| ID |
Date |
Author |
Topic |
Subject |
|
652
|
01 Oct 2009 |
Pierre-Andre Amaudruz | Bug Report | mfe.c: poll_event() before frontend_init() |
The latest version of mfe.c has a problem where poll_event() is called before
frontend_init() and this causes a crash because in poll_event() we try to access
VME before it is initialized in frontend_init(). K.O. |
|
651
|
30 Sep 2009 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | mh2sql does not build, Error invoking 'odbedit': db_validate_size |
> Linking CXX executable bin/mh2sql
> CMakeFiles/mh2sql.dir/utils/mh2sql.cxx.o: In function `main':
> /opt/DAQ/repos/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx:150: undefined reference to `MakeMidasHistoryODBC()'
Yes, I am in the process of changing the midas history interface and accidentally committed a version of
mh2sql (utility for converting MIDAS history .hst files to SQL database) that uses the new interface.
This is now fixed in svn rev 4571.
The new C++ interface to the MIDAS history is in include/history.h and implementations for data storage
using both midas .hst files and SQL (ODBC/MySQL) database are also committed (history_midas.cxx
and history_sql.cxx). The file history_odbc.cxx will be removed after some more testing of the new
interface.
(All the new code is not activated yet, pending more testing).
K.O. |
|
650
|
30 Sep 2009 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Error invoking 'odbedit': db_validate_size |
> $ odbedit -e expcvadc
> odbedit: /opt/DAQ/repos/bot/midas/src/odb.c:651: db_validate_sizes: Assertion
`sizeof(EQUIPMENT_INFO) == 400' failed.
Yes, this is now fixed, svn rev 4571 should be okey. Sorry about causing this problem - Stefan added
some useful additional data to EQUIPMENT_INFO and my check for binary compatibility caught it and
complained. Unfortunately on Saturday Stefan had to abruptly go back to PSI and things have been a little
bit chaotic because we did not complete the testing of all the new changes and additions.
K.O. |
|
649
|
29 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Error invoking 'odbedit': db_validate_size |
It seems to be fixed in svn-r4568:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
r4568 | olchanski | 2009-09-27 23:56:39 +0800 (日, 27 9月 2009) | 5 lines
mhttpd: compile using the C++ compiler.
mhttpd: fix wrong initialization of /History/ODBC_DSN
odb.c: size of EQUIPMENT_INFO has changed.
Makefile: use "-O2" compiler flag instead of "-O3" - to fix SL5 gcc crash (ICE)
But another compiling error:
Linking CXX executable bin/mh2sql
CMakeFiles/mh2sql.dir/utils/mh2sql.cxx.o: In function `main':
/opt/DAQ/repos/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx:150: undefined reference to `MakeMidasHistoryODBC()'
|
|
648
|
29 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Error invoking 'odbedit': db_validate_size |
Revision: r4567
Error output:
$ odbedit -e expcvadc
odbedit: /opt/DAQ/repos/bot/midas/src/odb.c:651: db_validate_sizes: Assertion `sizeof(EQUIPMENT_INFO) == 400' failed.
zsh: abort odbedit -e expcvadc
|
|
647
|
27 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Forum | deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’ |
> There is no "type conversions". The compiler is whining about code like this:
>
> /* data type names */
> static char *tid_name[] = {
> "NULL",
> "BYTE",
> ...
>
> I guess we should keep the compiler happy and make them "static const char*".
>
> BTW, my compiler is SL5.2 gcc-4.1.2 and it does not complain. What's your compiler?
>
> K.O.
Using built-in specs.
