| ID |
Date |
Author |
Topic |
Subject |
|
3073
|
17 Sep 2025 |
Mark Grimes | Bug Report | Midas no longer compiles on macOS |
Hi,
The current develop branch no longer compiles on macOS. I get lots of errors of the form
/Users/me/midas/src/history_schema.cxx:740:4: error: unknown type name 'off64_t'; did you mean 'off_t'?
740 | off64_t fDataOffset = 0;
| ^~~~~~~
| off_t
/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX15.5.sd
k/usr/include/sys/_types/_off_t.h:31:33: note: 'off_t' declared here
31 | typedef __darwin_off_t off_t;
| ^
There are also similar errors about lseek64. This appears to have come in with commit 9a6ad2e dated
23rd July, but I think it was merged into develop with commit 2beeca0 on 3rd of September.
Googling around it seems that off64_t is a GNU extension. I don't know of a cross platform solution but I'm
happy to test if someone has a suggestion.
Thanks,
Mark. |
|
3076
|
17 Sep 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Midas no longer compiles on macOS |
> The current develop branch no longer compiles on macOS. I get lots of errors of the form
> /Users/me/midas/src/history_schema.cxx:740:4: error: unknown type name 'off64_t' ...
Confirmed. No idea why off64_t is missing on MacOS. I will try to fix it next week.
K.O. |
|
3107
|
06 Nov 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | broken scroll on midas web pages |
midas web pages that use overlays (dlgPanel, etc) are currently broken - if
overlay does not fit in the visible window, it's bottom is truncated and control
buttons like "create" and "cancel" are not visible, not clickable, page does not
work.
when these pages were originally written, I am pretty sure these overlays were
scrollable and this problem did not exist. I think that was broken recently,
maybe withint the last year or so.
specific examples:
a) odb editor:
- open odb editor,
- click on "create odb link"
- click on "link target ...", a dialog overlay opens with a list of odb keys in
the current directory
- select a directory with a large number of entries (i.e. "/Programs")
- alternatively, make browser window smaller
- observe the "ok" and "cancel" buttons are not visible, cannot be clicked
- definitely, there used be a scroll bar and one could scroll down to see these
buttons.
b) history planel editor:
- open history plot,
- click on "configure this plot" icon,
- history editor opens,
- click "add active variables"
- select active event that has many variables
- observe that the list is cut off at the bottom, the very last variables are
not visible
- alternatively, make the browser window smaller
I wrote this page and at the time this problem did not exist, there was a scroll
bar and one could scroll up and down the list even if there were really many
variables there.
Maybe this breakage is not from us, I see similar problems on other sites, so
maybe browser behaviour changed recentlyshly.
I think Stefan write the dlgPanel code originally? I am not very familiar with
it and I do not know if anybody changed it recently?
K.O. |
|
3113
|
13 Nov 2025 |
Stefan Ritt | Bug Report | broken scroll on midas web pages |
I confirm the problem is there (at least under MacOSX Safari) and I will take care of it.
Stefan |
|
3116
|
14 Nov 2025 |
Stefan Ritt | Bug Report | broken scroll on midas web pages |
This problem was introduced by ZS in March 2023 with these commits:
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/25b13f875ff1f7e2f4e987273c81d6356dd2ff53
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/2a9e902e07156e12edecb5c2257e4dbd944f8377
by setting
d.style.position = "fixed";
which prevents the scrolling. I have no idea why this change was made, so it should be fixed by the original
author.
Stefan |
|
3117
|
16 Nov 2025 |
Zaher Salman | Bug Report | broken scroll on midas web pages |
Sorry about that. I could not figure out what was the reason for doing this. This was during the time I was working on the file_picker. I removed these lines and see no effect on the file_picker. I'll continue checking it affect anything else.
Zaher
> This problem was introduced by ZS in March 2023 with these commits:
>
> https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/25b13f875ff1f7e2f4e987273c81d6356dd2ff53
> https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/2a9e902e07156e12edecb5c2257e4dbd944f8377
>
> by setting
>
> d.style.position = "fixed";
>
> which prevents the scrolling. I have no idea why this change was made, so it should be fixed by the original
> author.
