Classes | |
| struct | FL_PARAM |
| struct | suspend_struct |
Macros | |
| #define | bin_to_ascii(c) ((c)>=38?((c)-38+'a'):(c)>=12?((c)-12+'A'):(c)+'.') |
| #define | N_STACK_HISTORY 500 |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct suspend_struct | SUSPEND_STRUCT |
Functions | |
| static void | check_shm_type (const char *shm_type) |
| static void | check_shm_host () |
| static int | ss_shm_name (const char *name, std::string &mem_name, std::string &file_name, std::string &shm_name) |
| INT | ss_shm_open (const char *name, INT size, void **adr, size_t *shm_size, HNDLE *handle, BOOL get_size) |
| INT | ss_shm_close (const char *name, void *adr, size_t shm_size, HNDLE handle, INT destroy_flag) |
| INT | ss_shm_delete (const char *name) |
| INT | ss_shm_protect (HNDLE handle, void *adr, size_t shm_size) |
| INT | ss_shm_unprotect (HNDLE handle, void **adr, size_t shm_size, BOOL read, BOOL write, const char *caller_name) |
| INT | ss_shm_flush_thread (void *p) |
| INT | ss_shm_flush (const char *name, const void *adr, size_t size, HNDLE handle, bool wait_for_thread) |
| INT | ss_get_struct_align () |
| INT | ss_get_struct_padding () |
| INT | ss_getpid (void) |
| BOOL | ss_pid_exists (int pid) |
| void | ss_kill (int pid) |
| std::string | ss_get_executable (void) |
| std::string | ss_get_cmdline (void) |
| midas_thread_t | ss_gettid (void) |
| std::string | ss_tid_to_string (midas_thread_t thread_id) |
| INT | ss_spawnv (INT mode, const char *cmdname, const char *const argv[]) |
| INT | ss_shell (int sock) |
| INT | ss_daemon_init (BOOL keep_stdout) |
| BOOL | ss_existpid (INT pid) |
| INT | ss_system (const char *command) |
| INT | ss_exec (const char *command, INT *pid) |
| std::string | ss_replace_env_variables (const std::string &inputPath) |
| std::string | ss_execs (const char *cmd) |
| midas_thread_t | ss_thread_create (INT(*thread_func)(void *), void *param) |
| INT | ss_thread_kill (midas_thread_t thread_id) |
| INT EXPRT | ss_thread_set_name (std::string name) |
| std::string EXPRT | ss_thread_get_name () |
| INT | ss_semaphore_create (const char *name, HNDLE *semaphore_handle) |
| INT | ss_semaphore_wait_for (HNDLE semaphore_handle, DWORD timeout_millisec) |
| INT | ss_semaphore_release (HNDLE semaphore_handle) |
| INT | ss_semaphore_delete (HNDLE semaphore_handle, INT destroy_flag) |
| INT | ss_mutex_create (MUTEX_T **mutex, BOOL recursive) |
| INT | ss_mutex_wait_for (MUTEX_T *mutex, INT timeout) |
| INT | ss_mutex_release (MUTEX_T *mutex) |
| INT | ss_mutex_delete (MUTEX_T *mutex) |
| bool | ss_timed_mutex_wait_for_sec (std::timed_mutex &mutex, const char *mutex_name, double timeout_sec) |
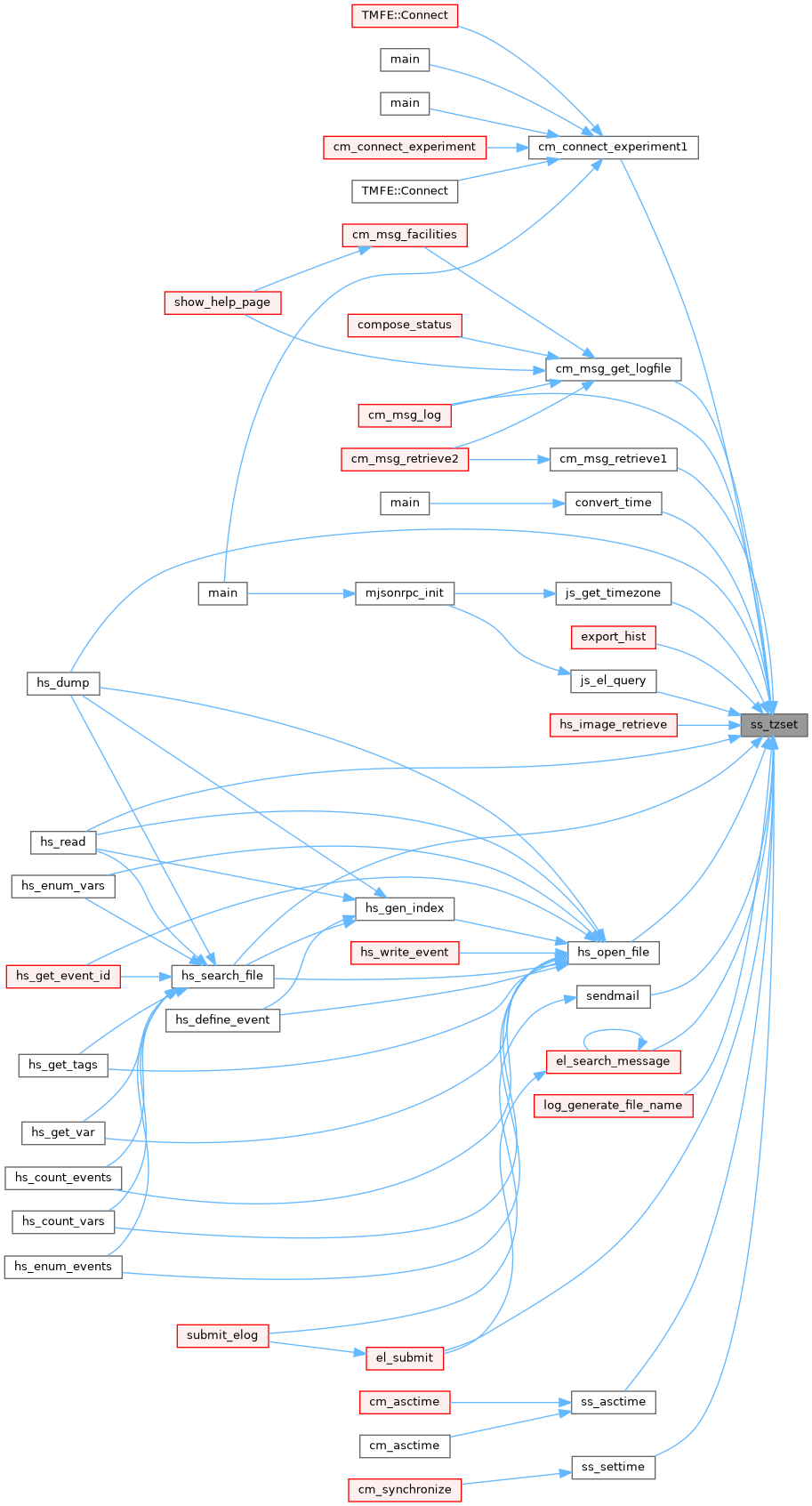
| void | ss_tzset () |
| time_t | ss_mktime (struct tm *tms) |
| DWORD | ss_millitime () |
| DWORD | ss_time () |
| double | ss_time_sec () |
| DWORD | ss_settime (DWORD seconds) |
| std::string | ss_asctime () |
| INT | ss_timezone () |
| INT | ss_sleep (INT millisec) |
| BOOL | ss_kbhit () |
| INT | ss_alarm (INT millitime, void(*func)(int)) |
| INT | ss_exception_handler (void(*func)(void)) |
| void * | ss_ctrlc_handler (void(*func)(int)) |
| static bool | ss_match_thread (midas_thread_t tid1, midas_thread_t tid2) |
| INT | ss_suspend_set_rpc_thread (midas_thread_t thread_id) |
| static INT | ss_suspend_init_struct (SUSPEND_STRUCT *psuspend) |
| SUSPEND_STRUCT * | ss_suspend_get_struct (midas_thread_t thread_id) |
| static void | ss_suspend_close (SUSPEND_STRUCT *psuspend) |
| INT | ss_suspend_exit () |
| INT | ss_suspend_set_server_listener (int listen_socket) |
| INT | ss_suspend_set_client_listener (int listen_socket) |
| INT | ss_suspend_set_client_connection (RPC_SERVER_CONNECTION *connection) |
| INT | ss_suspend_set_server_acceptions (RPC_SERVER_ACCEPTION_LIST *acceptions) |
| INT | ss_suspend_init_odb_port () |
| INT | ss_suspend_get_odb_port (INT *port) |
| INT | ss_suspend_get_buffer_port (midas_thread_t thread_id, INT *port) |
| static int | ss_suspend_process_ipc (INT millisec, INT msg, int ipc_recv_socket) |
| static int | ss_socket_check (int sock) |
| bool | ss_event_socket_has_data () |
| INT | ss_suspend (INT millisec, INT msg) |
| INT | ss_resume (INT port, const char *message) |
| int | ss_socket_wait (int sock, INT millisec) |
| INT | ss_socket_connect_tcp (const char *hostname, int tcp_port, int *sockp, std::string *error_msg_p) |
| INT | ss_socket_listen_tcp (bool listen_localhost, int tcp_port, int *sockp, int *tcp_port_p, std::string *error_msg_p) |
| INT | ss_socket_close (int *sockp) |
| INT | ss_socket_get_peer_name (int sock, std::string *hostp, int *portp) |