Target: x86_64-linux-gnu
Configured with: ../src/configure -v --with-pkgversion='Debian 4.3.4-2' --with-
bugurl=file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-4.3/README.Bugs --enable-
languages=c,c++,fortran,objc,obj-c++ --prefix=/usr --enable-shared --enable-multiarch -
-enable-linker-build-id --with-system-zlib --libexecdir=/usr/lib --without-included-
gettext --enable-threads=posix --enable-nls --with-gxx-include-dir=/usr/include/c++/4.3
--program-suffix=-4.3 --enable-clocale=gnu --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-objc-gc --
enable-mpfr --with-tune=generic --enable-checking=release --build=x86_64-linux-gnu --
host=x86_64-linux-gnu --target=x86_64-linux-gnu
Thread model: posix
gcc version 4.3.4 (Debian 4.3.4-2) |
|
646
|
27 Sep 2009 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Forum | deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’ |
> I encountered many warning while building MIDAS (svn r4556). Please see the
> attached log file. Most of them are caused by type conversion from string to
> "char*".
> Though I can ignore all the warning without any problem, I still hate to see
> them. :-)
There is no "type conversions". The compiler is whining about code like this:
/* data type names */
static char *tid_name[] = {
"NULL",
"BYTE",
...
I guess we should keep the compiler happy and make them "static const char*".
BTW, my compiler is SL5.2 gcc-4.1.2 and it does not complain. What's your compiler?
K.O. |
|
645
|
22 Sep 2009 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | New feature: Stop run after a certain time |
> A new feature has been implemented in revision 4561 which allows runs with a
> certain duration. To use this, one has to set the variaable
>
> /Logger/Run Duration
>
> to a non-zero value in seconds. After a run lasted for this duration, it gets
> stopped automatically by the logger. If the auto-restart flag is on, this allows
> sequences of automatically started and stopped runs with all then have the same
> duration.
A similar scheme has been implemented to pose a certain duration on subruns. This can
be controlled by the variable
/Logger/Subrun duration
when set to a non-zero value in seconds. |
|
644
|
21 Sep 2009 |
Stefan Ritt | Info | New feature: Stop run after a certain time |
A new feature has been implemented in revision 4561 which allows runs with a
certain duration. To use this, one has to set the variaable
/Logger/Run Duration
to a non-zero value in seconds. After a run lasted for this duration, it gets
stopped automatically by the logger. If the auto-restart flag is on, this allows
sequences of automatically started and stopped runs with all then have the same
duration. |
|
643
|
10 Sep 2009 |
Stefan Ritt | Forum | Retrieve start/stop time in offline |
> I set "/Analyzer/ODB Load" to true and analyzed a run in offline mode. After
> that, I found the start time and stop time in /RunInfo did not reflect the
> correct time as in online. How do I retrieve the correct start/stop time from
> the ODB in offline mode?
Most trees in the ODB are not loaded with "/Analyzer/ODB Load", since you might
want to have the start/stop time of the offline analysis there for example
(although I agree that the online start/stop time is more interesting). So you
have several options:
- modify mana.c. There is a function odb_load(), which first locks the whole ODB
and then unprotects "/Experiment/Run Parameters" for example. Just add three more
lines for "/Runinfo".
- write a run summary when running online. After each run, write a summary with
start/stop time, number of events, settings etc. into some file. I usually do this
in the EOR routine of the online analyzer and write directly into a CSV file which
I can import directly into Excel. There I can make filtering depending on certain
parameters, like show me all runs with more than x events where setting y was 10.
- extract the ODB from the .mid file with "odbhist -e filename.mid" and look into
that.
- The time stamp of each event is in UNIX time form (seconds since 1.1.1970), so
you now exactly when each event was recorded.
Hope one of this helps...
- Stefan |
|
642
|
09 Sep 2009 |
Jimmy Ngai | Forum | Retrieve start/stop time in offline |
Hi All,
I set "/Analyzer/ODB Load" to true and analyzed a run in offline mode. After
that, I found the start time and stop time in /RunInfo did not reflect the
correct time as in online. How do I retrieve the correct start/stop time from
the ODB in offline mode?
Thanks!
Jimmy |
|
641
|
07 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Forum | deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’ |
I encountered many warning while building MIDAS (svn r4556). Please see the
attached log file. Most of them are caused by type conversion from string to
"char*".