>
> Stefan |
|
3118
|
17 Nov 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | broken scroll on midas web pages |
> Sorry about that. I could not figure out what was the reason for doing this. This was during the time I was working on the file_picker. I removed these lines and see no effect on the file_picker. I'll continue checking it affect anything else.
I confirm reported problem seems to be fixed in commit:
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/7f2690b478d6dfb16b48fc98955093e6369b04c1
Big thanks to Stefan and Zaher for figuring it out quickly.
K.O. |
|
3119
|
18 Nov 2025 |
Lars Martin | Bug Report | TMFeEquipment fEqConfReadOn not written to ODB |
I'm constructing a TMFeEquipment with this constructor:
MagnetFe(const char *eqname, const char *eqfilename) // ctor
: TMFeEquipment(eqname, eqfilename)
{
fEqConfEventID = 3;
fEqConfBuffer = "SYSTEM";
fEqConfPeriodMilliSec = 1000; // in milliseconds
fEqConfLogHistory = 1;
fEqConfReadOn = RO_ALWAYS;
}
When I start with a fresh ODB, the directories are created correctly, and e.g. the
event ID is set correctly, but "Read on" is set to 1 (i.e. RO_RUNNING) instead of
0xFF.
Now when I set it to 0xFF manually and restart, it gets overwritten to 7
(RO_NONTRANS), which I guess is a relatively recent change and doesn't affect me
negatively. |
|
3130
|
21 Nov 2025 |
Scott Oser | Bug Report | Cannot edit values in a subtree containing only a single array of BOOLs using the ODB web interface |
I think I've found a bug in MIDAS ...
Description: If you have an ODB subtree that contains only an array of BOOLs, you cannot edit them from the ODB webpage, although you can change them using odbedit (and probably from code as well).
(If you use the dropdown menu to change any value from No to Yes, it just flips back to No immediately.)
But if you create a new key in that directory (doesn't seem to matter what), then you can edit the BOOLs from webpage. Delete that key, and once again you can't edit the BOOLs. |
|
3134
|
24 Nov 2025 |
Stefan Ritt | Bug Report | Cannot edit values in a subtree containing only a single array of BOOLs using the ODB web interface |
Can you please update to the latest develop versiokn of midas, and clear your browser cache so that the updated JavaScript midas library is loaded. Should be fixed by now. See attached screen shot where I changed every second value via the ODB editor.
Stefan
|
| Attachment 1: Screenshot_2025-11-24_at_15.32.12.png
|
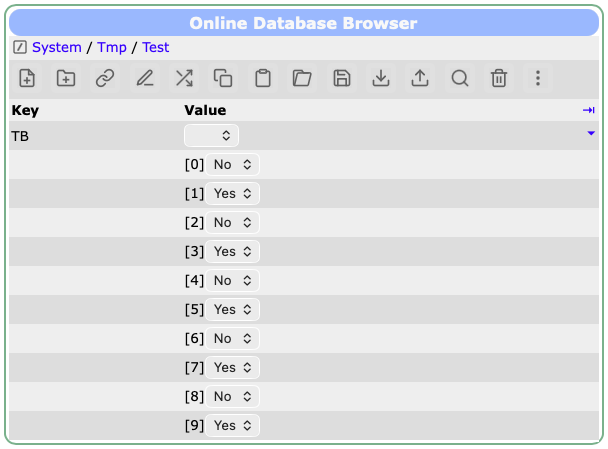
|
|
3135
|
24 Nov 2025 |
Scott Oser | Bug Report | Cannot edit values in a subtree containing only a single array of BOOLs using the ODB web interface |
| Stefan Ritt wrote: |
|
Can you please update to the latest develop versiokn of midas, and clear your browser cache so that the updated JavaScript midas library is loaded. Should be fixed by now. See attached screen shot where I changed every second value via the ODB editor.
Stefan
|
Thanks --- it looks like this commit (which we just missed by four days when we last updated MIDAS) resolves the issue for us:
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/6af72c1d218798064a7762bae6e65ad3407de9d1
Thanks to Ben Smith for pointing us at exactly the right commit. |
|
3139
|
25 Nov 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Cannot edit values in a subtree containing only a single array of BOOLs using the ODB web interface |
> Thanks --- it looks like this commit resolves the issue for us ...