| INT | send_tcp (int sock, char *buffer, DWORD buffer_size, INT flags) |
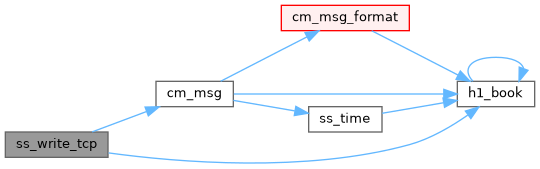
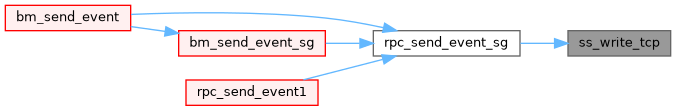
| INT | ss_write_tcp (int sock, const char *buffer, size_t buffer_size) |
| INT | recv_string (int sock, char *buffer, DWORD buffer_size, INT millisec) |
| INT | recv_tcp (int sock, char *net_buffer, DWORD buffer_size, INT flags) |
| INT | recv_tcp2 (int sock, char *net_buffer, int buffer_size, int timeout_ms) |
| INT | ss_recv_net_command (int sock, DWORD *routine_id, DWORD *param_size, char **param_ptr, int timeout_ms) |
| std::string | ss_gethostname () |
| INT | ss_gethostname (char *buffer, int buffer_size) |
| std::string | ss_getcwd () |
| INT | ss_tape_open (char *path, INT oflag, INT *channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_close (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_status (char *path) |
| INT | ss_tape_write (INT channel, void *pdata, INT count) |
| INT | ss_tape_read (INT channel, void *pdata, INT *count) |
| INT | ss_tape_write_eof (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_fskip (INT channel, INT count) |
| INT | ss_tape_rskip (INT channel, INT count) |
| INT | ss_tape_rewind (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_spool (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_mount (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_unmount (INT channel) |
| INT | ss_tape_get_blockn (INT channel) |
| double | ss_disk_free (const char *path) |
| INT | ss_file_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, char **plist) |
| INT | ss_file_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, STRING_LIST *plist) |
| INT | ss_dir_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, char **plist) |
| INT | ss_dir_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, STRING_LIST *plist) |
| INT | ss_dirlink_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, char **plist) |
| INT | ss_dirlink_find (const char *path, const char *pattern, STRING_LIST *plist) |
| INT | ss_file_remove (const char *path) |
| double | ss_file_size (const char *path) |
| time_t | ss_file_time (const char *path) |
| double | ss_disk_size (const char *path) |
| int | ss_file_exist (const char *path) |
| int | ss_file_link_exist (const char *path) |
| int | ss_dir_exist (const char *path) |
| int | ss_file_copy (const char *src, const char *dst, bool append) |
| void | ss_clear_screen () |
| void | ss_set_screen_size (int x, int y) |
| void | ss_printf (INT x, INT y, const char *format,...) |
| char * | ss_getpass (const char *prompt) |
| INT | ss_getchar (BOOL reset) |
| char * | ss_gets (char *string, int size) |
| INT | ss_directio_give_port (INT start, INT end) |
| INT | ss_directio_lock_port (INT start, INT end) |
| char * | ss_crypt (const char *buf, const char *salt) |
| double | ss_nan () |
| int | ss_isnan (double x) |
| int | ss_isfin (double x) |
| INT | ss_stack_get (char ***string) |
| void | ss_stack_print () |
| void | ss_stack_history_entry (char *tag) |
| void | ss_stack_history_dump (char *filename) |
| bool | ss_is_valid_utf8 (const char *string) |
| bool | ss_repair_utf8 (char *string) |
| bool | ss_repair_utf8 (std::string &s) |
| std::chrono::time_point< std::chrono::high_resolution_clock > | ss_us_start () |
| unsigned int | ss_us_since (std::chrono::time_point< std::chrono::high_resolution_clock > start) |
| int | rpc_flush_event_socket (int timeout_msec) |
Variables | ||
| struct { | ||
| char c | ||
| double d | ||
| } | test_align | |
| struct { | ||
| double d | ||
| char c | ||
| } | test_padding | |
| static BOOL | _daemon_flag | |
| static std::atomic_bool | s_semaphore_trace {false} | |
| static std::atomic_int | s_semaphore_nest_level {0} | |
| static std::mutex | gTzMutex | |
| void(* | MidasExceptionHandler )(void) | |
| static std::vector< SUSPEND_STRUCT * > | _ss_suspend_vector | |
| static midas_thread_t | _ss_odb_thread = 0 | |
| static SUSPEND_STRUCT * | _ss_suspend_odb = NULL | |
| static midas_thread_t | _ss_listen_thread = 0 | |
| static int | _ss_server_listen_socket = 0 | |
| static int | _ss_client_listen_socket = 0 | |
| static midas_thread_t | _ss_client_thread = 0 | |
| static RPC_SERVER_CONNECTION * | _ss_client_connection = NULL | |
| static midas_thread_t | _ss_server_thread = 0 | |
| static RPC_SERVER_ACCEPTION_LIST * | _ss_server_acceptions = NULL | |
| static bool | gSocketTrace = false | |
| char | stack_history [N_STACK_HISTORY][80] | |
| int | stack_history_pointer = -1 | |
Detailed Description
dox
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ bin_to_ascii
Definition at line 7967 of file system.cxx.
