 18 Jan 2019, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS 18 Jan 2019, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS
|
> I am having difficulty getting the custom scripts to work within the updated MIDAS. Before the
> update I was using something like :
>
> <input type=submit name=customscript value="test">
>
> on my custom page to run a script under /CustomScript/test, however, with the update to
> MIDAS this is no longer working. I can't find any information about this functionality being
> updated in the latest version - has this changed? Or should it still work?
>
> Thanks,
> Becky (g-2 DAQ)
I do not see any messages about anybody changing this function. I hope it did not break by accident.
Right now I am working on the event buffer code, and did not plan to look at mhttpd, but it looks like
your problem is important and there is at least on more problem (but it has a work-around),
so I may look at it sooner than later...
K.O. |
 22 Jan 2019, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS 22 Jan 2019, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS
|
I just check that feature and found it's still working as expected.
On trap I fell in was that a custom page needs the <input type=submit ...> to be imbedded into a pair of
<form>
...
</form>
tags in order to work. Otherwise the browser will not execute the submit request. Has nothing to do with midas.
There was a small bug that after executing such a script, the URL was set to http://<host>/CS which is non-existent,
so I fixed that to redirect to the page which called the script. Submitted to develop branch. |
 24 Jan 2019, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS 24 Jan 2019, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, Custom script with new MIDAS
|
> <input type=submit name=customscript value="test">
Stefan is right, input-type-submit has to be inside a form. This type of rpc call is "old school". Today, we should
have a json-rpc request to execute a custom script.
https://bitbucket.org/tmidas/midas/issues/163/need-json-rpc-method-to-execute-custom
K.O. |
 12 Dec 2008, Jimmy Ngai, Info, Custom page which executes custom function 12 Dec 2008, Jimmy Ngai, Info, Custom page which executes custom function
|
Dear All,
How can I add a button at the top of the "Status" webpage which will show a
page similar to the "CNAF" one after I click on it? and how can I make a
custom page similar to "CNAF" which allow me to call some custom funtions? I
want to make a page which is particularly for doing calibration.
Thank you for your attention!
Best Regards,
Jimmy Ngai |
 14 Dec 2008, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page which executes custom function 14 Dec 2008, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page which executes custom function
|
> How can I add a button at the top of the "Status" webpage which will show a
> page similar to the "CNAF" one after I click on it? and how can I make a
> custom page similar to "CNAF" which allow me to call some custom funtions? I
> want to make a page which is particularly for doing calibration.
The CNAF page calls directly functions through the RPC layer of midas, which is
not possible from custom pages. All you can do is to execute a scrip on the
server side, which then causes some action. For details please consult the
documentation. |
 01 Jan 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Custom page which executes custom function 01 Jan 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Custom page which executes custom function
|
> How can I add a button at the top of the "Status" webpage which will show a
> page similar to the "CNAF" one after I click on it? and how can I make a
> custom page similar to "CNAF" which allow me to call some custom funtions? I
> want to make a page which is particularly for doing calibration.
I was going to say that you can do this by using the MIDAS "hot-link" function.
In your equipment program, you create a string /eq/xxx/Settings/Command, and hot-link
it to the function you want to be called. (See midas function db_open_record() for details
and examples). (To test it, you put a call to printf("Hello world!\n") into your handler function,
then change the value of "command" using odbedit or the mhttpd odb editor
and observe that your function gets called and that it receives the correct value of "command").
Then on your custom web page you create 2 buttons "aaa" and "bbb" attached to javascript
ODBset("/eq/xxx/Settings/Command","aaa") and "bbb" respectively. When you push the button,
the specified string is written into ODB, and your hot-link handler function is called with the contents
of "command", which you can then look at to find out which web button was pushed.
But after looking at the hot-link data paths (see https://ladd00.triumf.ca/elog/Midas/546), I see 2
problems that make the above scheme unreliable and maybe unusable in some applications:
1) the data path contains one UDP communication and it is well known that UDP datagrams can be (and
are) lost with low or high probability, depending on not-well-understood external factors.
The effect is that the hot-link fails to "fire": odb contents is changed but your function is not called.