> Thanks to Ben Smith for pointing us at exactly the right commit
I would like to take the opportunity to encourage all to report bug fixes like this one to this mailing list.
This looks like a serious bug, many midas users would like to know when it was introduced, when found, when fixed
and who takes the credit.
K.O. |
|
3147
|
26 Nov 2025 |
Lars Martin | Bug Report | Error(?) in custom page documentation |
https://daq00.triumf.ca/MidasWiki/index.php/Custom_Page#modb
says that
If the ODB path does not point to an individual value but to a subdirectory, the
whole subdirectory is mapped to this.value as a JavaSctipt object such as
<div class="modb" data-odb-path="/Runinfo" onchange="func(this.value)">
<script>function func(value) { console.log(value["run number"]); }</script>
In fact, it seems to return the JSON string of said object, so you'd have to write
console.log(JSON.parse(value)["run number"]) |
|
3148
|
27 Nov 2025 |
Stefan Ritt | Bug Report | Error(?) in custom page documentation |
Indeed a bug. Fixed in commit
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/5c1133df073f493d74d1fc4c03fbcfe80a3edae4
Stefan |
|
3150
|
27 Nov 2025 |
Zaher Salman | Bug Report | Error(?) in custom page documentation |
This commit breaks the sequencer pages...
> Indeed a bug. Fixed in commit
>
> https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/5c1133df073f493d74d1fc4c03fbcfe80a3edae4
>
> Stefan |
|
3152
|
27 Nov 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Error(?) in custom page documentation |
the double-decode bug strikes again!
> This commit breaks the sequencer pages...
>
> > Indeed a bug. Fixed in commit
> >
> > https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/5c1133df073f493d74d1fc4c03fbcfe80a3edae4
> >
> > Stefan |
|
3172
|
08 Dec 2025 |
Zaher Salman | Bug Report | Error(?) in custom page documentation |
The sequencer pages were adjusted to the work with this bug fix.
> This commit breaks the sequencer pages...
>
> > Indeed a bug. Fixed in commit
> >
> > https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/commits/5c1133df073f493d74d1fc4c03fbcfe80a3edae4
> >
> > Stefan |
|
3173
|
08 Dec 2025 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | odbxx memory leak with JSON ODB dump |
I was testing odbxx with manalyzer, decided to print an odb value in every event,
and it worked fine in online mode, but bombed out when running from a data file
(JSON ODB dump). The following code has a memory leak. No idea if XML ODB dump
has the same problem.
int memory_leak()
{
midas::odb::set_odb_source(midas::odb::STRING, std::string(run.fRunInfo-
>fBorOdbDump.data(), run.fRunInfo->fBorOdbDump.size()));
while (1) {
int time = midas::odb("/Runinfo/Start time binary");
printf("time %d\n", time);
}
}
K.O. |
|
3176
|
09 Dec 2025 |
Stefan Ritt | Bug Report | odbxx memory leak with JSON ODB dump |
Thanks for reporting this. It was caused by a
MJsonNode* node = MJsonNode::Parse(str.c_str());
not followed by a
delete node;
I added that now in odb::odb_from_json_string(). Can you try again?
Stefan |
|
3177
|
09 Dec 2025 |
Mark Grimes | Bug Report | manalyzer fails to compile on some systems because of missing #include <cmath> |
Hi,
We're getting errors in our build system like:
/code/midas/manalyzer/manalyzer.cxx: In member function ‘void Profiler::Begin(TARunInfo*,
std::vector<TARunObject*>)’:
/code/midas/manalyzer/manalyzer.cxx:799:27: error: ‘pow’ was not declared in this scope
799 | bins[i] = TimeRange*pow(1.1,i)/pow(1.1,Nbins);
The solution is to add "#include <cmath>" at the top of manalyzer.cxx; I guess on a lot of systems the
include is implicit from some other include so doesn't cause errors. I don't have the permissions to push
branches, could this be added please?
Thanks,
Mark. |