtime(&atime); 00236 00237 if (year) *year = ptm->tm_year + 1900; 00238 if (month) *month = ptm->tm_mon + 1; 00239 if (day) *day = ptm->tm_mday; 00240 00241 return (1900+ptm->tm_year)*10000 + (1+ptm->tm_mon)*100 + ptm->tm_mday; 00242 00243 }
| TVldTimeStamp TVldTimeStamp::GetEOT | ( | ) | [static] |
Static method to return the "end of time" which is sometime in the future and near or at the limit of TVldTimeStamp's ability to hold large times.
Definition at line 69 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References TVldTimeStamp().
00070 { 00071 return TVldTimeStamp((time_t)INT_MAX,0); 00072 }

| Int_t TVldTimeStamp::GetNanoSec | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get nanoseconds after the second.
Definition at line 164 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References fNanoSec.
Referenced by operator-().
00164 { return fNanoSec; }
| TVldTimeStamp TVldTimeStamp::GetNBOT | ( | ) | [static] |
Static method to return the "negative beginning of time", i.e. the earliest time prior to start of Unix EPOCH which is negative seconds.
Definition at line 74 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References TVldTimeStamp().
00075 { 00076 return TVldTimeStamp((time_t)INT_MIN,0); 00077 }

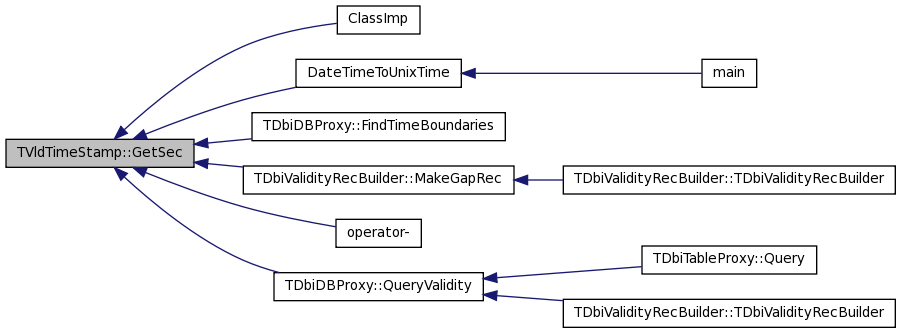
| time_t TVldTimeStamp::GetSec | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get (integral) seconds after the EPOCH.
Definition at line 162 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References fSec.
Referenced by ClassImp(), DateTimeToUnixTime(), TDbiDBProxy::FindTimeBoundaries(), TDbiValidityRecBuilder::MakeGapRec(), operator-(), and TDbiDBProxy::QueryValidity().
00162 { return fSec;}
| Double_t TVldTimeStamp::GetSeconds | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
| Int_t TVldTimeStamp::GetTime | ( | Bool_t | inUTC = kTRUE, |
|
| Int_t | secOffset = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | hour = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | min = 0, |
|||
| UInt_t * | sec = 0 | |||
| ) | const |
Return time in form of 123623 (i.e. 12:36:23), if non-zero pointers supplied for hour, min, sec fill those as well
Definition at line 246 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fSec.
Referenced by TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().
00248 { 00249 // Return time in form of 123623 (i.e. 12:36:23), 00250 // if non-zero pointers supplied for hour, min, sec fill those as well 00251 00252 time_t atime = fSec + secOffset; 00253 struct tm *ptm = (inUTC) ? gmtime(&atime) : localtime(&atime); 00254 00255 if (hour) *hour = ptm->tm_hour; 00256 if (min) *min = ptm->tm_min; 00257 if (sec) *sec = ptm->tm_sec; 00258 00259 return ptm->tm_hour*10000 + ptm->tm_min*100 + ptm->tm_sec; 00260 00261 }

| timespec_t TVldTimeStamp::GetTimeSpec | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get timestamp as a timespec_t.
Definition at line 158 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
References fNanoSec, and fSec.
Referenced by TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().