◆ N_STACK_HISTORY
| #define N_STACK_HISTORY 500 |
Definition at line 8068 of file system.cxx.
Typedef Documentation
◆ SUSPEND_STRUCT
| typedef struct suspend_struct SUSPEND_STRUCT |
Function Documentation
◆ check_shm_host()
|
static |
Definition at line 170 of file system.cxx.
◆ check_shm_type()
|
static |
Definition at line 82 of file system.cxx.
◆ recv_string()
Definition at line 5471 of file system.cxx.
◆ recv_tcp()
Definition at line 5526 of file system.cxx.
◆ recv_tcp2()
Definition at line 5634 of file system.cxx.
◆ rpc_flush_event_socket()
| int rpc_flush_event_socket | ( | int | timeout_msec | ) |
Definition at line 17525 of file midas.cxx.

◆ send_tcp()
Definition at line 5357 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_alarm()
Definition at line 3809 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_asctime()
| std::string EXPRT ss_asctime | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3621 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_clear_screen()
| void EXPRT ss_clear_screen | ( | ) |
Definition at line 7377 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_crypt()
| char EXPRT * ss_crypt | ( | const char * | buf, |
| const char * | salt | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 7969 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_ctrlc_handler()
| void EXPRT * ss_ctrlc_handler | ( | void(*)(int) | func | ) |
Definition at line 3971 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_daemon_init()
Definition at line 2073 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_dir_exist()
Definition at line 7264 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_dir_find() [1/2]
Definition at line 6874 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_dir_find() [2/2]
| INT EXPRT ss_dir_find | ( | const char * | path, |
| const char * | pattern, | ||
| STRING_LIST * | plist | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 6892 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_directio_give_port()
Definition at line 7889 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_directio_lock_port()
Definition at line 7925 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_dirlink_find() [1/2]
Definition at line 6950 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_dirlink_find() [2/2]
| INT EXPRT ss_dirlink_find | ( | const char * | path, |
| const char * | pattern, | ||
| STRING_LIST * | plist | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 6968 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_disk_free()
| double EXPRT ss_disk_free | ( | const char * | path | ) |
Definition at line 6698 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_disk_size()
| double EXPRT ss_disk_size | ( | const char * | path | ) |
Definition at line 7126 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_event_socket_has_data()
| bool ss_event_socket_has_data | ( | ) |
Definition at line 4592 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_exception_handler()
| INT ss_exception_handler | ( | void(*)(void) | func | ) |
Definition at line 3916 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_exec()
Definition at line 2204 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_execs()
| std::string EXPRT ss_execs | ( | const char * | cmd | ) |
Definition at line 2309 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_existpid()
Definition at line 2140 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_copy()
| int EXPRT ss_file_copy | ( | const char * | src, |
| const char * | dst, | ||
| bool | append | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 7297 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_exist()
Definition at line 7196 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_find() [1/2]
Definition at line 6791 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_find() [2/2]
| INT EXPRT ss_file_find | ( | const char * | path, |
| const char * | pattern, | ||
| STRING_LIST * | plist | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 6809 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_link_exist()
Definition at line 7232 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_remove()
Definition at line 7030 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_file_size()
| double EXPRT ss_file_size | ( | const char * | path | ) |
Definition at line 7050 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_file_time()
| time_t EXPRT ss_file_time | ( | const char * | path | ) |
Definition at line 7088 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_get_cmdline()
| std::string ss_get_cmdline | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1519 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_get_executable()
| std::string ss_get_executable | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1490 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_get_struct_align()
Definition at line 1321 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_get_struct_padding()
Definition at line 1347 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_getchar()
Definition at line 7581 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_getcwd()
| std::string EXPRT ss_getcwd | ( | ) |
Definition at line 5848 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_gethostname() [1/2]
| std::string ss_gethostname | ( | ) |
Definition at line 5784 of file system.cxx.