2) there is a timing problem with multiple odb writes: the odb lock is dropped before the "hot-link" gets
to see the new contents of odb: db_data_set()->lock odb->change data->send notification->unlock
odb->xxx->notification received by client->read the data->call user function. If something else is
written into odb during "xxx" above, the client may never see the data written by the first odb write. For
local clients, the delay between "send notification" and "notification is received by client" is not bounded in
time (can be arbitrary long, depending on the system load, etc). For remote clients, there is an additional
delay as the udp datagram is received by the local mserver and is forwarded to the remote client through
a tcp rpc connection (another source of unbounded delay).
The effect is that if buttons "aaa" and "bbb" are pushed quickly one right after the other, while your
function will be called 2 times (if neither udp packet is dropped), you may never see the value of "aaa"
as is it will be overwritten by "bbb" by the time you receive the first notification.
Probability of malfunction increases with code written like this: { ODBset("command", "open door");
ODBset("command", "walk through doorway"); }. You may see the "open door" command sometimes
mysteriously disappear...
The net effect is that sometimes you will push the button but nothing will happen. This may be okey,
depending on your application and depending on how often it happens in practice on your specific system
If you are lucky, you may never see either of the 2 problems listed above ad hot-links will work for you
perfectly. At TRIUMF, in the past, we have seen hot-links misbehave in the TWIST experiment, and now I
think I understand why (because of the 2 problems described above).
K.O. |
 13 Jan 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page which executes custom function 13 Jan 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page which executes custom function
|
The UDP connection you mention is only used locally for inter-process communication. When I implemented that, I
made extensive tests and found that there is never a packet being dropped. This happens for UDP only if the packet
goes over a physical network. Maybe this is different in modern Linux versions, so one should double check this
again.
For remote hot-link notification, the notification is sent over the TCP link, so it should not be lost either. But
your second point is correct. The hot-link mechanism was developed to change parameters in front-end programs for
example. So by design it is guaranteed that if you change a value in the ODB, any client hot-linked to that will
see the change (sooner or later). If there are many changes in short intervals (or the callback function on the
remote client takes long time), only the last change is guaranteed to arrive. Therefore, as you correctly state,
the hot-link mechanism is not a save replacement for the RPC layer (That's why the RPC layer is there after all). |
 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page showing ROOT analyzer output 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page showing ROOT analyzer output  
|
Many midas experiments work with ROOT based analyzers today. One problem there is that the graphical output of the root analyzer can only be seen through the X server and not through the web. At the MEG experiment, we solved this problem in an elegant way: The ROOT analyzer runs in the background, using a "virtual" X server called Xvfb. It plots its output (several panels) normally using this X server, then saves this panels every ten seconds into GIF files. These GIF files are then served through mhttpd using a custom page. The output looks like this:
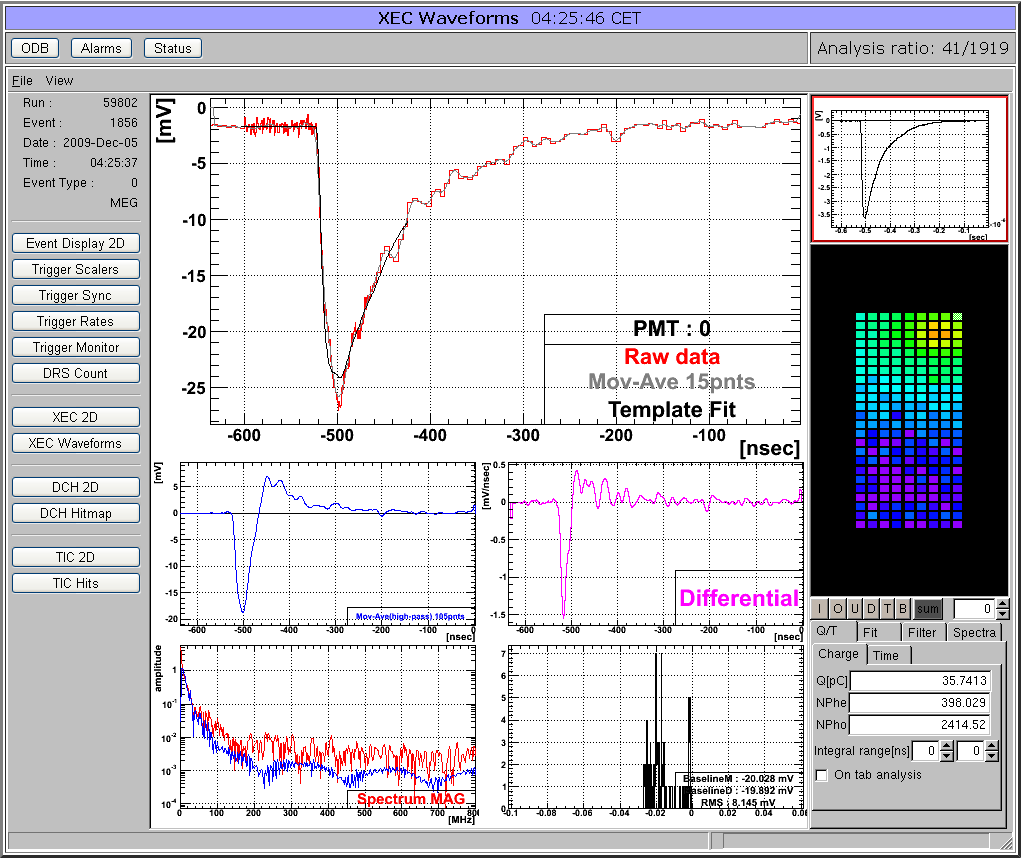