Though I can ignore all the warning without any problem, I still hate to see
them. :-) |
| Attachment 1: make-warnings.log
|
Scanning dependencies of target midas-static
[ 1%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/ftplib.c.o
[ 3%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/midas.c.o
[ 5%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/system.c.o
[ 7%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/mrpc.c.o
[ 9%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/odb.c.o
[ 11%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/ybos.c.o
[ 13%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history.c.o
[ 15%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/alarm.c.o
[ 17%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/elog.c.o
[ 19%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/opt/DAQ/bot/mxml/mxml.c.o
[ 21%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/opt/DAQ/bot/mxml/strlcpy.c.o
[ 23%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
Linking CXX static library lib/libmidas.a
[ 23%] Built target midas-static
Scanning dependencies of target dio
[ 25%] Building C object CMakeFiles/dio.dir/utils/dio.c.o
Linking C executable bin/dio
[ 25%] Built target dio
Scanning dependencies of target fal
[ 25%] Generating fal.o
[ 26%] Built target fal
Scanning dependencies of target hmana
[ 26%] Generating hmana.o
[ 28%] Built target hmana
Scanning dependencies of target lazylogger
[ 30%] Building C object CMakeFiles/lazylogger.dir/src/lazylogger.c.o
Linking C executable bin/lazylogger
[ 30%] Built target lazylogger
Scanning dependencies of target mana
[ 30%] Generating mana.o
[ 32%] Built target mana
Scanning dependencies of target mchart
[ 34%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mchart.dir/utils/mchart.c.o
Linking C executable bin/mchart
[ 34%] Built target mchart
Scanning dependencies of target mcnaf
[ 36%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mcnaf.dir/utils/mcnaf.c.o
[ 38%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mcnaf.dir/drivers/camac/camacrpc.c.o
Linking C executable bin/mcnaf
[ 38%] Built target mcnaf
Scanning dependencies of target mdump
[ 40%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mdump.dir/utils/mdump.c.o
Linking C executable bin/mdump
[ 40%] Built target mdump
Scanning dependencies of target melog
[ 42%] Building C object CMakeFiles/melog.dir/utils/melog.c.o
Linking C executable bin/melog
[ 42%] Built target melog
Scanning dependencies of target mfe
[ 42%] Generating mfe.o
[ 44%] Built target mfe
Scanning dependencies of target mh2sql
[ 46%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/mh2sql.dir/utils/mh2sql.cxx.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx: In function ‘int main(int, char**)’:
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx:144: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx:144: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mh2sql.cxx:144: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
[ 48%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/mh2sql.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
Linking CXX executable bin/mh2sql
[ 48%] Built target mh2sql
Scanning dependencies of target mhdump
[ 50%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/mhdump.dir/utils/mhdump.cxx.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/utils/mhdump.cxx:91: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
Linking CXX executable bin/mhdump
[ 50%] Built target mhdump
Scanning dependencies of target mhist
[ 51%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mhist.dir/utils/mhist.c.o
Linking C executable bin/mhist
[ 51%] Built target mhist
Scanning dependencies of target mhttpd
[ 53%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mhttpd.dir/src/mhttpd.c.o
[ 55%] Building C object CMakeFiles/mhttpd.dir/src/mgd.c.o
Linking CXX executable bin/mhttpd
[ 55%] Built target mhttpd
Scanning dependencies of target midas-shared
[ 57%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/ftplib.c.o
[ 59%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/midas.c.o
[ 61%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/system.c.o
[ 63%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/mrpc.c.o
[ 65%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/odb.c.o
[ 67%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/ybos.c.o
[ 69%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/history.c.o
[ 71%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/alarm.c.o
[ 73%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/elog.c.o
[ 75%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/opt/DAQ/bot/mxml/mxml.c.o
[ 76%] Building C object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/opt/DAQ/bot/mxml/strlcpy.c.o
[ 78%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/midas-shared.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
Linking CXX shared library lib/libmidas.so
[ 78%] Built target midas-shared
Scanning dependencies of target mlogger
[ 80%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/mlogger.dir/src/mlogger.c.o
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:81: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c: In function ‘INT ftp_open(char*, FTP_CON**)’:
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:952: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:956: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:960: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:960: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:965: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:970: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c: In function ‘EVENT_DEF* db_get_event_definition(short int)’:
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:1339: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:1341: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:1343: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:1345: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/mlogger.c:1347: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’
... 75 more lines ...
