| ID |
Date |
Author |
Topic |
Subject |
|
817
|
26 Jun 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | midas vme benchmarks | > > > > I am recording here the results from a test VME system using four VF48
waveform digitizers
Last message from this series. After all the tuning, I reduce the trigger rate
from 120 Hz to 100 Hz to see
what happens when the backend computer is not overloaded and has some spare
capacity.
event rate: 100 Hz (down from 120 Hz)
data rate: 37 Mbytes/sec (down from 50 M/s)
mlogger cpu use: 65% (down from 99%)
Attached:
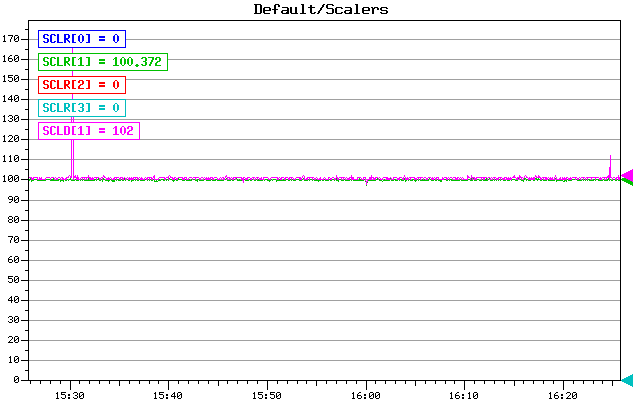
1) trigger rate event plot: now the rate is solid 100 Hz without dropouts
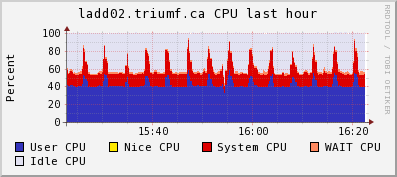
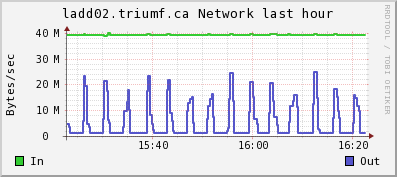
2) CPU and Network plots frog ganglia: the spikes is lazylogger saving mid.gz
files to HDFS storage
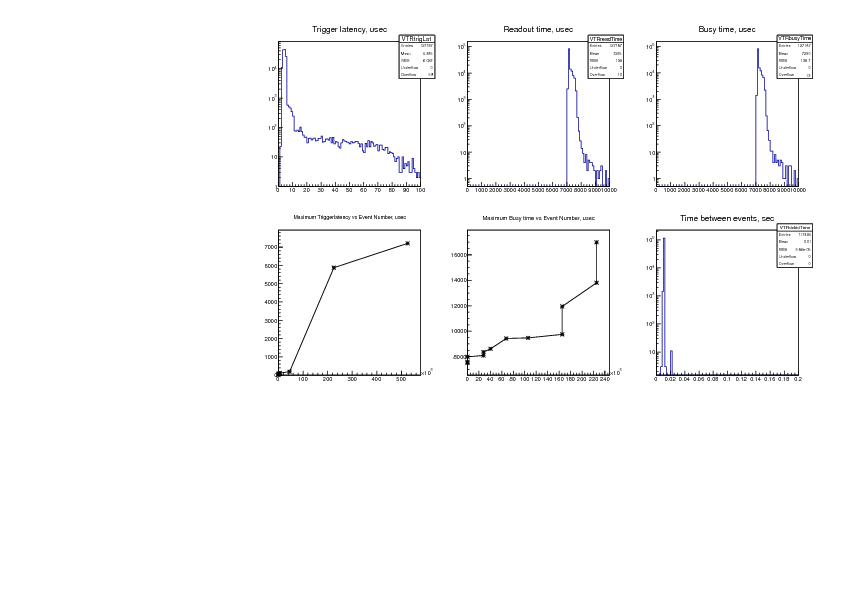
3) time structure plots:
a) trigger latency: mean 5 us, most below 10 us, 59 events (0.046%) longer than
100 us, (bottom left graph) 7000 us is longest latency observed.
b) readout time is 7000-8000 us (same as before - VME data rate is independant
from the trigger rate)
c) busy time: mean 7.2 us, 12 events (0.0094%) longer than 10 ms, longest busy
time ever observed is 17 ms (bottom middle graph)
d) time between events is 10 ms (100 Hz pulser trigger), 1 event was missed
about 10 times (spike at 20 ms) (0.0085%), more than 1 event missed never (no
spike at 30 ms, 40 ms, etc).