The buttons on the left sides are actually HTML buttons on that custom page overlaid to the GIF image, which in this case shows one of our 800 PMT channels digitized at 1.6 GSPS. With these buttons one can cycle through the different GIF images, which then automatically update ever ten seconds. Of course it is not possible to feed interaction back to the analyzer (like the waveform cannot be fitted interactively) but for monitoring an experiment in production mode this tools is extremely helpful, since it is seamlessly integrated into mhttpd. All the magic is done with JavaScript, and the buttons are overlaid to the graphics using CSS with absolute positioning. The analysis ratio on the top right is also done with JavaScript pulling the right info out of the ODB.
The used custom page file is attached. For details using Xvfb server, please contact Ryu Sawada <sawada@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp>. |
 23 Sep 2013, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented 23 Sep 2013, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented 
|
Due to popular request, I implemented a custom header for mhttpd. This allows to inject some HTML code
to be shown on top of the menu bar on all mhttpd pages. One possible application is to bring back the old
status line with the name of the current experiment, the actual time and the refresh interval.
To use this feature, one can put a new entry into the ODB under
/Custom/Header
which can be either a string (to show some short HTML code directly) or the name of a file containing some
HTML code. If /Custom/Path is present, that path is used to locate the header file. A simple header file to
recreate the GOT look (good-old-times) is here:
<div id="footerDiv" class="footerDiv">
<div style="display:inline; float:left;">MIDAS experiment "Test"</div>
<div id="refr" style="display:inline; float:right;"></div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var r = document.getElementById('refr');
var now = new Date();
var c = document.cookie.split('midas_refr=');
r.innerHTML = now.toString() + ' ' + 'Refr:' + c.pop().split(';').shift();
</script>
The JavaScript code is used to retrieve the midas_refr cookie which stores the refresh interval and displays
it together with the current time.
Another application of this feature might be to check certain values in the ODB (via the ODBGet function)
and some some important status or error condition.
/Stefan |
 12 Feb 2014, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented 12 Feb 2014, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented
|
As reported in the bug tracker, the proposed header does not work if no specific (= different from the default 60 sec.) update period is specified,
since then no cookie is present. Here is the updated code which works for all cases:
<div id="footerDiv" class="footerDiv">
<div style="display:inline; float:left;">MIDAS experiment "Test"</div>
<div id="refr" style="display:inline; float:right;"></div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var r = document.getElementById('refr');
var now = new Date();
var refr;
if (document.cookie.search('midas_refr') == -1)
refr = 60;
else {
var c = document.cookie.split('midas_refr=');
refr = c.pop().split(';').shift();
}
r.innerHTML = now.toString() + ' ' + 'Refr:' + refr;
</script>
/Stefan |
 18 Feb 2014, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Custom page header implemented 18 Feb 2014, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Custom page header implemented
|
I am not sure what to do with the javascript snippet - I understand it should be somehow connected to /Custom/Header, but if I create the /Custom/Header string, I cannot put this snippet
into this string using odbedit - if I try to cut&paste it into odbedit, it is truncated to the first line - nor using the mhttpd odb editor - when I cut&paste it into the odb editor text entry box, it
is truncated to the first 519 bytes (must be a hard limit somewhere). K.O.