|
|
640
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Suggestion | Could not create strings other than 32 characters with odbedit -c "..." command |
> > Ok, I added a command
> >
> > odbedit -c "create STRING Test[8][40]"
> >
> > which works now. Please update to SVN revision 4555 of odbedit.c
> >
> > - Stefan
>
> If I want to create only one string, should I write like this:
>
> odbedit -c "create STRING Test[] [256]"
>
> OK. I need it. I will try the new odbedit.
"create STRING test[1][256]" works. |
|
639
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Delete key "/A_Str" problem |
> Another problem while using odbedit.
> I tried the batch mode of "odbedit". I created a key as "/A_Str" by mistake and
> wanted to delete it. Then "odbedit" failed to accept the "Return" key. Please see
> the screen-shot attached. :-(
This bug has been fixed in the latest repository.
I encountered it in svn-r4488. |
|
638
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Suggestion | Updated "CMakeLists.txt" |
Add installation commands. Please see the attachment. |
| Attachment 1: CMakeLists.txt
|
#-*- mode: cmake -*-
## CMake pre-settings
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)
cmake_policy(VERSION 2.6)
cmake_policy(SET CMP0011 NEW)
set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${CMAKE_MODULE_PATH} "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake/")
## Project setup
project(MIDAS)
set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/bin)
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
enable_language(C)
enable_language(CXX)
## Include utilities and options
# Find mxml
include(FindMXML)
include_directories(include ${MXML_PATH})
# OS specific flags
# OS-related CMake variables:
# 1. OS_EXTRA_UTILS --- Extra utilities for specific OS
# 2. OS_EXTRA_LDFLAGS --- Extra link flags for specific OS
# 3. OS_EXTRA_DEFS --- Extra definitions for specific OS
# 4. Other flags switched on for specific OS
include(OSflags)
include(FindROOT) # Find ROOT environment
include(FindMySQL) # Find MySQL
include(FindODBC) # Find ODBC
include(FindZLIB) # Find zlib
## Options for MIDAS
set(NEED_CERNLIB TRUE) # Need CERNLIB or not?
set(NEED_SHLIB TRUE) # Need shared library?
set(NEED_ROOT TRUE) # Need root?
set(NEED_FTPLIB TRUE) # Need ftp protocol?
#set(NEED_STRLCPY TRUE) # Need strlcpy.h? -- maybe opened in OSflags.cmake
#set(MIDAS_MAX_EVENT_SIZE 1000000) # maxmimum event size = ?
##############################################################################
## Setup options
## OS-specific
add_definitions(${OS_EXTRA_DEFS})
set(LDFLAGS "${LDFLAGS} ${OS_EXTRA_LDFLAGS}")
set(EXTRA_UTILS ${EXTRA_UTILS} ${OS_EXTRA_UTILS})
## Midas max event size
if(MIDAS_MAX_EVENT_SIZE)
add_definitions(-DMAX_EVENT_SIZE=${MIDAS_MAX_EVENT_SIZE})
endif(MIDAS_MAX_EVENT_SIZE)
## strlcpy in "MXML"?
if(NEED_STRLCPY)
set(EXTRA_OBJS ${EXTRA_OBJS} strlcpy)
add_definitions( -DHAVE_STRLCPY )
message(STATUS "Using Stephen's own strlcpy()")
endif(NEED_STRLCPY)
## FTPLIB needed?
if(NEED_FTPLIB)
set(FTPLIB ftplib)
add_definitions(-DINCLUDE_FTPLIB)
message(STATUS "Using ftplib (FTP library)")
endif(NEED_FTPLIB)
## ODBC: -lodbc or -liodbc
if(ODBC_FOUND)
message(STATUS "Add ODBC-specified targets using ${ODBC_LIBRARY}")
set(EXTRA_UTILS ${EXTRA_UTILS} mh2sql)
add_definitions(-DHAVE_ODBC)
set(LDFLAGS "${LDFLAGS} -l${ODBC_NAME}")
else(ODBC_FOUND)
message(STATUS "ODBC not found!")