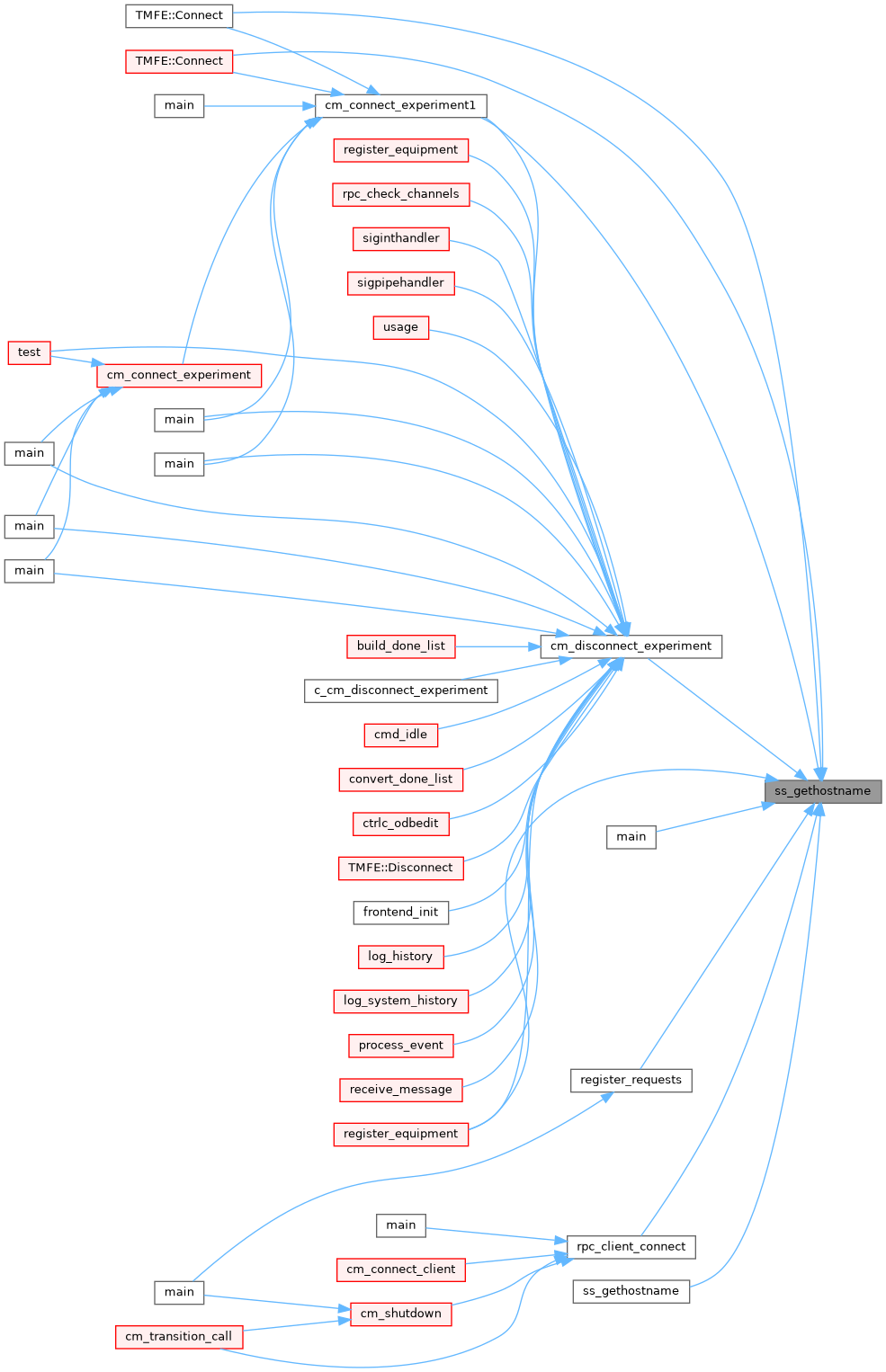
◆ ss_gethostname() [2/2]
| INT ss_gethostname | ( | char * | buffer, |
| int | buffer_size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 5818 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_getpass()
| char EXPRT * ss_getpass | ( | const char * | prompt | ) |
Definition at line 7518 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_getpid()
Definition at line 1379 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_gets()
| char EXPRT * ss_gets | ( | char * | string, |
| int | size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 7848 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_gettid()
| midas_thread_t EXPRT ss_gettid | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1591 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_is_valid_utf8()
| bool ss_is_valid_utf8 | ( | const char * | string | ) |
Definition at line 8146 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_isfin()
| int EXPRT ss_isfin | ( | double | x | ) |
Definition at line 8044 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_isnan()
| int EXPRT ss_isnan | ( | double | x | ) |
Definition at line 8039 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_kbhit()
Definition at line 3736 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_kill()
| void ss_kill | ( | int | pid | ) |
Definition at line 1473 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_match_thread()
|
static |
Definition at line 4065 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_millitime()
Returns the actual time in milliseconds with an arbitrary origin. This time may only be used to calculate relative times.
Overruns in the 32 bit value don't hurt since in a subtraction calculated with 32 bit accuracy this overrun cancels (you may think about!)..
- Returns
- millisecond time stamp.
Definition at line 3465 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_mktime()
Definition at line 3437 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_mutex_create()
Definition at line 3013 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_mutex_delete()
Definition at line 3283 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_mutex_release()
Definition at line 3229 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_mutex_wait_for()
Definition at line 3109 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_nan()
| double EXPRT ss_nan | ( | ) |
Definition at line 8018 of file system.cxx.
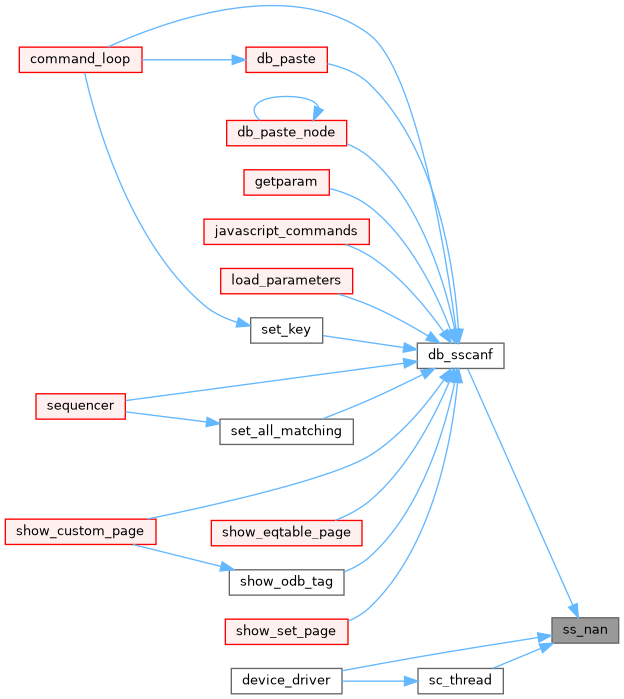
◆ ss_pid_exists()
| BOOL ss_pid_exists | ( | int | pid | ) |
Definition at line 1442 of file system.cxx.
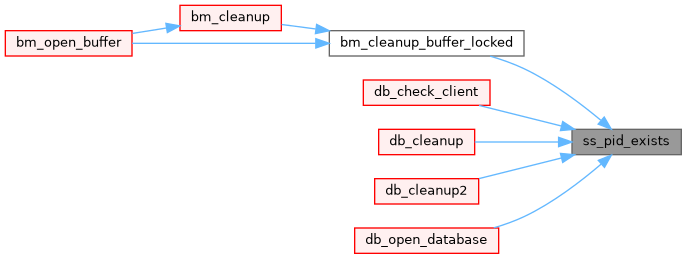
◆ ss_printf()
Definition at line 7460 of file system.cxx.