CPU use on the backend computer:
top - 16:30:59 up 75 days, 35 min, 6 users, load average: 0.98, 0.99, 1.01
Tasks: 206 total, 3 running, 203 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
Cpu(s): 39.3%us, 8.2%sy, 0.0%ni, 39.4%id, 5.7%wa, 0.3%hi, 7.2%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 3925556k total, 3404192k used, 521364k free, 8792k buffers
Swap: 32766900k total, 296304k used, 32470596k free, 2477268k cached
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
5826 trinat 20 0 441m 292m 287m R 65.8 7.6 2215:16 mlogger
26756 trinat 20 0 310m 288m 288m S 16.8 7.5 34:32.03 mserver
29005 olchansk 20 0 206m 39m 17m R 14.7 1.0 26:19.42 ana_vf48.exe
7878 olchansk 20 0 99m 3988 740 S 7.7 0.1 27:06.34 sshd
29012 trinat 20 0 314m 288m 288m S 2.8 7.5 4:22.14 mserver
23317 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 1.4 0.0 24:21.52 flush-9:3
K.O. |
| Attachment 1: Scalers.gif
|
|
| Attachment 2: ladd02-cpu.png
|
|
| Attachment 3: ladd02-net.png
|
|
| Attachment 4: canvas-1000-100Hz.pdf
|
|
|
818
|
29 Jun 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | lazylogger write to HADOOP HDFS | > Anyhow, the new lazylogger writes into HDFS just fine and I expect that it would also work for writing into
> DCACHE using PNFS (if ever we get the SL6 PNFS working with our DCACHE servers).
>
> Writing into our test HDFS cluster runs at about 20 MiBytes/sec for 1GB files with replication set to 3.
Minor update to lazylogger and mlogger:
lazylogger default timeout 60 sec is too short for writing into HDFS - changed to 10 min.
mlogger checks for free space were insufficient and it would fill the output disk to 100% full before stopping
the run. Now for disks bigger than 100GB, it will stop the run if there is less than 1GB of free space. (100%
disk full would break the history and the elog if they happen to be on the same disk).
Also I note that mlogger.cxx rev 5297 includes a fix for a performance bug introduced about 6 month ago (mlogger
would query free disk space after writing each event - depending on your filesystem configuration and the event
rate, this bug was observed to extremely severely reduce the midas disk writing performance).
svn rev 5296, 5297
K.O.
P.S. I use these lazylogger settings for writing to HDFS. Write speed varies around 10-20-30 Mbytes/sec (4-node
cluster, 3 replicas of each file).
[local:trinat_detfac:S]Settings>pwd
/Lazy/HDFS/Settings
[local:trinat_detfac:S]Settings>ls -l
Key name Type #Val Size Last Opn Mode Value
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Period INT 1 4 7m 0 RWD 10
Maintain free space (%) INT 1 4 7m 0 RWD 20
Stay behind INT 1 4 7m 0 RWD 0
Alarm Class STRING 1 32 7m 0 RWD
Running condition STRING 1 128 7m 0 RWD ALWAYS
Data dir STRING 1 256 7m 0 RWD /home/trinat/online/data
Data format STRING 1 8 7m 0 RWD MIDAS
Filename format STRING 1 128 7m 0 RWD run*
Backup type STRING 1 8 7m 0 RWD Disk
Execute after rewind STRING 1 64 7m 0 RWD
Path STRING 1 128 7m 0 RWD /hdfs/users/trinat/data
Capacity (Bytes) FLOAT 1 4 7m 0 RWD 5e+09
List label STRING 1 128 7m 0 RWD HDFS
Execute before writing file STRING 1 64 7m 0 RWD
Execute after writing file STRING 1 64 7m 0 RWD
Modulo.Position STRING 1 8 7m 0 RWD
Tape Data Append BOOL 1 4 7m 0 RWD y
K.O. |
|
819
|
04 Jul 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Crash after recursive use of rpc_execute() | I am looking at a MIDAS kaboom when running out of space on the data disk - everything was freezing
up, even the VME frontend crashed sometimes.
The freeze was traced to ROOT use in mlogger - it turns out that ROOT intercepts many signal handlers,
including SIGSEGV - but instead of crashing the program as God intended, ROOT SEGV handler just hangs,
and the rest of MIDAS hangs with it. One solution is to always build mlogger without ROOT support -
does anybody use this feature anymore? Or reset the signal handlers back to the default setting somehow.
Freeze fixed, now I see a crash (seg fault) inside mlogger, in the newly introduced memmove() function
inside the MIDAS RPC code rpc_execute(). memmove() replaced memcpy() in the same place and I am
surprised we did not see this crash with memcpy().
The crash is caused by crazy arguments passed to memmove() - looks like corrupted RPC arguments
data.
Then I realized that I see a recursive call to rpc_execute(): rpc_execute() calls tr_stop() calls cm_yield() calls
ss_suspend() calls rpc_execute(). The second rpc_execute successfully completes, but leave corrupted
data for the original rpc_execute(), which happily crashes. At the moment of the crash, recursive call to
rpc_execute() is no longer visible.
Note that rpc_execute() cannot be called recursively - it is not re-entrant as it uses a global buffer for RPC
argument processing. (global tls_buffer structure).