endif(ODBC_FOUND)
## ZLIB
if(ZLIB_FOUND)
add_definitions(-DHAVE_ZLIB)
set(LDFLAGS "${LDFLAGS} -lz")
endif(ZLIB_FOUND)
## ROOT
if(NEED_ROOT AND ROOT_FOUND)
message(STATUS "Using ROOT at ${ROOTSYS}")
if(NEED_RPATH) # Add rpath ..
set(ROOT_LIBS "${ROOT_LIBS} -Wl,-rpath,${ROOTSYS}/lib")
endif(NEED_RPATH)
## libRoot.a: Static ROOT library
if(NEED_LIBROOTA AND ROOT_LIBA)
set(LDFLAGS "${LDFLAGS} ${ROOTSYS}/lib/libRoot.a -lssl -ldl -lcrypt")
message(STATUS "Using statlic ROOT library: ${ROOT_LIBA}")
endif(NEED_LIBROOTA AND ROOT_LIBA)
endif(NEED_ROOT AND ROOT_FOUND)
####### MIDAS library and objects #########################
## Objects needed to build the libmidas(.a,.so,..)
foreach(obj ${FTPLIB} midas system mrpc odb ybos history alarm elog)
set(LIB_OBJS ${LIB_OBJS} src/${obj}.c)
endforeach(obj)
foreach(obj mxml ${EXTRA_OBJS})
set(LIB_OBJS ${LIB_OBJS} ${MXML_PATH}/${obj}.c)
endforeach(obj)
if(ODBC_FOUND)
set(LIB_OBJS ${LIB_OBJS} src/history_odbc.cxx)
endif(ODBC_FOUND)
## Library definition
## Add static lib
add_library(midas-static STATIC ${LIB_OBJS})
set_target_properties(midas-static PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME "midas")
if(NEED_SHLIB) # Add shared lib
add_library(midas-shared SHARED ${LIB_OBJS})
set_target_properties(midas-shared PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME "midas")
endif(NEED_SHLIB)
########## Utilities ######################################
## Core Utilties
set(CORE_UTILS mserver mhttpd mlogger odbedit lazylogger)
add_executable(mserver src/mserver.c)
add_executable(mlogger src/mlogger.c)
add_executable(mhttpd src/mhttpd.c src/mgd.c )
add_executable(odbedit src/odbedit.c src/cmdedit.c )
add_executable(lazylogger src/lazylogger.c)
foreach(exe ${CORE_UTILS})
target_link_libraries(${exe} midas-static)
set_target_properties(${exe} PROPERTIES LINK_FLAGS "${LDFLAGS}")
endforeach(exe)
set_target_properties( mhttpd PROPERTIES
LINK_FLAGS "-lm ${LDFLAGS}" LINKER_LANGUAGE CXX )