> As reported in the bug tracker, the proposed header does not work if no specific (= different from the default 60 sec.) update period is specified,
> since then no cookie is present. Here is the updated code which works for all cases:
>
>
>
> <div id="footerDiv" class="footerDiv">
> <div style="display:inline; float:left;">MIDAS experiment "Test"</div>
> <div id="refr" style="display:inline; float:right;"></div>
> </div>
> <script type="text/javascript">
> var r = document.getElementById('refr');
> var now = new Date();
> var refr;
> if (document.cookie.search('midas_refr') == -1)
> refr = 60;
> else {
> var c = document.cookie.split('midas_refr=');
> refr = c.pop().split(';').shift();
> }
> r.innerHTML = now.toString() + ' ' + 'Refr:' + refr;
> </script>
>
>
>
> /Stefan |
 19 Feb 2014, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented 19 Feb 2014, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page header implemented
|
> I am not sure what to do with the javascript snippet
Just read elog:908, it tells you to put this into a file, name it header.html for example, and put into the ODB:
/Custom/Header [string32] = header.html
make sure that you put the file into the directory indicated by /Custom/Path.
Cheers,
Stefan |
 25 Jul 2017, Stefan Ritt, Info, Current git repository "develop" branch broken 25 Jul 2017, Stefan Ritt, Info, Current git repository "develop" branch broken
|
Dear all,
we are currently undergoing major modifications in the way mhttpd is working. I realized that
we are now at a state where mhttpd is currently broken, and it will take a few weeks in order to
get everything converted to the new scheme we plan to use. Therefore I moved the git branch
"master" to the last known stable version of midas. So for any practical purpose, please do
NOT update your "develop" branch until further notice. To get the last stable version, you can
do a
$ git checkout master
which moves you right before we started to make major modifications. Once we are finished,
we will announce this here in the forum.
Best regards,
Stefan |
 10 Mar 2004, Jan Wouters, , Creation of secondary Midas output file. 10 Mar 2004, Jan Wouters, , Creation of secondary Midas output file. 
|
Dear Midas Team,
I have run into a problem with Midas and was wondering if you could explain what I
am doing wrong. I have included a simple demo to illustrate what I am doing and
can send a small input data file if needed.
WHAT I AM TRYING TO DO:
Every midas event for the DANCE experiment consists of many physics events. I am
trying to create a secondary mid file where the event boundaries are now the
physics events rather than the midas events. This secondary mid file will be
analyzed using a second stage midas analyzer.
For the demo, I use the data from EV02 (one of our 15 frontends), which consists of a
variable number of fixed length structures where each structure contains the data for
one crystal from the DANCE detector.
I treat each crystal as a separate physics event and write it out in the TREK bank,
which is a demo calculated output bank, as a separate event.
(The only difference between this demo and our real system is that we would include
all the crystals from the other frontends that have approximately the same time stamp
in the output bank. Thus the output bank would consist of a varing number of
crystals in one event rather than the fixed one crystal per event used in this demo.)
THE CHANGES TO analyzer.c AND adccalib.c
I loop through the EV02 bank examining each crystal structure in turn. I calculate
"calibrated" parameters and put them into an output bank called TREK. The unusual
part of this example is that the TREK bank is no longer part of the main list of input
banks, ana_trigger_bank_list[]. Instead it is now part of a new bank list called
ana_physics_bank_list[]. See the analyzer.c file for this definition.
In adccalib.c I create the space for this new bank as follows.
EVENT_HEADER gPhysicsEventHeaders[ MAX_EVENT_SIZE / sizeof(
EVENT_HEADER ) ];
WORD* gPhysicsEventData = ( WORD * )( gPhysicsEventHeaders + 1 );
In the adc_calib routine I create the bank header as follows. Note that the serial
numbers will restart at 0 at the beginning of each midas event. Should I let the serial
number increment monotonically until the end of the run?:
gPhysicsEventHeaders->serial_number = (DWORD) - 1;
gPhysicsEventHeaders->event_id = 2;
gPhysicsEventHeaders->trigger_mask = 0;
gPhysicsEventHeaders->time_stamp = pheader->time_stamp;
In a loop that loops through all the crystals contained in EV02, I extract each crystal,
calibrate it, and store it in a TREK structure. In creating the TREK bank I assume that
each one will be a separate physics event thus I update the event serial number and
use bk_init32 to initialize the memory.