Here is the mlogger stack trace:
#0 0x00000032a8032885 in raise () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x00000032a8034065 in abort () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#2 0x00000032a802b9fe in __assert_fail_base () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#3 0x00000032a802bac0 in __assert_fail () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#4 0x000000000041d3e6 in rpc_execute (sock=14, buffer=0x7ffff73fc010 "\340.", convert_flags=0) at
src/midas.c:11478
#5 0x0000000000429e41 in rpc_server_receive (idx=1, sock=<value optimized out>, check=<value
optimized out>) at src/midas.c:12955
#6 0x0000000000433fcd in ss_suspend (millisec=0, msg=0) at src/system.c:3927
#7 0x0000000000429b12 in cm_yield (millisec=100) at src/midas.c:4268
#8 0x00000000004137c0 in close_channels (run_number=118, p_tape_flag=0x7fffffffcd34) at
src/mlogger.cxx:3705
#9 0x000000000041390e in tr_stop (run_number=118, error=<value optimized out>) at
src/mlogger.cxx:4148
#10 0x000000000041cd42 in rpc_execute (sock=12, buffer=0x7ffff73fc010 "\340.", convert_flags=0) at
src/midas.c:11626
#11 0x0000000000429e41 in rpc_server_receive (idx=0, sock=<value optimized out>, check=<value
optimized out>) at src/midas.c:12955
#12 0x0000000000433fcd in ss_suspend (millisec=0, msg=0) at src/system.c:3927
#13 0x0000000000429b12 in cm_yield (millisec=1000) at src/midas.c:4268
#14 0x0000000000416c50 in main (argc=<value optimized out>, argv=<value optimized out>) at
src/mlogger.cxx:4431
K.O. |
|
820
|
04 Jul 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | Crash after recursive use of rpc_execute() | > ... I see a recursive call to rpc_execute(): rpc_execute() calls tr_stop() calls cm_yield() calls
> ss_suspend() calls rpc_execute()
> ... rpc_execute() cannot be called recursively - it is not re-entrant as it uses a global buffer
It turns out that rpc_server_receive() also need protection against recursive calls - it also uses
a global buffer to receive network data.
My solution is to protect rpc_server_receive() against recursive calls by detecting recursion and returning SS_SUCCESS (to ss_suspend()).
I was worried that this would cause a tight loop inside ss_suspend() but in practice, it looks like ss_suspend() tries to call
us about once per second. I am happy with this solution. Here is the diff:
@@ -12813,7 +12815,7 @@
/********************************************************************/
-INT rpc_server_receive(INT idx, int sock, BOOL check)
+INT rpc_server_receive1(INT idx, int sock, BOOL check)
/********************************************************************\
Routine: rpc_server_receive
@@ -13047,7 +13049,28 @@
return status;
}
+/********************************************************************/
+INT rpc_server_receive(INT idx, int sock, BOOL check)
+{
+ static int level = 0;
+ int status;
+ // Provide protection against recursive calls to rpc_server_receive() and rpc_execute()
+ // via rpc_execute() calls tr_stop() calls cm_yield() calls ss_suspend() calls rpc_execute()
+
+ if (level != 0) {
+ //printf("*** enter rpc_server_receive level %d, idx %d sock %d %d -- protection against recursive use!\n", level, idx, sock, check);
+ return SS_SUCCESS;
+ }
+
+ level++;
+ //printf(">>> enter rpc_server_receive level %d, idx %d sock %d %d\n", level, idx, sock, check);
+ status = rpc_server_receive1(idx, sock, check);
+ //printf("<<< exit rpc_server_receive level %d, idx %d sock %d %d, status %d\n", level, idx, sock, check, status);
+ level--;
+ return status;
+}
+
/********************************************************************/
INT rpc_server_shutdown(void)
/********************************************************************\
ladd02:trinat~/packages/midas>svn info src/midas.c
Path: src/midas.c
Name: midas.c
URL: svn+ssh://svn@savannah.psi.ch/repos/meg/midas/trunk/src/midas.c
Repository Root: svn+ssh://svn@savannah.psi.ch/repos/meg/midas
Repository UUID: 050218f5-8902-0410-8d0e-8a15d521e4f2
Revision: 5297
Node Kind: file
Schedule: normal
Last Changed Author: olchanski
Last Changed Rev: 5294
Last Changed Date: 2012-06-15 10:45:35 -0700 (Fri, 15 Jun 2012)
Text Last Updated: 2012-06-29 17:05:14 -0700 (Fri, 29 Jun 2012)
Checksum: 8d7907bd60723e401a3fceba7cd2ba29
K.O. |
|
829
|
17 Aug 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | launching roody kills the analyzer | > I've installed midas (Rev:5294) on SLC6.3 (64bit), along with recent trunk versions of rootana and roody.
>
> #6 root_server_thread (arg=ox7f54fc001150) at src/mana.c:5154
You are connecting to mana, the old midas analyzer. The code for connecting to it is still present in roody,
but I cannot support the matching server code in mana.c - it is 2 revolutions behind the current state of
the ROOT object server (look in ROOTANA - the NetDirectory stuff and the latest is the XmlServer stuff).
I can offer 2 solutions - switch from mana.c to a ROOTANA based analyzer or graft the XmlServer code
into your analyzer (it is very simple - you need to create an XmlServer object and tell it which ROOT
containers you want to make visible to ROODY).
I guess you can also debug the old midas server code inside mana.c...
K.O. |
|
837
|
26 Sep 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | launching roody kills the analyzer | > >
> > I guess you can also debug the old midas server code inside mana.c...
> >
I ended up doing this. (After receiving some discussion by email).