## for mlogger --- It's BAD to name a CXX source using ".c" file extension !!!
set_target_properties( mlogger
PROPERTIES
LINK_FLAGS "${MYSQL_LIBS} ${ROOT_LIBS} ${LDFLAGS}"
LINKER_LANGUAGE CXX
COMPILE_FLAGS "${ROOT_CFLAGS}" )
set_source_files_properties( src/mlogger.c PROPERTIES LANGUAGE CXX )
## Utilities
set(UTILS mtape mhist mstat mdump mchart
webpaw odbhist melog mcnaf
mhdump mtransition # C++ codes
${EXTRA_UTILS} )
foreach(exe mtape mhist mstat mdump melog mchart odbhist webpaw)
add_executable(${exe} utils/${exe}.c)
endforeach(exe)
add_executable(mhdump utils/mhdump.cxx)
add_executable(mcnaf utils/mcnaf.c drivers/camac/camacrpc.c)
add_executable(mtransition src/mtransition.cxx)
# optional utilities
if("${UTILS}" MATCHES "mh2sql")
add_executable(mh2sql utils/mh2sql.cxx src/history_odbc.cxx )
endif("${UTILS}" MATCHES "mh2sql")
if("${UTILS}" MATCHES "mlxspeaker")
add_executable(mlxspeaker utils/mlxspeaker.c)
endif("${UTILS}" MATCHES "mlxspeaker")
if("${UTILS}" MATCHES "dio")
add_executable(dio utils/dio.c)
endif("${UTILS}" MATCHES "dio")
foreach(exe ${UTILS})
add_dependencies(${exe} midas-static)
target_link_libraries(${exe} midas-static)
set_target_properties(${exe} PROPERTIES LINK_FLAGS "${LDFLAGS}")
endforeach(exe)
## Scripts
set(SCRIPTS stripchart.tcl ) # TCL script
## Special targets
## for generating mfe.o
add_custom_command( OUTPUT mfe.o DEPENDS src/mfe.c
COMMAND ${CMAKE_C_COMPILER}
ARGS -I${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include -c ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mfe.c
WORKING_DIRECTORY lib )
add_custom_target(mfe ALL DEPENDS mfe.o)
## for generating mfe.o
add_custom_command( OUTPUT fal.o DEPENDS src/fal.c
COMMAND ${CMAKE_C_COMPILER}
ARGS -I${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include -Dextname -DMANA_LITE
-c ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/fal.c
WORKING_DIRECTORY lib )
add_custom_target(fal ALL DEPENDS fal.o)
## analyzer objects: mana.o
add_custom_command( OUTPUT mana.o DEPENDS src/mana.c
COMMAND ${CMAKE_C_COMPILER}
ARGS -I${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include -c ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mana.c
WORKING_DIRECTORY lib )
add_custom_target(mana ALL DEPENDS mana.o)
set(EXTRA_MOBJS mfe.o fal.o mana.o)
# rmana.o
if(NEED_ROOT)
set(ARG_LIST "-DUSE_ROOT ${ROOT_CFLAGS} -I${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include -o rmana.o -c ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mana.c")
separate_arguments(ARG_LIST)
add_custom_command( OUTPUT rmana.o DEPENDS src/mana.c
COMMAND ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}
ARGS ${ARG_LIST} WORKING_DIRECTORY lib )
add_custom_target(rmana ALL DEPENDS rmana.o )
set(EXTRA_MOBJS ${EXTRA_MOBJS} rmana.o )
endif(NEED_ROOT)
## hmana.o
if(NEED_CERNLIB)
add_custom_command( OUTPUT hmana.o DEPENDS src/mana.c
COMMAND ${CMAKE_C_COMPILER}
ARGS -I${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include -Dextname -DHAVE_HBOOK -o hmana.o
-c ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mana.c
WORKING_DIRECTORY lib )
add_custom_target(hmana ALL DEPENDS hmana.o)
set(EXTRA_MOBJS ${EXTRA_MOBJS} hmana.o )
endif(NEED_CERNLIB)
########## Drivers and modules ################################
#
########## Examples ###########################################
#
########## Installation########################################
#
## Library and objects (custom targets)
install(TARGETS midas-static ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib)
if(NEED_SHLIB)
install(TARGETS midas-shared LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
PERMISSIONS OWNER_READ OWNER_WRITE OWNER_EXECUTE
GROUP_READ GROUP_EXECUTE WORLD_EXECUTE WORLD_READ)