for ( short i = 0; i < nItems; i++ )
{ ++(gPhysicsEventHeaders->serial_number); // Update serial number.
bk_init32( gPhysicsEventData ); // Initialize storage.
bk_create( gPhysicsEventData, "TREK", TID_STRUCT, &trek );
trek->one = (double) pev->areahg * 1.0;
trek->two = (float) pev->timelo * 1.0;
bk_close( gPhysicsEventData, trek+1 );
pev++; // Loop to next crystal's data.
}
The output bank should consist of multiple events for each individual EV02 midas
input event.
As far as I can tell the code compiles and runs fine, but I get no data in the .mid
output file except for the ODB. I have a print statement at the beginning of each
midas event stating how many crystals were found in the EV02 bank. I also print out
the calibrated value for each crystal as it is being placed in its own TREK output
bank. The data appears correct.
I cannot place TREK in the input bank the way it normally is done in the examples
because there is not a one-to-one correspondence between a midas event and a
true physics event. Instead one midas event has many physics events. Thus the
output bank needs to be in a new memory area so that I can create a custom header
and increment the serial number properly for each event. Our follow-on analysis
using a second Midas analyzer only needs to analyze one physics event at a time
rather than one Midas event at a time, which is why we are going to all the trouble to
get this paradigm working.
I include all the code for this very simple example.
RUNNING THE CODE:
To run the example just use the run01220.mid file I will send:
./analyzer -i run01220.mid.gz -o run01220out.mid -c settings.odb_cfg -n 50
The only thing done by the settings.odb_cfg file is to turn on the TREK output bank. I
have verified that the bank is on.
SUMMARY:
I believe that I must not be creating the new TREK output bank correctly so that
midas understands that the event-by-event calculated physics data should be written
out event-by-event. I have pointed out several places in the above discussion where
I might be making a mistake.
I would like to get both this example running and a similar which create Root trees,
though the Root trees are of secondary importance. With this example I can finish
writing the second stage analyzer and get the DANCE collaboration moving forward
with their analysis. Currently, we cannot use this paradigm because I cannot create
a secondary mid file in our stage one analysis. I would be very grateful if you could
take a look at this example and tell me what I am doing incorrectly.
Jan |
 10 Mar 2004, Stefan Ritt, , Creation of secondary Midas output file. 10 Mar 2004, Stefan Ritt, , Creation of secondary Midas output file. 
|
Dear Jan,
I had a look at your code. You create a gPhysicsEventHeader array, fill it, and expect the
framework to write it to disk. But how can the framework "guess" that you want your private
global array being written? Unfortunately it cannot do magic!
Do do what you want, you have to write a "secondary" midas file yourself. I modified your
code to do that. First, I define the event storage like
BYTE gSecEvent[ MAX_EVENT_SIZE ];
EVENT_HEADER *gPhysicsEventHeader = (EVENT_HEADER *) gSecEvent;
WORD* gPhysicsEventData = ( WORD * )( gPhysicsEventHeader + 1 );
I use gSecEvent as a BYTE array, since it only contains one avent at a time, so this is more
appropriate. Then, in the BOR routine, I open a file:
sprintf(str, "sec%05d.mid", run_number);
sec_fh = open(str, O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_BINARY, 0644);
and close it in the EOR routine
close(sec_fh);
The event routine now manually fills events into the secondary file:
/* write event to secondary .mid file */
gPhysicsEventHeader->data_size = bk_size(gPhysicsEventData);
write(sec_fh, gPhysicsEventHeader, sizeof(EVENT_HEADER)+bk_size(gPhysicsEventData));
Note that this code is placed *inside* the for() loop over nItems, so for each detector you
create and event and write it.
That's all you need, the full file adccalib.c is attached. I tried to produce a sec01220.mid
file and was able to read it back with the mdump utility.
Best regards,
Stefan |
 11 Mar 2004, Renee Poutissou, , Creation of secondary Midas output file. 11 Mar 2004, Renee Poutissou, , Creation of secondary Midas output file.
|
Jan ,
Do you need to log this stage 1 output? If not, you would use the
eventbuilder mechanism to create your stage 2 events.