| Int_t TVldTimeStamp::GetZoneOffset | ( | ) | [static] |
Static method returning local (current) time zone offset from UTC. This is the difference in seconds between UTC and local standard time.
Definition at line 264 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
Referenced by TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().
00265 { 00266 // Static method returning local (current) time zone offset from UTC. 00267 // This is the difference in seconds between UTC and local standard time. 00268 00269 // ?? should tzset (_tzset) be called? 00270 #ifndef R__WIN32 00271 tzset(); 00272 #if !defined(R__MACOSX) && !defined(R__FBSD) 00273 return timezone; /* unix has extern long int */ 00274 #else 00275 time_t *tp = 0; 00276 time(tp); 00277 return localtime(tp)->tm_gmtoff; 00278 #endif 00279 #else 00280 _tzset(); 00281 return _timezone; /* Win32 prepends "_" */ 00282 #endif 00283 }

| Bool_t TVldTimeStamp::IsLeapYear | ( | Int_t | year | ) | [static] |
Is the given year a leap year.
Definition at line 534 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
Referenced by MktimeFromUTC().
00535 { 00536 // Is the given year a leap year. 00537 00538 00539 // The calendar year is 365 days long, unless the year is exactly divisible 00540 // by 4, in which case an extra day is added to February to make the year 00541 // 366 days long. If the year is the last year of a century, eg. 1700, 1800, 00542 // 1900, 2000, then it is only a leap year if it is exactly divisible by 00543 // 400. Therefore, 1900 wasn't a leap year but 2000 was. The reason for 00544 // these rules is to bring the average length of the calendar year into 00545 // line with the length of the Earth's orbit around the Sun, so that the 00546 // seasons always occur during the same months each year. 00547 00548 if (year%4 != 0) { 00549 return false; 00550 } 00551 else { 00552 if (year%400 == 0) { 00553 return true; 00554 } 00555 else { 00556 if (year%100 == 0) { 00557 return false; 00558 } 00559 else { 00560 return true; 00561 } 00562 } 00563 } 00564 00565 }

| time_t TVldTimeStamp::MktimeFromUTC | ( | tm_t * | tmstruct | ) | [static] |
Equivalent of standard routine "mktime" but using the assumption that tm struct is filled with UTC, not local, time.
This version *ISN'T* configured to handle every possible weirdness of out-of-range values in the case of normalizing the tm struct.
This version *DOESN'T* correctly handle values that can't be fit into a time_t (i.e. beyond year 2038-01-18 19:14:07, or before the start of Epoch).
Definition at line 476 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References IsLeapYear().
Referenced by Set().
00477 { 00478 // Equivalent of standard routine "mktime" but 00479 // using the assumption that tm struct is filled with UTC, not local, time. 00480 00481 // This version *ISN'T* configured to handle every possible 00482 // weirdness of out-of-range values in the case of normalizing 00483 // the tm struct. 00484 00485 // This version *DOESN'T* correctly handle values that can't be 00486 // fit into a time_t (i.e. beyond year 2038-01-18 19:14:07, or 00487 // before the start of Epoch). 00488 00489 const Int_t days[] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 00490 const Int_t daysLeap[] = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 00491 00492 Int_t year = tmstruct->tm_year + 1900; 00493 Bool_t isleap = TVldTimeStamp::IsLeapYear(year); 00494 00495 const Int_t *daysInMonth = days; 00496 if (isleap) daysInMonth = daysLeap; 00497 00498 // fill in tmstruct->tm_yday 00499 00500 int &ref_tm_mon = tmstruct->tm_mon; 00501 int &ref_tm_mday = tmstruct->tm_mday; 00502 // count days in months past 00503 tmstruct->tm_yday = 0; 00504 for (Int_t imonth = 0; imonth < ref_tm_mon; imonth++) { 00505 tmstruct->tm_yday += daysInMonth[imonth]; 00506 } 00507 tmstruct->tm_yday += ref_tm_mday - 1; // day [1-31] but yday [0-365] 00508 00509 // adjust if day in this month is more than the month has 00510 while (ref_tm_mday > daysInMonth[ref_tm_mon]) { 00511 ref_tm_mday -= daysInMonth[ref_tm_mon]; 00512 ref_tm_mon++; 00513 } 00514 00515 // *should* calculate tm_wday (0-6) here ... 00516 00517 // UTC is never DST 00518 tmstruct->tm_isdst = 0; 00519 00520 // Calculate seconds since the Epoch based on formula in 00521 // POSIX IEEEE Std 1003.1b-1993 pg 22 00522 00523 Int_t utc_sec = tmstruct->tm_sec + 00524 tmstruct->tm_min*60 + 00525 tmstruct->tm_hour*3600 + 00526 tmstruct->tm_yday*86400 + 00527 (tmstruct->tm_year-70)*31536000 + 00528 ((tmstruct->tm_year-69)/4)*86400; 00529 00530 return utc_sec; 00531 }
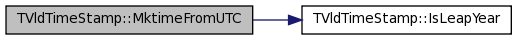