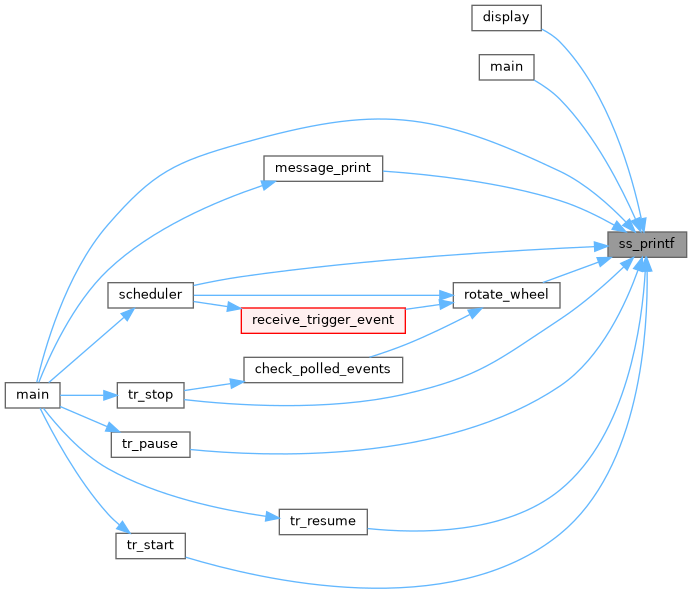
◆ ss_recv_net_command()
| INT EXPRT ss_recv_net_command | ( | int | sock, |
| DWORD * | routine_id, | ||
| DWORD * | param_size, | ||
| char ** | param_ptr, | ||
| int | timeout_ms | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 5707 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_repair_utf8() [1/2]
| bool ss_repair_utf8 | ( | char * | string | ) |
Definition at line 8229 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_repair_utf8() [2/2]
| bool ss_repair_utf8 | ( | std::string & | s | ) |
Definition at line 8325 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_replace_env_variables()
| std::string EXPRT ss_replace_env_variables | ( | const std::string & | inputPath | ) |
Definition at line 2284 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_resume()
Definition at line 4916 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_semaphore_create()
Definition at line 2532 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_semaphore_delete()
Definition at line 2941 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_semaphore_release()
Definition at line 2853 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_semaphore_wait_for()
Definition at line 2711 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_set_screen_size()
| void ss_set_screen_size | ( | int | x, |
| int | y | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 7427 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_settime()
Definition at line 3547 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_shell()
| INT ss_shell | ( | int | sock | ) |
Definition at line 1832 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_close()
Definition at line 757 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_delete()
Definition at line 911 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_flush()
| INT ss_shm_flush | ( | const char * | name, |
| const void * | adr, | ||
| size_t | size, | ||
| HNDLE | handle, | ||
| bool | wait_for_thread | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 1178 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_flush_thread()
| INT ss_shm_flush_thread | ( | void * | p | ) |
Definition at line 1138 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_shm_name()
|
static |
Definition at line 232 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_open()
| INT ss_shm_open | ( | const char * | name, |
| INT | size, | ||
| void ** | adr, | ||
| size_t * | shm_size, | ||
| HNDLE * | handle, | ||
| BOOL | get_size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 326 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_shm_protect()
Definition at line 1005 of file system.cxx.
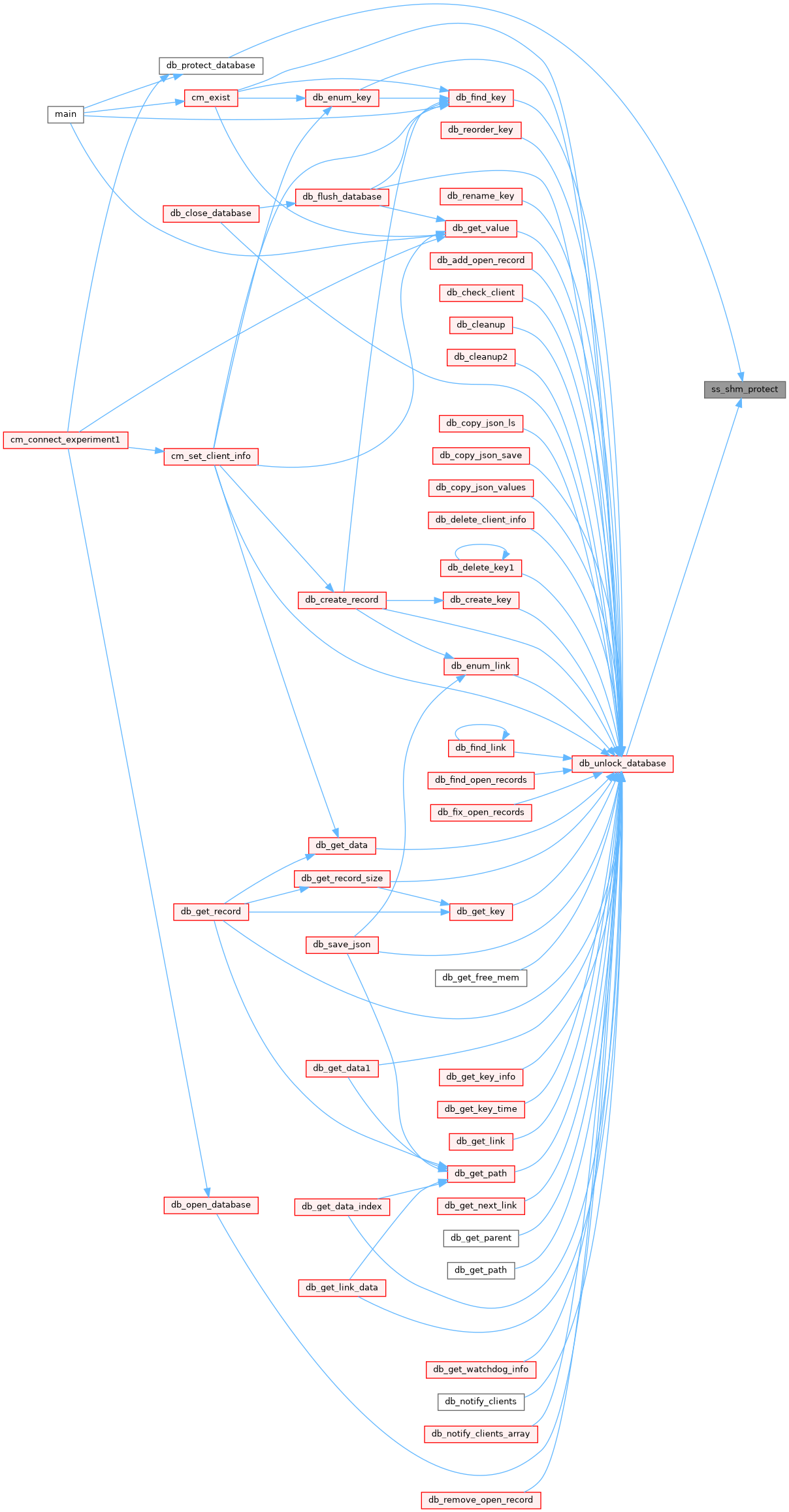
◆ ss_shm_unprotect()
| INT ss_shm_unprotect | ( | HNDLE | handle, |
| void ** | adr, | ||
| size_t | shm_size, | ||
| BOOL | read, | ||
| BOOL | write, | ||
| const char * | caller_name | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 1062 of file system.cxx.