Remembered that this is an old problem with the old midasServer network
protocol in mana.c - if mana.c is compiled 32-bit, it sends 32-bit pointers, if compiled 64-bit
it sends 64-bit pointers. On the receiving end (in roody), the ROOT TMessage object does not
provide any easy way to tell between them (i.e. object length is reported as 12 or 16 for the two cases).
To make things more interesting, the midasServer code in ROOTANA always sends 32-bit "pointers",
(which are not pointers but 32-bit integer cookies).
I use the ROOTANA midasServer to test ROODY (I have no working mana.c analyzers available),
and ROODY expects to receive 32-bit "pointers", so the two are consistent.
But if I compile my midasServer to send/receive 64-bit "pointers" (cookies), I reproduce this crash. What I can reproduce I can "fix".
If I change the code in ROODY to receive and return 64-bit "pointers" (cookies), both 32-bit and 64-bit midasServer seems to work okey.
This is committed as roody svn rev 248. (https://ladd00.triumf.ca/svn/roody/trunk)
It is the same fix as suggested by Cheng-Ju Stephen Lin [cjslin@lbl.gov].
I hope this helps (or breaks the ROODY midasServer connection for everybody. I hope not).
K.O. |
|
843
|
13 Dec 2012 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Report | ss_thread_kill() kills entire program | > Hi, I'm having some trouble getting ss_thread_kill() to work properly. It seems
> to kill the entire program instead of just the thread.
You cannot kill a thread. It's not a well defined operation. Most OSes do have the
technical possibility to kill threads, but if you use them, you will not like the
results. For a taste of small trouble, if a thread is holding a lock and you kill
it, who's job is it to release the lock?
The best you can do is to ask the thread to gracefully shutdown itself. (I.e. by
using global variable flags).
P.S. I did not implement the ss_thread stuff, I do not know what ss_thread_kill()
does, but I recommend that you do not use it.
P.P.S. Programming using threads is complicated, I recommend that you read at least
some literature on the topic before using threads. At the least you must understand
the common pitfalls and mistakes. At the least, you must know about deadlocks,
livelocks, race conditions and semaphore priority inversions.
K.O. |
|
854
|
24 Jan 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Compression benchmarks | In the DEAP experiment, the normal MIDAS mlogger gzip compression is not fast enough for some data
taking modes, so I am doing tests of other compression programs. Here is the results.
Executive summary:
fastest compression is no compression (cat at 1800 Mbytes/sec - memcpy speed), next best are:
"lzf" at 300 Mbytes/sec and "lzop" at 250 Mbytes/sec with 50% compression
"gzip -1" at around 70 Mbytes/sec with around 70% compression
"bzip2" at around 12 Mbytes/sec with around 80% compression
"pbzip2", as advertised, scales bzip2 compression linearly with the number of CPUs to 46 Mbytes/sec (4
real CPUs), then slower to a maximum 60 Mbytes/sec (8 hyper-threaded CPUs).
This confirms that our original choice of "gzip -1" method for compression using zlib inside mlogger is
still a good choice. bzip2 can gain an additional 10% compression at the cost of 6 times more CPU
utilization. lzo/lzf can do 50% compression at GigE network speed and at "normal" disk speed.
I think these numbers make a good case for adding lzo/lzf compression to mlogger.
Comments about the data:
- time measured is the "elapsed" time of the compression program. it excludes the time spent flushing
the compressed output file to disk.
- the relevant number is the first rate number (input data rate)
- test machine has 32GB of RAM, so all I/O is cached, disk speed does not affect these results
- "cat" gives a measure of overall machine "speed" (but test file is too small to give precise measurement)
- "gzip -1" is the recommended MIDAS mlogger compression setting
- "pbzip2 -p8" uses 8 "hyper-threaded" CPUs, but machine only has 4 "real" CPU cores
<pre>
cat : time 0.2s, size 431379371 431379371, comp 0%, rate 1797M/s 1797M/s
cat : time 0.6s, size 1013573981 1013573981, comp 0%, rate 1809M/s 1809M/s
cat : time 1.1s, size 2027241617 2027241617, comp 0%, rate 1826M/s 1826M/s
gzip -1 : time 6.4s, size 431379371 141008293, comp 67%, rate 67M/s 22M/s
gzip : time 30.3s, size 431379371 131017324, comp 70%, rate 14M/s 4M/s
gzip -9 : time 94.2s, size 431379371 133071189, comp 69%, rate 4M/s 1M/s
gzip -1 : time 15.2s, size 1013573981 347820209, comp 66%, rate 66M/s 22M/s
gzip -1 : time 29.4s, size 2027241617 638495283, comp 69%, rate 68M/s 21M/s
bzip2 -1 : time 34.4s, size 431379371 91905771, comp 79%, rate 12M/s 2M/s
bzip2 : time 33.9s, size 431379371 86144682, comp 80%, rate 12M/s 2M/s
bzip2 -9 : time 34.2s, size 431379371 86144682, comp 80%, rate 12M/s 2M/s