endif(NEED_SHLIB)
foreach(obj ${EXTRA_MOBJS})
install(FILES ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib/${obj} DESTINATION lib)
endforeach(obj)
## Core and extra utilities, scripts
install(TARGETS ${CORE_UTILS} ${UTILS}
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin
PERMISSIONS OWNER_READ OWNER_WRITE OWNER_EXECUTE
GROUP_READ GROUP_EXECUTE WORLD_EXECUTE WORLD_READ)
#install ${SCRIPTS}
foreach(script ${SCRIPTS})
install(FILES utils/${script} DESTINATION bin
PERMISSIONS OWNER_READ OWNER_WRITE OWNER_EXECUTE
GROUP_READ GROUP_EXECUTE WORLD_EXECUTE WORLD_READ)
endforeach(script)
## include, src, examples, drivers
# install(DIRECTORY include/ DESTINATION include/midas
# FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h")
# install(DIRECTORY src DESTINATION share/midas)
# install(DIRECTORY examples DESTINATION share/midas)
# install(DIRECTORY drivers DESTINATION share/midas)
install(DIRECTORY include/ DESTINATION include
FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h")
install(DIRECTORY src/ DESTINATION src)
install(DIRECTORY examples/ DESTINATION examples)
install(DIRECTORY drivers/ DESTINATION drivers)
|
|
637
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Fix | Maybe a fix |
Changing "SQLINTEGER" to "SQLLEN" maybe let the compiling pass. See the attached diff.
But I failed in another error. It was the problem in CMakeLists.txt. (FIXED) |
| Attachment 1: history_odbc.cxx.diff
|
diff --git a/src/history_odbc.cxx b/src/history_odbc.cxx
index 5f00016..392062f 100644
--- a/src/history_odbc.cxx
+++ b/src/history_odbc.cxx
@@ -584,7 +584,7 @@ int SqlODBC::Exec(const char* sql)
int SqlODBC::GetNumRows()
{
- SQLINTEGER nrows = 0;
+ SQLLEN nrows = 0;
/* How many rows are there */
int status = SQLRowCount(fStmt, &nrows);
if (!SQL_SUCCEEDED(status)) {
@@ -634,7 +634,7 @@ int SqlODBC::Done()
const char* SqlODBC::GetColumn(int icol)
{
static char buf[1024];
- SQLINTEGER indicator;
+ SQLLEN indicator;
int status = SQLGetData(fStmt, icol, SQL_C_CHAR, buf, sizeof(buf), &indicator);
if (!SQL_SUCCEEDED(status)) {
|
|
636
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Compiling error of "src/history_odbc.cxx" |
| Exaos Lee wrote: | Version svn-r4556, I got a compiling error as below:
The detail error log is attached. I used my CMake script without any optimization flags. I will try the default Makefile again. |
BUG is confirmed using the default "Makefile". |
|
635
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Compiling error of "src/history_odbc.cxx" |
Version svn-r4556, I got a compiling error as below:
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx: In member function 'virtual int
SqlODBC::GetNumRows()':
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:589: error: cannot convert 'SQLINTEGER*'
to 'long int*' for argument '2' to 'SQLRETURN SQLRowCount(void*, long int*)'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx: In member function 'virtual const char*
SqlODBC::GetColumn(int)':
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:638: error: cannot convert 'SQLINTEGER*'
to 'long int*' for argument '6' to 'SQLRETURN SQLGetData(void*, SQLUSMALLINT,
SQLSMALLINT, void*, long int, long int*)'
make[2]: *** [CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o] Error 1
make[2]: Leaving directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
make[1]: *** [CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/all] Error 2
make[1]: Leaving directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
The detail error log is attached. I used my CMake script without any optimization flags. I will try the default Makefile again. |
| Attachment 1: build-err.log
|