I use the eventbuilder mechanism with success for my TWIST experiment.
Renee |
 16 Sep 2024, Marius Köppel, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch 16 Sep 2024, Marius Köppel, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch 
|
Hi all,
last week I was running MIDAS with the commit 3ad98c5. Today I updated MIDAS and now all my watch functions are crashing. Attached I have a minimal example frontend of the problem.
In our software we have two functions one which sets up the ODB values of the frontend and another one which sets up all watch functions. So overall we connect two time to the ODB during fronend_init one time to create the values and one time to create the watch. In the example code a simple version of this setup is shown:
INT frontend_init() {
cm_msg(MINFO, "frontend_init() setup", "Test FE");
odb settings = {
{"Test", 123},
{"sub", {}}
};
settings.connect_and_fix_structure("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
// settings.watch(watch); <-- this works without segmentation fault
odb new_settings("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
new_settings.watch(watch); // <-- here I am getting a segmentation fault
return CM_SUCCESS;
}
When I directly set the watch everything runs fine however, when I create a new ODB object and use this one to set a watch I am getting the following segmentation fault:
Process 18474 stopped
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x34)
frame #0: 0x000000010004fa38 test_fe`midas::odb::watch_callback(hDB=<unavailable>, hKey=<unavailable>, index=0, info=0x00006000002001c0) at odbxx.cxx:96:25 [opt]
93 if (po->m_data == nullptr)
94 mthrow("Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope");
95 midas::odb *poh = search_hkey(po, hKey);
-> 96 poh->m_last_index = index;
97 po->m_watch_callback(*poh);
98 poh->m_last_index = -1;
99 }
Best,
Marius |
 16 Sep 2024, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch 16 Sep 2024, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch
|
The answer is in the error message: „Object went out of scope“. When your frontent_init() exits, the odb objects are destroyed. When you get a callback, it‘s linked to the
destroyed object. This is like if you have a local string and pass a reference to that string in the return of the function.
Use a global object (bad) or use „new“ (potential memory leak). I would use a global structure which holds all odb objects.
Stefan
>
> last week I was running MIDAS with the commit 3ad98c5. Today I updated MIDAS and now all my watch functions are crashing. Attached I have a minimal example frontend of the problem.
>
> In our software we have two functions one which sets up the ODB values of the frontend and another one which sets up all watch functions. So overall we connect two time to the ODB during fronend_init one time to create the values and one time to create the watch. In the example code a simple version of this setup is shown:
>
> INT frontend_init() {
>
> cm_msg(MINFO, "frontend_init() setup", "Test FE");
>
> odb settings = {
> {"Test", 123},
> {"sub", {}}
> };
> settings.connect_and_fix_structure("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> // settings.watch(watch); <-- this works without segmentation fault
>
> odb new_settings("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> new_settings.watch(watch); // <-- here I am getting a segmentation fault
>
> return CM_SUCCESS;
> }
>
> When I directly set the watch everything runs fine however, when I create a new ODB object and use this one to set a watch I am getting the following segmentation fault:
>
> Process 18474 stopped
> * thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x34)
> frame #0: 0x000000010004fa38 test_fe`midas::odb::watch_callback(hDB=<unavailable>, hKey=<unavailable>, index=0, info=0x00006000002001c0) at odbxx.cxx:96:25 [opt]
> 93 if (po->m_data == nullptr)
> 94 mthrow("Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope");
> 95 midas::odb *poh = search_hkey(po, hKey);
> -> 96 poh->m_last_index = index;
> 97 po->m_watch_callback(*poh);
> 98 poh->m_last_index = -1;
> 99 }
>
> Best,
> Marius |
 16 Sep 2024, Marius Koeppel, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch 16 Sep 2024, Marius Koeppel, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch
|
This is not the case here. Note that the error message: "Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope" is not called! The segmentation fault happens later line 96.
> The answer is in the error message: „Object went out of scope“. When your frontent_init() exits, the odb objects are destroyed. When you get a callback, it‘s linked to the
> destroyed object. This is like if you have a local string and pass a reference to that string in the return of the function.
>
> Use a global object (bad) or use „new“ (potential memory leak). I would use a global structure which holds all odb objects.