pbzip2 -p1 : time 34.9s, size 431379371 86152857, comp 80%, rate 12M/s 2M/s (1 CPU)
pbzip2 -p1 -1 : time 34.6s, size 431379371 91935441, comp 79%, rate 12M/s 2M/s
pbzip2 -p1 -9 : time 34.8s, size 431379371 86152857, comp 80%, rate 12M/s 2M/s
pbzip2 -p2 : time 17.6s, size 431379371 86152857, comp 80%, rate 24M/s 4M/s (2 CPU)
pbzip2 -p3 : time 11.9s, size 431379371 86152857, comp 80%, rate 36M/s 7M/s (3 CPU)
pbzip2 -p4 : time 9.3s, size 431379371 86152857, comp 80%, rate 46M/s 9M/s (4 CPU)
pbzip2 -p4 : time 45.3s, size 2027241617 384406870, comp 81%, rate 44M/s 8M/s
pbzip2 -p8 : time 33.3s, size 2027241617 384406870, comp 81%, rate 60M/s 11M/s
lzop -1 : time 1.6s, size 431379371 213416336, comp 51%, rate 261M/s 129M/s
lzop : time 1.7s, size 431379371 213328371, comp 51%, rate 249M/s 123M/s
lzop : time 4.3s, size 1013573981 515317099, comp 49%, rate 234M/s 119M/s
lzop : time 7.3s, size 2027241617 978374154, comp 52%, rate 277M/s 133M/s
lzop -9 : time 176.6s, size 431379371 157985635, comp 63%, rate 2M/s 0M/s
lzf : time 1.4s, size 431379371 210789363, comp 51%, rate 299M/s 146M/s
lzf : time 3.6s, size 1013573981 523007102, comp 48%, rate 282M/s 145M/s
lzf : time 6.7s, size 2027241617 972953255, comp 52%, rate 303M/s 145M/s
lzma -0 : time 27s, size 431379371 112406964, comp 74%, rate 15M/s 4M/s
lzma -1 : time 35s, size 431379371 111235594, comp 74%, rate 12M/s 3M/s
lzma: > 5 min, killed
xz -0 : time 28s, size 431379371 112424452, comp 74%, rate 15M/s 4M/s
xz -1 : time 35s, size 431379371 111252916, comp 74%, rate 12M/s 3M/s
xz: > 5 min, killed
</pre>
Columns are:
compression program
time: elapsed time of the compression program (excludes the time to flush output file to disk)
size: size of input file, size of output file
comp: compression ration (0%=no compression, 100%=file compresses into nothing)
rate: input data rate (size of input file divided by elapsed time), output data rate (size of output file
divided by elapsed time)
Machine used for testing (from /proc/cpuinfo):
Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3820 CPU @ 3.60GHz
quad core cpu with hyper-threading (8 CPU total)
32 GB quad-channel DDR3-1600.
Script used for testing:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
my $x = join(" ", @ARGV);
my $in = "test.mid";
my $out = "test.mid.out";
my $tout = "test.time";
my $cmd = "/usr/bin/time -o $tout -f \"%e\" /usr/bin/time $x < test.mid > test.mid.out";
print $cmd,"\n";
my $t0 = time();
system $cmd;
my $t1 = time();
my $c = `cat $tout`;
print "Elapsed time: $c";
my $t = $c;
#system "/bin/ls -l $in $out";
my $sin = -s $in;
my $sout = -s $out;
my $xt = $t1-$t0;
$xt = 1 if $xt<1;
print "Total time: $xt\n";
print sprintf("%-20s: time %5.1fs, size %12d %12d, comp %3.0f%%, rate %3dM/s %3dM/s", $x, $t, $sin,
$sout, 100*($sin-$sout)/$sin, ($sin/$t)/1e6, ($sout/$t)/1e6), "\n";
exit 0;
# end
Typical output:
[deap@deap00 pet]$ ./r.perl lzf
/usr/bin/time -o test.time -f "%e" /usr/bin/time lzf < test.mid > test.mid.out
1.27user 0.15system 0:01.44elapsed 99%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 2800maxresident)k
0inputs+411704outputs (0major+268minor)pagefaults 0swaps
Elapsed time: 1.44
Total time: 3
lzf : time 1.4s, size 431379371 210789363, comp 51%, rate 299M/s 146M/s
K.O. |
|
863
|
13 Feb 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Review of github and bitbucket | I have done a review of github and bitbucket as candidates for hosting GIT repositories for collaborative
DAQ-type projects. Here is my impressions.
1. GIT as a software management tool seems to be a reasonable choice for DAQ-type projects. "master"
repositories can be hosted at places like github or self-hosted (in the simplest case, only
http://host/~user web access is required to host a git repository), for each "daq project" aka "experiment"
one would "clone" the master repository, perform any local modifications as required, with full local
version control, and when desired feed the changes back to the master repository as direct commits (git
push), as patches posted to github ("pull requests") or patches emailed to the maintainers (git format-
patch).
2. Modern requirements for hosting a DAQ-type project include:
a) code repository (GIT, etc) with reasonably easy user access control (i.e. commit privileges should be
assigned by the project administrators directly, regardless of who is on the payroll at which lab or who is
a registered user of CERN or who is in some LDAP database managed by some IT departement
somewhere).
b) a wiki for documentation, with similar user access control requirements.
c) a mailing list, forum or bug tracking system for communication and "community building"
d) an ability to web host large static files (schematics, datasheets, firmware files, etc)
e) reasonable web-based tools for browsing the files, looking at diffs, "cvs annotate/git blame", etc.