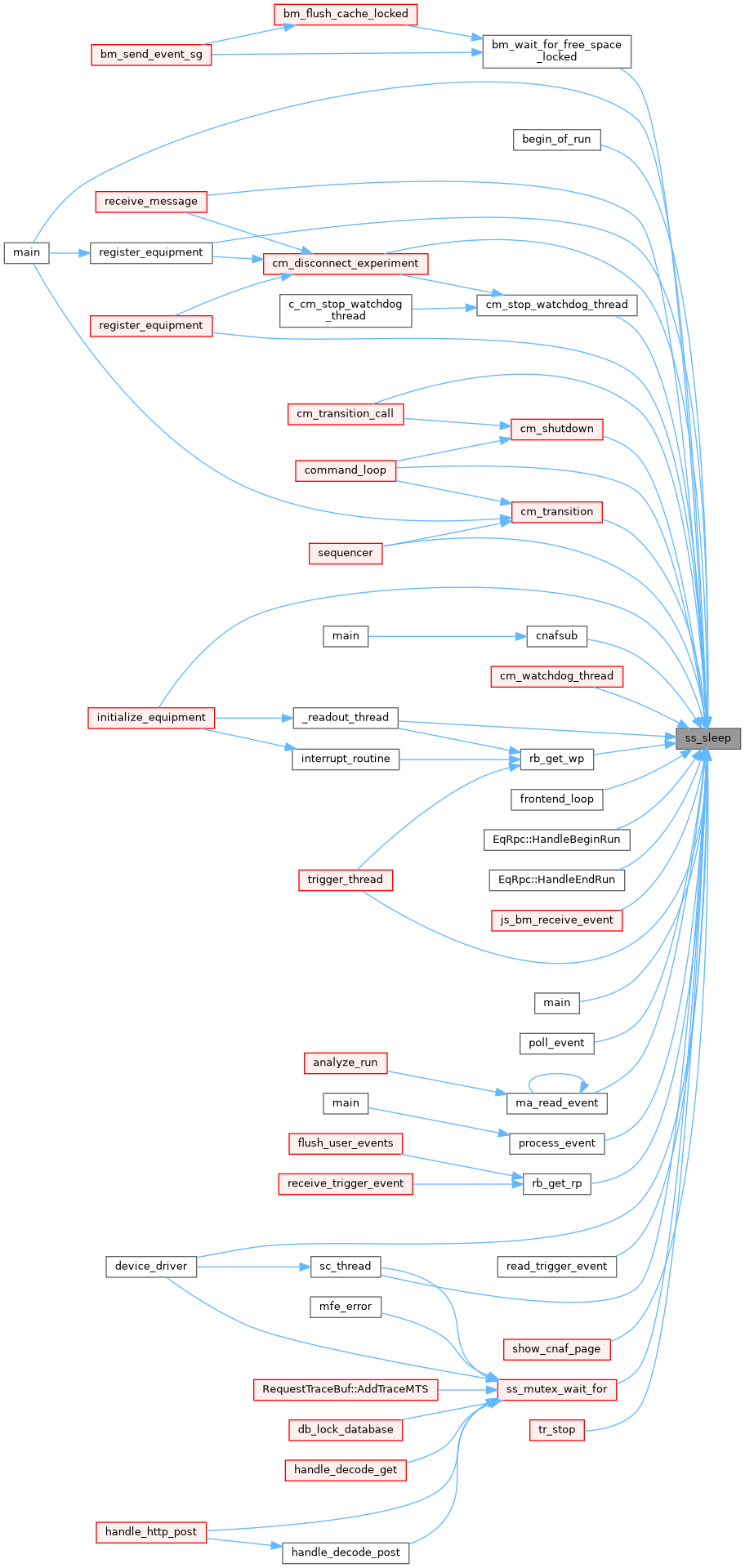
◆ ss_sleep()
Suspend the calling process for a certain time.
The function is similar to the sleep() function, but has a resolution of one milliseconds. Under VxWorks the resolution is 1/60 of a second. It uses the socket select() function with a time-out. See examples in ss_time()
- Parameters
-
millisec Time in milliseconds to sleep. Zero means infinite (until another process calls ss_wake)
- Returns
- SS_SUCCESS
Definition at line 3700 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_socket_check()
|
static |
Definition at line 4565 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_socket_close()
Definition at line 5303 of file system.cxx.
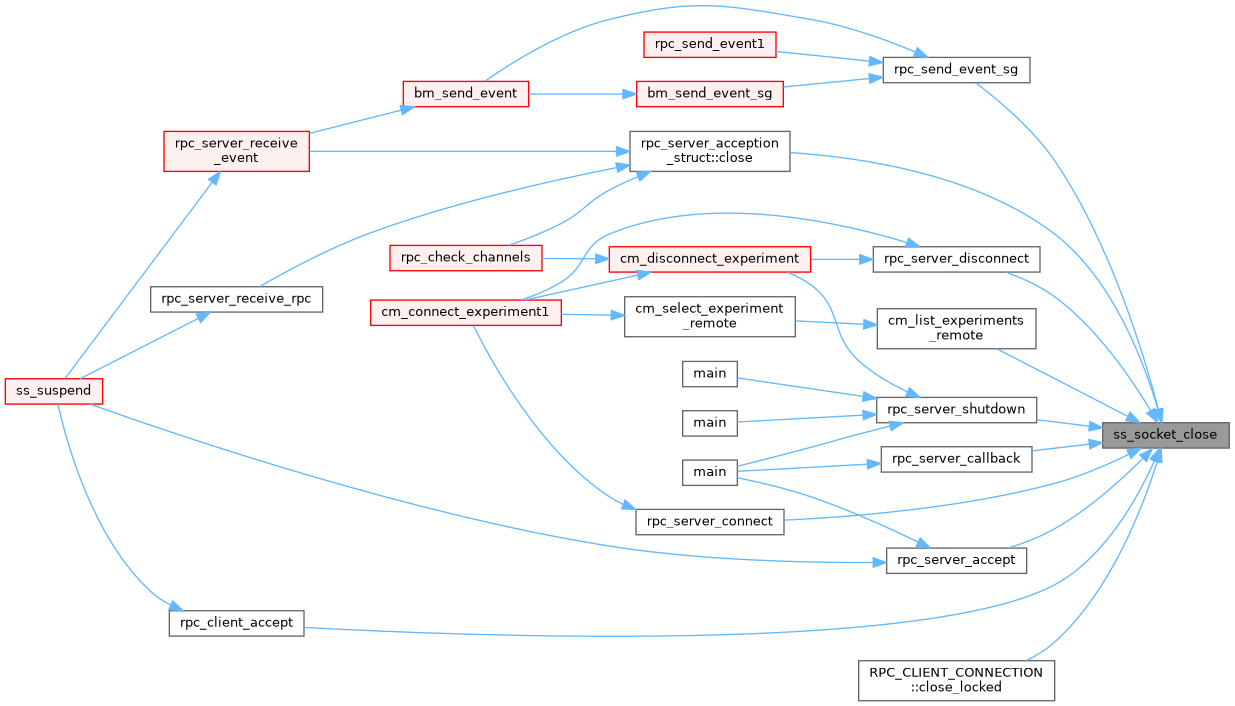
◆ ss_socket_connect_tcp()
| INT EXPRT ss_socket_connect_tcp | ( | const char * | hostname, |
| int | tcp_port, | ||
| int * | sockp, | ||
| std::string * | error_msg_p | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 5039 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_socket_get_peer_name()
Definition at line 5318 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_socket_listen_tcp()
| INT EXPRT ss_socket_listen_tcp | ( | bool | listen_localhost, |
| int | tcp_port, | ||
| int * | sockp, | ||
| int * | tcp_port_p, | ||
| std::string * | error_msg_p | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 5134 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_socket_wait()
Definition at line 4970 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_spawnv()
Definition at line 1702 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_stack_get()
Definition at line 8072 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_stack_history_dump()
| void EXPRT ss_stack_history_dump | ( | char * | filename | ) |
Definition at line 8122 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_stack_history_entry()
| void EXPRT ss_stack_history_entry | ( | char * | tag | ) |
Definition at line 8100 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_stack_print()
| void EXPRT ss_stack_print | ( | ) |
◆ ss_suspend()
- only watch the event tcp connection belonging to this thread */
Definition at line 4615 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_close()
|
static |
Definition at line 4279 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_exit()
| INT ss_suspend_exit | ( | ) |
Definition at line 4298 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_get_buffer_port()
| INT ss_suspend_get_buffer_port | ( | midas_thread_t | thread_id, |
| INT * | port | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 4425 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_get_odb_port()
Definition at line 4399 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_get_struct()
| SUSPEND_STRUCT * ss_suspend_get_struct | ( | midas_thread_t | thread_id | ) |
Definition at line 4237 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_init_odb_port()
| INT ss_suspend_init_odb_port | ( | ) |
Definition at line 4377 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_init_struct()
|
static |
Definition at line 4084 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_process_ipc()
Definition at line 4458 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_suspend_set_client_connection()
| INT ss_suspend_set_client_connection | ( | RPC_SERVER_CONNECTION * | connection | ) |
Definition at line 4363 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_set_client_listener()
| INT ss_suspend_set_client_listener | ( | int | listen_socket | ) |
Definition at line 4356 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_set_rpc_thread()
| INT ss_suspend_set_rpc_thread | ( | midas_thread_t | thread_id | ) |