/usr/bin/cmake -H/opt/DAQ/bot/midas -B/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build --check-build-system CMakeFiles/Makefile.cmake 0
/usr/bin/cmake -E cmake_progress_start /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build/CMakeFiles /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build/CMakeFiles/progress.make
make -f CMakeFiles/Makefile2 all
make[1]: Entering directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
make -f CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/build.make CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/depend
make[2]: Entering directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
cd /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build && /usr/bin/cmake -E cmake_depends "Unix Makefiles" /opt/DAQ/bot/midas /opt/DAQ/bot/midas /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build/CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/DependInfo.cmake --color=
make[2]: Leaving directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
make -f CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/build.make CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/build
make[2]: Entering directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
/usr/bin/cmake -E cmake_progress_report /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build/CMakeFiles 41
[ 1%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o
/usr/bin/c++ -DOS_LINUX -D_LARGEFILE64_SOURCE -DHAVE_STRLCPY -DINCLUDE_FTPLIB -DHAVE_ODBC -DHAVE_ZLIB -I/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/include -I/opt/DAQ/bot/mxml -o CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o -c /opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:95: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:116: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:136: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to 'char*'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx: In member function 'virtual int SqlODBC::GetNumRows()':
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:589: error: cannot convert 'SQLINTEGER*' to 'long int*' for argument '2' to 'SQLRETURN SQLRowCount(void*, long int*)'
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx: In member function 'virtual const char* SqlODBC::GetColumn(int)':
/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/src/history_odbc.cxx:638: error: cannot convert 'SQLINTEGER*' to 'long int*' for argument '6' to 'SQLRETURN SQLGetData(void*, SQLUSMALLINT, SQLSMALLINT, void*, long int, long int*)'
make[2]: *** [CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/src/history_odbc.cxx.o] Error 1
make[2]: Leaving directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
make[1]: *** [CMakeFiles/midas-static.dir/all] Error 2
make[1]: Leaving directory `/opt/DAQ/bot/midas/build'
make: *** [all] Error 2
|
|
634
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Suggestion | Could not create strings other than 32 characters with odbedit -c "..." command |
> Ok, I added a command
>
> odbedit -c "create STRING Test[8][40]"
>
> which works now. Please update to SVN revision 4555 of odbedit.c
>
> - Stefan
If I want to create only one string, should I write like this:
odbedit -c "create STRING Test[] [256]"
OK. I need it. I will try the new odbedit. |
|
633
|
06 Sep 2009 |
Exaos Lee | Bug Report | Delete key "/A_Str" problem |
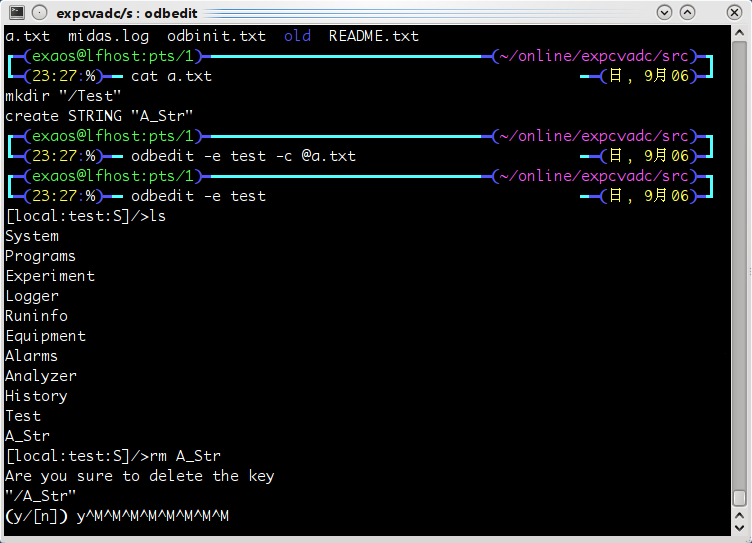
Another problem while using odbedit.
I tried the batch mode of "odbedit". I created a key as "/A_Str" by mistake and
wanted to delete it. Then "odbedit" failed to accept the "Return" key. Please see
the screen-shot attached. :-( |
| Attachment 1: odbedit.png
|
|