| void TVldTimeStamp::NormalizeNanoSec | ( | ) | [private] |
Definition at line 460 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, and fSec.
Referenced by Add(), Set(), and TVldTimeStamp().
00461 { 00462 // Ensure that the fNanoSec field is in range [0,99999999]. 00463 00464 // deal with negative values 00465 while (fNanoSec < 0) { 00466 fNanoSec += kNsPerSec; 00467 fSec -= 1; 00468 } 00469 // deal with values inf fNanoSec greater than one sec 00470 while (fNanoSec >= kNsPerSec) { 00471 fNanoSec -= kNsPerSec; 00472 fSec += 1; 00473 } 00474 }
| TVldTimeStamp::operator double | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Implicitly convert a TVldTimeStamp to a double.
- Warning:
- This will truncate precision to no better than about 1 microsecond. Do not compare/subtract TVldTimeStamps that have been converted to doubles if you require the full nanosecond precision!
Definition at line 154 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
| TVldTimeStamp& TVldTimeStamp::operator= | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | source | ) | [inline] |
| void TVldTimeStamp::Print | ( | Option_t * | option = "" |
) | const |
Definition at line 308 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References AsString().
Referenced by TVldValidate::TestTimeStamp().
00309 { 00310 // Print date and time. 00311 00312 printf("Date/Time = %s\n", AsString(option)); 00313 00314 }


| void TVldTimeStamp::Set | ( | Int_t | date, | |
| Int_t | time, | |||
| Int_t | nsec, | |||
| Bool_t | isUTC, | |||
| Int_t | secOffset | |||
| ) | [private] |
Definition at line 419 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References Set().
00421 { 00422 // Set date/time from integers of the form [yy]YYMMDD and HHMMSS, 00423 // assume UTC (UTC) components: 00424 // 00425 // MM: 01=January .. 12=December 00426 // DD: 01 .. 31 00427 // 00428 // HH: 00=midnight .. 23 00429 // MM: 00 .. 59 00430 // SS: 00 .. 69 00431 // 00432 // Date must be in format 980418 or 19980418 00433 // 1001127 or 20001127 (i.e. year 100 = 2000). 00434 // Time must be in format 224512 (second precision). 00435 // Date must be >= 700101. 00436 00437 Int_t year = date/10000; 00438 Int_t month = (date-year*10000)/100; 00439 Int_t day = date%100; 00440 00441 // protect against odd attempts at time offsets 00442 const Int_t oneday = 240000; 00443 while (time < 0) { 00444 time += oneday; 00445 day -= 1; 00446 } 00447 while (time > oneday) { 00448 time -= oneday; 00449 day += 1; 00450 } 00451 Int_t hour = time/10000; 00452 Int_t min = (time-hour*10000)/100; 00453 Int_t sec = time%100; 00454 00455 Set(year, month, day, hour, min, sec, nsec, isUTC, secOffset); 00456 00457 }