3. Both github and bitbucket satisfy most of these requirements in similar ways:
a) GIT repositories:
aa) access using git, ssh and https with password protection. ssh keys can be uploaded to the server,
permitting automatic commits from scripts and cron jobs.
bb) anonymous checkout possible (cannot be disabled)
cc) user management is simple: participants have to self-register, confirm their email address, the project
administrator to gives them commit access to specific git repositories (and wikis).
dd) for the case of multiple project administrators, one creates "teams" of participants. In this
configuration the repositories are owned by the "team" and all designated "team administrators" have
equal administrative access to the project.
b) Wiki:
aa) both github and bitbucket provide rudimentary wikis, with wiki pages stored in secondary git
repositories (*NOT* as a branch or subdirectory of the main repo).
bb) github supports "markdown" and "mediawiki" syntax
cc) bitbucket supports "markdown" and "creole" syntax (all documentation and examples use the "creole"
syntax).
dd) there does not seem to be any way to set the "project standard" syntax - both wikis have the "new
page" editor default to the "markdown" syntax.
ee) compared to mediawiki (wikipedia, triumf daq wiki) and even plone, both github and bitbucket wikis
lack important features:
1) cannot edit individual sections of a page, only the whole page at once, bad if you have long pages.
2) cannot upload images (and other documents) directly through the web editor/interface. Both wikis
require that you clone the wiki git repository, commit image and other files locally and push the wiki git
repo into the server (hopefully without any collisions), only then you can use the images and documents
in the wiki.
3) there is no "preview" function for images - in mediawiki I can have small size automatically generated
"preview" images on the wiki page, when I click on them I get the full size image. (Even "elog" can do this!)
ff) to be extra helpful, the wiki git repository is invisible to the normal git repository graphical tools for
looking at revisions, branches, diffs, etc. While github has a special web page listing all existing wiki
pages, bitbucket does not have such a page, so you better write down the filenames on a piece of paper.
c) mailing list/forum/bug tracking:
aa) both github and bitbucket implement reasonable bug tracking systems (but in both systems I do not
see any button to export the bug database - all data is stuck inside the hosting provider. Perhaps there is
a "hidden button" somewhere).
bb) bitbucket sends quite reasonable email notifications
cc) github is silent, I do not see any email notifications at all about anything. Maybe github thinks I do not
want to see notices about my own activities, good of it to make such decisions for me.
d) hosting of large files: both git and wiki functions can host arbitrary files (compared to mediawiki only
accepting some file types, i.e. Quartus pof files are rejected).
e) web based tools: thumbs up to both! web interfaces are slick and responsive, easy to use.
Conclusions:
Both github and bitbucket provide similar full-featured git repository hosting, user management and bug
tracking.
Both provide very rudimentary wiki systems. Compared to full featured wikis (i.e. mediawiki), this is like
going back to SCCS for code management (from before RCS, before CVS, before SVN). Disappointing. A
deal breaker if my vote counts.
K.O. |
|
866
|
08 Mar 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | ODB /Experiment/MAX_EVENT_SIZE | Somebody pointed out an error in the MIDAS documentation regarding maximum event size
supported by MIDAS and the MAX_EVENT_SIZE #define in midas.h.
Since MIDAS svn rev 4801 (August 2010), one can create events with size bigger than
MAX_EVENT_SIZE in midas.h (without having to recompile MIDAS):
To do so, one must increase:
- the value of ODB /Experiment/MAX_EVENT_SIZE
- the size of the SYSTEM shared memory event buffer (and any buffers used by the event builder,
etc)
- max_event_size & co in your frontend.
Actual limits on the bank size and event size are written up here:
https://ladd00.triumf.ca/elog/Midas/757
The bottom line is that the maximum event size is limited by the size of the SYSTEM buffer which is
limited by the physical memory of your computer. No recompilation of MIDAS necessary.
K.O. |
|
868
|
02 Apr 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Review of github and bitbucket | Hi, thanks for your positive feedback. I have been using git for small private projects for a few years now
and I like it. It is similar to the old SCCS days - good version control without having to setup servers,
accounts, doodads, etc.
> * No central repo. Have all the history with you on the train.
> * Branching and merging, with stable branches and feature branches.
> Happy hacking while my students do analysis on a stable version.
> Or multiple development branches for several features.
This is the part that worries me the most. Without a "central" "authoritative" repository,
in just a few quick days, everybody will have their own incompatible version of midas.
I guess I am okey with your private midas diverging from mainstream, but when *I* end up
with 10 different incompatible versions just in *my* repository, can that be good?
> And merging really works, including fixing up merge conflicts.
But somebody still has to do it. With a central repository, the problem takes care of
itself - each developer has to do their own merging - with svn, you cannot commit
to the head without merging the head into your code first. But with git, I can just throw
my changes int some branch out there hoping that somebody else would do the merging.