>
> Stefan
>
> >
> > last week I was running MIDAS with the commit 3ad98c5. Today I updated MIDAS and now all my watch functions are crashing. Attached I have a minimal example frontend of the problem.
> >
> > In our software we have two functions one which sets up the ODB values of the frontend and another one which sets up all watch functions. So overall we connect two time to the ODB during fronend_init one time to create the values and one time to create the watch. In the example code a simple version of this setup is shown:
> >
> > INT frontend_init() {
> >
> > cm_msg(MINFO, "frontend_init() setup", "Test FE");
> >
> > odb settings = {
> > {"Test", 123},
> > {"sub", {}}
> > };
> > settings.connect_and_fix_structure("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> > // settings.watch(watch); <-- this works without segmentation fault
> >
> > odb new_settings("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> > new_settings.watch(watch); // <-- here I am getting a segmentation fault
> >
> > return CM_SUCCESS;
> > }
> >
> > When I directly set the watch everything runs fine however, when I create a new ODB object and use this one to set a watch I am getting the following segmentation fault:
> >
> > Process 18474 stopped
> > * thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x34)
> > frame #0: 0x000000010004fa38 test_fe`midas::odb::watch_callback(hDB=<unavailable>, hKey=<unavailable>, index=0, info=0x00006000002001c0) at odbxx.cxx:96:25 [opt]
> > 93 if (po->m_data == nullptr)
> > 94 mthrow("Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope");
> > 95 midas::odb *poh = search_hkey(po, hKey);
> > -> 96 poh->m_last_index = index;
> > 97 po->m_watch_callback(*poh);
> > 98 poh->m_last_index = -1;
> > 99 }
> >
> > Best,
> > Marius |
 16 Sep 2024, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch 16 Sep 2024, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, Crash using ODB watch
|
Well, the object *went* out of scope. For my code it‘s hard to realize this, so the error reporting is poor. Also the first object should have the same
problem. Just by accident that it does not crash.
Stefan
> This is not the case here. Note that the error message: "Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope" is not called! The segmentation fault happens later line 96.
>
> > The answer is in the error message: „Object went out of scope“. When your frontent_init() exits, the odb objects are destroyed. When you get a callback, it‘s linked to the
> > destroyed object. This is like if you have a local string and pass a reference to that string in the return of the function.
> >
> > Use a global object (bad) or use „new“ (potential memory leak). I would use a global structure which holds all odb objects.
> >
> > Stefan
> >
> > >
> > > last week I was running MIDAS with the commit 3ad98c5. Today I updated MIDAS and now all my watch functions are crashing. Attached I have a minimal example frontend of the problem.
> > >
> > > In our software we have two functions one which sets up the ODB values of the frontend and another one which sets up all watch functions. So overall we connect two time to the ODB during fronend_init one time to create the values and one time to create the watch. In the example code a simple version of this setup is shown:
> > >
> > > INT frontend_init() {
> > >
> > > cm_msg(MINFO, "frontend_init() setup", "Test FE");
> > >
> > > odb settings = {
> > > {"Test", 123},
> > > {"sub", {}}
> > > };
> > > settings.connect_and_fix_structure("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> > > // settings.watch(watch); <-- this works without segmentation fault
> > >
> > > odb new_settings("/Equipment/Test FE/Settings");
> > > new_settings.watch(watch); // <-- here I am getting a segmentation fault
> > >
> > > return CM_SUCCESS;
> > > }
> > >
> > > When I directly set the watch everything runs fine however, when I create a new ODB object and use this one to set a watch I am getting the following segmentation fault:
> > >
> > > Process 18474 stopped
> > > * thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x34)
> > > frame #0: 0x000000010004fa38 test_fe`midas::odb::watch_callback(hDB=<unavailable>, hKey=<unavailable>, index=0, info=0x00006000002001c0) at odbxx.cxx:96:25 [opt]
> > > 93 if (po->m_data == nullptr)
> > > 94 mthrow("Callback received for a midas::odb object which went out of scope");
> > > 95 midas::odb *poh = search_hkey(po, hKey);
> > > -> 96 poh->m_last_index = index;
> > > 97 po->m_watch_callback(*poh);
> > > 98 poh->m_last_index = -1;
> > > 99 }
> > >
> > > Best,
> > > Marius |
|