| void TVldTimeStamp::Set | ( | Int_t | year, | |
| Int_t | month, | |||
| Int_t | day, | |||
| Int_t | hour, | |||
| Int_t | min, | |||
| Int_t | sec, | |||
| Int_t | nsec, | |||
| Bool_t | isUTC, | |||
| Int_t | secOffset | |||
| ) | [private] |
Definition at line 367 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, fSec, MktimeFromUTC(), NormalizeNanoSec(), and SK_DBI_Info.
00370 { 00371 // Set Date/Time from components. 00372 // 00373 // month & day both use normal 1..12 and 1..31 counting 00374 // hours, min, sec run from 0 to 23, 59, 59 respectively; 00375 // secOffset provides method for adjusting for alternative timezones 00376 // 00377 // "year" | 0 1 ... 37 | 38...69 | 70 .. 100 101 .. 137 00378 // true | 2000 2001 2037 | undefined | 1970 2000 2001 .. 2037 00379 // 00380 // "year" | 138...1969 | 1970 .. 2037 | ... 00381 // true | undefined | 1970 .. 2037 | undefined 00382 // 00383 00384 00385 // deal with special formats of year 00386 if (year <= 37) year += 2000; 00387 if (year >= 70 && year <= 137) year += 1900; 00388 // tm.tm_year is years since 1900 00389 if (year >= 1900) year -= 1900; 00390 00391 struct tm tmstruct; 00392 tmstruct.tm_year = year; // years since 1900 00393 tmstruct.tm_mon = month-1; // months since Jan [0,11] 00394 tmstruct.tm_mday = day; // day of the month [1,31] 00395 tmstruct.tm_hour = hour; // hours since midnight [0,23] 00396 tmstruct.tm_min = min; // minutes after the hour [0,59] 00397 tmstruct.tm_sec = sec + secOffset; // seconds after the minute [0,59] 00398 tmstruct.tm_isdst = -1; // let "mktime" determine DST setting 00399 00400 const time_t bad_time_t = (time_t) -1; 00401 // convert tm struct to time_t, if values are given in UTC then 00402 // no standard routine exists and we'll have to use our homegrown routine, 00403 // if values are given in local time then use "mktime" 00404 // which also normalizes the tm struct as a byproduct 00405 time_t utc_sec = (isUTC) ? MktimeFromUTC(&tmstruct) : mktime(&tmstruct); 00406 00407 // TVldTimeStamp::Dump_tm_struct(tmstruct); 00408 00409 if (utc_sec == bad_time_t) 00410 SK_DBI_Info( "VldTimeStamp::Set mktime returned -1" << " "); 00411 00412 fSec = utc_sec; 00413 fNanoSec = nsec; 00414 00415 NormalizeNanoSec(); 00416 }
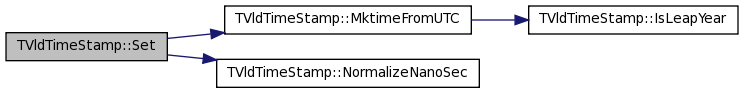
| void TVldTimeStamp::Set | ( | ) | [private] |
Definition at line 317 of file TVldTimeStamp.cxx.
References fNanoSec, and fSec.
Referenced by Set(), and TVldTimeStamp().
00318 { 00319 // Set Date/Time to current time as reported by the system. 00320 // no accounting for nanoseconds with std ANSI functions, 00321 // ns part faked so that subsequent calls simply add 1 to it 00322 // this ensures that calls within the same second come back 00323 // distinct (and sortable). 00324 00325 #ifdef R__WIN32 00326 ULARGE_INTEGER time; 00327 GetSystemTimeAsFileTime((FILETIME *)&time); 00328 // NT keeps time in FILETIME format which is 100ns ticks since 00329 // Jan 1, 1601. TTimeStamps use time in 100ns ticks since Jan 1, 1970. 00330 // The difference is 134774 days. 00331 fNanoSec = Int_t((time.QuadPart * (unsigned __int64) 100) % 00332 (unsigned __int64) 1000000000); 00333 time.QuadPart -= 00334 (unsigned __int64) (1000*1000*10) // seconds 00335 * (unsigned __int64) (60 * 60 * 24) // days 00336 * (unsigned __int64) (134774); // # of days 00337 00338 fSec = Int_t(time.QuadPart/(unsigned __int64) (1000*1000*10)); 00339 #else 00340 // this should work on UNIX to get microsec precision 00341 // we'll stick to a ns hack to make calls unique 00342 struct timeval now; 00343 if (!gettimeofday(&now,0)) { 00344 fSec = now.tv_sec; 00345 fNanoSec = now.tv_usec * 1000; 00346 } 00347 else { 00348 time_t nowtime; 00349 time(&nowtime); 00350 fSec = nowtime; 00351 fNanoSec = 0; 00352 } 00353 #endif 00354 static Int_t sec = 0, nsec = 0, fake_ns = 0; 00355 00356 if (fSec == sec && fNanoSec == nsec) 00357 fNanoSec += ++fake_ns; 00358 else { 00359 fake_ns = 0; 00360 sec = fSec; 00361 nsec = fNanoSec; 00362 } 00363 00364 }
Friends And Related Function Documentation
| Bool_t operator!= | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| TVldTimeStamp operator- | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| Bool_t operator< | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| Bool_t operator<= | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| Bool_t operator== | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| Bool_t operator> | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
| Bool_t operator>= | ( | const TVldTimeStamp & | lhs, | |
| const TVldTimeStamp & | rhs | |||
| ) | [friend] |
Member Data Documentation
Int_t TVldTimeStamp::fNanoSec [private] |
Definition at line 258 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
Referenced by Add(), AsString(), Copy(), GetNanoSec(), GetSeconds(), GetTimeSpec(), NormalizeNanoSec(), operator double(), operator!=(), operator<(), operator<=(), operator=(), operator==(), operator>(), operator>=(), and Set().
Int_t TVldTimeStamp::fSec [private] |
Definition at line 257 of file TVldTimeStamp.hxx.
Referenced by Add(), AsString(), Copy(), GetDate(), GetSec(), GetSeconds(), GetTime(), GetTimeSpec(), NormalizeNanoSec(), operator double(), operator!=(), operator<(), operator<=(), operator=(), operator==(), operator>(), operator>=(), and Set().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- src/TVldTimeStamp.hxx
- src/TVldTimeStamp.cxx

 1.6.1
1.6.1