But guess what, there aint anybody home but us chickens. We do not have a mad finn here
to enforce discipline and keep us in shape...
As an example, look at the HADOOP/HDFS code development, they have at least 3 "mainstream"
branches going, neither has all the features combined together and each branch has bugs with
the fixes in a different branch. What a way to run a railroad.
> * "git bisect" for finding which commit introduced a (reproducible) bug.
> * "gitk --all"
>
> Go for git. :-)
Absolutely. For me, as soon as I can wrap my head around this business of "who does all the merging".
K.O. |
|
872
|
05 Apr 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | ODB JSON support | odbedit can now save ODB in JSON-formatted files. (JSON is a popular data encoding standard associated
with Javascript). The intent is to eventually use the ODB JSON encoder in mhttpd to simplify passing of
ODB data to custom web pages. In mhttpd I also intend to support the JSON-P variation of JSON (via the
jQuery "callback=?" notation).
JSON encoding implementation follows specifications at:
http://json.org/
http://www.json-p.org/
http://api.jquery.com/jQuery.getJSON/ (seek to JSONP)
The result passes validation by:
http://jsonlint.com/
Added functions:
INT EXPRT db_save_json(HNDLE hDB, HNDLE hKey, const char *file_name);
INT EXPRT db_copy_json(HNDLE hDB, HNDLE hKey, char **buffer, int *buffer_size, int *buffer_end, int
save_keys, int follow_links);
For example of using this code, see odbedit.c and odb.c::db_save_json().
Example json file:
Notes:
1) hex numbers are quoted "0x1234" - JSON does not permit "hex numbers", but Javascript will
automatically convert strings containing hex numbers into proper integers.
2) "double" is encoded with full 15 digit precision, "float" with full 7 digit precision. If floating point values
are actually integers, they are encoded as integers (10.0 -> "10" if (value == (int)value)).
3) in this example I deleted all the "name/key" entries except for "stringvalue" and "sbyte2". I use the
"/key" notation for ODB KEY data because the "/" character cannot appear inside valid ODB entry names.
Normally, depending on the setting of "save_keys" argument, KEY data is present or absent for all entries.
ladd03:midas$ odbedit
[local:testexpt:S]/>cd /test
[local:testexpt:S]/test>save test.js
[local:testexpt:S]/test>exit
ladd03:midas$ more test.js
# MIDAS ODB JSON
# FILE test.js
# PATH /test
{
"test" : {
"intarr" : [ 15, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 9 ],
"dblvalue" : 2.2199999999999999e+01,
"fltvalue" : 1.1100000e+01,
"dwordvalue" : "0x0000007d",
"wordvalue" : "0x0141",
"boolvalue" : true,
"stringvalue" : [ "aaa123bbb", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "" ],
"stringvalue/key" : {
"type" : 12,
"num_values" : 10,
"item_size" : 1024,
"last_written" : 1288592982
},
"byte1" : 10,
"byte2" : 241,
"char1" : "1",
"char2" : "-",
"sbyte1" : 10,
"sbyte2" : -15,
"sbyte2/key" : {
"type" : 2,
"last_written" : 1365101364
}
}
}
svn rev 5356
K.O. |
|
874
|
11 Apr 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Forum | Persistent ipcrm error | > [system.c:308:ss_shm_open,ERROR] Shared memory segment with key 0x4d008002 already exists,
please remove it manually: ipcrm -M 0x4d008002
> [midas.c:1950:cm_connect_experiment1,ERROR] cannot open database
> Unexpected error #304
For the record, the SYSV shared memory with it's keys and segments has always been brittle and hard to
debug with problems such as you describe.
Also SYSV shared memory suffers from key aliasing - shared memory segments created with different
names all map into the same key, collide and nothing works. You may not see this if all the files are
located on a local disk, but if the .SHM files are located on an NFS disk, it can happen (and did happen in
T2K).
For this reason, since around August 2010, MIDAS also implements the POSIX shared memory and for new
MIDAS installations, POSIX shared memory is the default. (On MacOS, POSIX shared memory was always
the default because MacOS has very small maximum SYSV shared memory size).
The type of shared memory is set by the contents of .SHM_TYPE.TXT and it is possible to switch between
SYSV and POSIX shared memory at will. (Ask me).
MIDAS still uses SYSV semaphores because they have a built-in feature to automatically unlock the
semaphore if the program that locked it dies for any reason. POSIX semaphores do not have this built-in
feature and we would have to implement some kind of detection and recovery for the case when a
semaphore is locked by a program that died (and will never unlock it back).
K.O.
P.S. I will address the rest of Prof. Thorsten's question in a private email.
P.P.S. Please post elog messages in the "plain" format. NOT HTML or ELCODE. |
|
881
|
30 Apr 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | ROOT switched to GIT | Latest news - the ROOT project switched from SVN to GIT.