Definition at line 4074 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_set_server_acceptions()
| INT ss_suspend_set_server_acceptions | ( | RPC_SERVER_ACCEPTION_LIST * | acceptions | ) |
Definition at line 4370 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_suspend_set_server_listener()
| INT ss_suspend_set_server_listener | ( | int | listen_socket | ) |
Definition at line 4349 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_system()
Execute command in a separate process, close all open file descriptors invoke ss_exec() and ignore pid.
- Parameters
-
command Command to execute.
- Returns
- SS_SUCCESS or ss_exec() return code
Definition at line 2188 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_close()
Definition at line 5980 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_fskip()
Definition at line 6310 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_tape_get_blockn()
Definition at line 6646 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_mount()
Definition at line 6534 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_open()
Definition at line 5889 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_read()
Definition at line 6170 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_rewind()
Definition at line 6426 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_rskip()
Definition at line 6370 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_tape_spool()
Definition at line 6478 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_status()
Definition at line 6024 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_unmount()
Definition at line 6590 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tape_write()
Definition at line 6110 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_tape_write_eof()
Definition at line 6244 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_thread_create()
| midas_thread_t EXPRT ss_thread_create | ( | INT(*)(void *) | thread_func, |
| void * | param | ||
| ) |
Creates and returns a new thread of execution.
Note the difference when calling from vxWorks versus Linux and Windows. The parameter pointer for a vxWorks call is a VX_TASK_SPAWN structure, whereas for Linux and Windows it is a void pointer. Early versions returned SS_SUCCESS or SS_NO_THREAD instead of thread ID.
Example for VxWorks
Example for Linux
- Parameters
-
(*thread_func) Thread function to create. param a pointer to a VX_TASK_SPAWN structure for vxWorks and a void pointer for Unix and Windows
- Returns
- the new thread id or zero on error
Definition at line 2382 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_thread_get_name()
| std::string ss_thread_get_name | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2516 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_thread_kill()
| INT EXPRT ss_thread_kill | ( | midas_thread_t | thread_id | ) |
Destroys the thread identified by the passed thread id. The thread id is returned by ss_thread_create() on creation.
- Parameters
-
thread_id the thread id of the thread to be killed.
- Returns
- SS_SUCCESS if no error, else SS_NO_THREAD
Definition at line 2455 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_thread_set_name()
Definition at line 2498 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_tid_to_string()
| std::string ss_tid_to_string | ( | midas_thread_t | thread_id | ) |
Definition at line 1643 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_time()
Returns the actual time in seconds since 1.1.1970 UTC.
- Returns
- Time in seconds
Definition at line 3534 of file system.cxx.
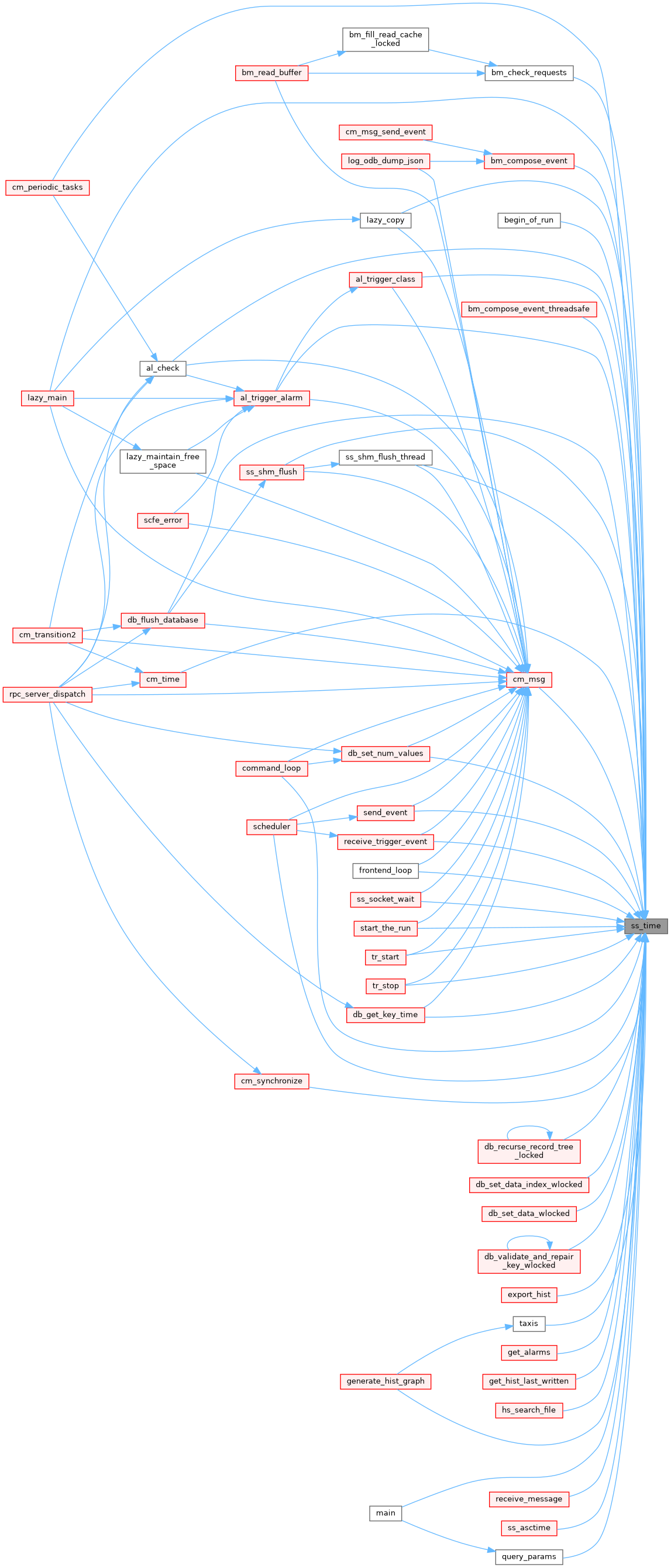
◆ ss_time_sec()
| double EXPRT ss_time_sec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3539 of file system.cxx.