Announcement:
http://root.cern.ch/drupal/content/root-has-moved-git
Fons's presentation with details on the conversion process, repository size and performance
improvements:
https://indico.cern.ch/getFile.py/access?contribId=0&resId=0&materialId=slides&confId=246803
"no switch yard" work flow:
http://root.cern.ch/drupal/content/suggested-work-flow-distributed-projects-nosy
GIT cheat sheet:
http://root.cern.ch/drupal/content/git-tips-and-tricks
K.O. |
|
882
|
06 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Recent-ish SVN changes at PSI | A little while ago, PSI made some changes to the SVN hosting. The main SVN URL seems to remain the
same, but SVN viewer moved to a new URL (it seems a bit faster compared to the old viewer):
https://savannah.psi.ch/viewvc/meg_midas/trunk/
Also the SSH host key has changed to:
savannah.psi.ch,192.33.120.96 ssh-rsa
AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAwVWEoaOmF9uggkUEV2/HhZo2ncH0zUfd0ExzzgW1m0HZQ5df1OYIb
pyBH6WD7ySU7fWkihbt2+SpyClMkWEJMvb5W82SrXtmzd9PFb3G7ouL++64geVKHdIKAVoqm8yGaIKIS0684
dyNO79ZacbOYC9l9YehuMHPHDUPPdNCFW2Gr5mkf/uReMIoYz81XmgAIHXPSgErv2Nv/BAA1PCWt6THMMX
E2O2jGTzJCXuZsJ2RoyVVR4Q0Cow1ekloXn/rdGkbUPMt/m3kNuVFhSzYGdprv+g3l7l1PWwEcz7V1BW9LNPp
eIJhxy9/DNUsF1+funzBOc/UsPFyNyJEo0p0Xw==
Fingerprint: a3:18:18:c4:14:f9:3e:79:2c:9c:fa:90:9a:d6:d2:fc
The change of host key is annoying because it makes "svn update" fail with an unhelpful message (some
mumble about ssh -q). To fix this fault, run "ssh svn@savannah.psi.ch", then fixup the ssh host key as
usual.
K.O. |
|
883
|
06 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | TRIUMF MIDAS page moved to DAQWiki | The MIDAS web page at TRIUMF (http://midas.triumf.ca) moved from the daq-plone site to the DAQWiki
(MediaWiki) site. Links were updated, checked and corrected:
https://www.triumf.info/wiki/DAQwiki/index.php/MIDAS
Included is the link to our MIDAS installation instructions. These are more complete compared to the
instructions in the MIDAS documentation:
https://www.triumf.info/wiki/DAQwiki/index.php/Setup_MIDAS_experiment
K.O. |
|
884
|
07 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Updated: javascript custom page examples | I updated the MIDAS javascript examples in examples/javascript1. All existing mhttpd.js functions are
now exampled. (yes).
Here is the full list of functions, with notes:
ODBSet(path, value, pwdname);
ODBGet(path, format, defval, len, type);
ODBMGet(paths, callback, formats); --- doc incomplete - no example of callback() use
ODBGetRecord(path);
ODBExtractRecord(record, key);
new ODBKey(path); --- doc incomplete, wrong - one has to use "new ODBKey" - last_used was added.
ODBCopy(path, format); -- no doc
ODBRpc_rev0(name, rpc, args); --- doc refer to example
ODBRpc_rev1(name, rpc, max_reply_length, args); --- same
ODBGetMsg(n);
ODBGenerateMsg(m);
ODBGetAlarms(); --- no doc
ODBEdit(path); --- undoc - forces page reload
As annotated, the main documentation is partially incomplete and partially wrong (i.e. ODBKey() has to be
invoked as "new ODBKey()"). I hope this will be corrected soon. In the mean time, I recommend that
everybody uses this example as best documentation available.
http://ladd00.triumf.ca/~daqweb/doc/midas/html/RC_mhttpd_custom_js_lib.html
svn rev 5360
K.O. |
|
885
|
10 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Bug Fix | Fixed: crash if alarm "write elog message" is enabled | If the MIDAS Alarm property "write elog message" is enabled, an uninitialized variable "tag" is passed to
el_submit() and depending on your luck, cause a crash. "tag" is supposed to be and is now a NUL-
terminated string. The only other use of el_submit() is in mhttpd.cxx and mserver.c, where it is called
correctly.
alarm.c svn rev 5361
K.O. |
|
886
|
10 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | mhttpd JSON support | > odbedit can now save ODB in JSON-formatted files.
> Added functions:
> INT EXPRT db_save_json(HNDLE hDB, HNDLE hKey, const char *file_name);
> INT EXPRT db_copy_json(HNDLE hDB, HNDLE hKey, char **buffer, int *buffer_size, int *buffer_end, int save_keys, int follow_links);
>
Added JSON encoding format to Javascript ODBCopy() ("jcopy"). Use format="json", Javascript example updated with an example example.
Also updated db_copy_json():
- always return NUL-terminated string
- "save_keys" values: 0 - do not save any KEY data, 1 - save all KEY data, 2 - save only KEY.last_written
odb.c, mhttpd.cxx, example.html
svn rev 5362
K.O. |
|
887
|
10 May 2013 |
Konstantin Olchanski | Info | Updated: javascript custom page examples | > ODBCopy(path, format); -- no doc
Updated example of ODBCopy:
format="" returns data in traditional ODB save format
format="xml" returns data in XML encoding
format="json" returns data in JSON encoding.
K.O. |
|