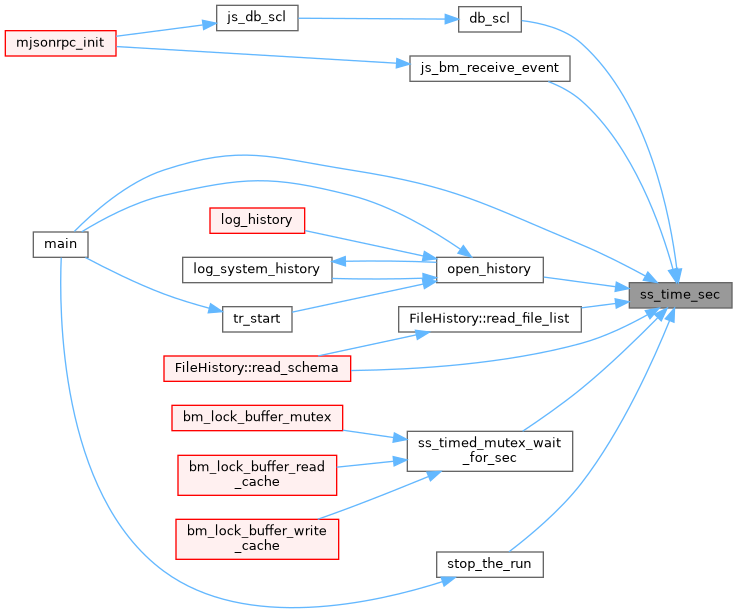
◆ ss_timed_mutex_wait_for_sec()
| bool EXPRT ss_timed_mutex_wait_for_sec | ( | std::timed_mutex & | mutex, |
| const char * | mutex_name, | ||
| double | timeout_sec | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 3337 of file system.cxx.
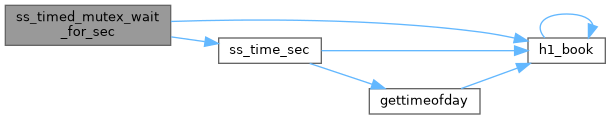
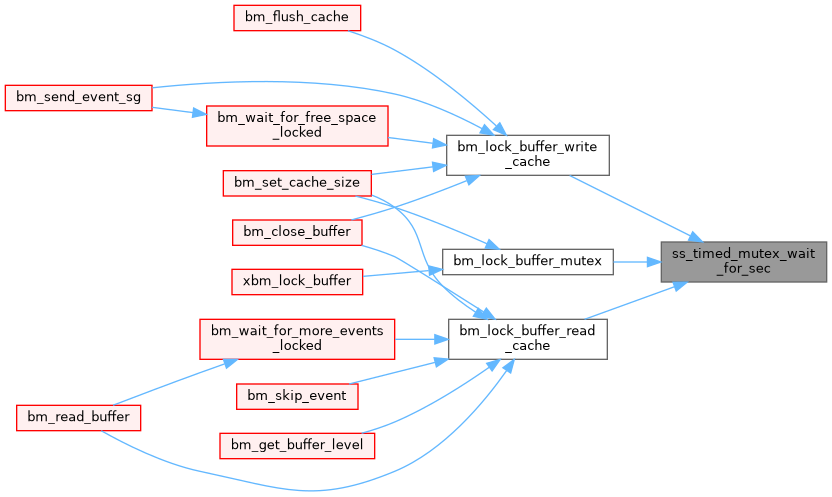
◆ ss_timezone()
Definition at line 3652 of file system.cxx.

◆ ss_tzset()
| void EXPRT ss_tzset | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3427 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_us_since()
| unsigned int ss_us_since | ( | std::chrono::time_point< std::chrono::high_resolution_clock > | start | ) |
Definition at line 8338 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_us_start()
| std::chrono::time_point< std::chrono::high_resolution_clock > ss_us_start | ( | ) |
Definition at line 8333 of file system.cxx.
◆ ss_write_tcp()
Definition at line 5424 of file system.cxx.
Variable Documentation
◆ _daemon_flag
|
static |
Definition at line 2071 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_client_connection
|
static |
Definition at line 4059 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_client_listen_socket
|
static |
Definition at line 4056 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_client_thread
|
static |
Definition at line 4058 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_listen_thread
|
static |
Definition at line 4054 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_odb_thread
|
static |
Definition at line 4051 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_server_acceptions
|
static |
Definition at line 4062 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_server_listen_socket
|
static |
Definition at line 4055 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_server_thread
|
static |
Definition at line 4061 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_suspend_odb
|
static |
Definition at line 4052 of file system.cxx.
◆ _ss_suspend_vector
|
static |
Definition at line 4049 of file system.cxx.
◆ [] [1/2]
| char { ... } ::c |
Definition at line 1312 of file system.cxx.
◆ [] [2/2]
| char { ... } ::c |
Definition at line 1318 of file system.cxx.
◆ [] [1/2]
| double { ... } ::d |
Definition at line 1313 of file system.cxx.
◆ [] [2/2]
| double { ... } ::d |
Definition at line 1317 of file system.cxx.
◆ gSocketTrace
|
static |
Definition at line 5036 of file system.cxx.
◆ gTzMutex
|
static |
Definition at line 3425 of file system.cxx.
◆ MidasExceptionHandler
| void(* MidasExceptionHandler) (void) | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 3861 of file system.cxx.
◆ s_semaphore_nest_level
|
static |
Definition at line 2530 of file system.cxx.
◆ s_semaphore_trace
|
static |
Definition at line 2529 of file system.cxx.
◆ stack_history
| char stack_history[N_STACK_HISTORY][80] |
Definition at line 8069 of file system.cxx.
◆ stack_history_pointer
| int stack_history_pointer = -1 |
Definition at line 8070 of file system.cxx.
◆ [struct]
| struct { ... } test_align |
◆ [struct]
| struct { ... } test_padding |