 17 Sep 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Added mserver host based access control 17 Sep 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Added mserver host based access control
|
In svn rev 4825, I added host based access control to mserver (the MIDAS RPC server). The implementation
is a verbatim copy mhttpd host based access control list (-a command line switch).
Same as for mhttpd, "mserver -a hostname" enables access control and only permits access from listed
host names (supply multiple -a switches for multiple hostnames).
This access control does not apply yet for the MIDAS RPC socket connections between MIDAS clients used
to do RPC callbacks, i.e. to request run transitions. Each MIDAS program is listening for MIDAS RPC
connections on a high TCP port and at present accepts connections from anybody. To implement access
controls one could add "-a" switches to every midas application (lot of work) or fill the access control list
automatically from ODB. mserver still has to use the "-a" command line switches because there is no ODB
connection when it has to accept or reject remote sockets.
svn rev 4825
K.O. |
 04 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default 04 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default
|
As of svn rev 4800, YBOS support was made optional, disabled by default. (But note that ybos.c is still used
by mdump). See HAVE_YBOS in the Makefile.
K.O. |
 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default
|
> As of svn rev 4800, YBOS support was made optional, disabled by default. (But note that ybos.c is still used
> by mdump). See HAVE_YBOS in the Makefile.
It looks like some example drivers in .../drivers/class want to link against YBOS libraries. This fails because ybos.o is missing from the MIDAS library.
After discussions with SR and PAA, we think YBOS support can be removed or made optional, but there are too many of these drivers for me to fix
them all right now in five minutes. Please accept my apology and use these workarounds:
If you get linker errors because of missing YBOS functions:
1) enable YBOS suport in the Makefile (uncomment HAVE_YBOS=1), or
2) "#ifdef HAVE_YBOS" all places that call YBOS functions
Solution (2) is preferable as it permits us to eventually remove YBOS completely. If you fix files from MIDAS svn, please do send me patches or diffs (or
post them here).
K.O. |
 08 Sep 2010, Stefan Ritt, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default 08 Sep 2010, Stefan Ritt, Info, YBOS support now optional, disabled by default
|
> It looks like some example drivers in .../drivers/class want to link against YBOS libraries.
> This fails because ybos.o is missing from the MIDAS library.
I fixed the class drivers in meantime (SVN 4814).
There is however another problem: The lazylogger needs YBOS support compiled in if the FTP transfer mode is used.
At PSI we are stuck at the moment to FTP, so we still need YBOS there (although none of the data is in YBOS format).
Maybe there is a chance that this will be fixed some time and we can get rid of YBOS. |
 30 Jul 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, macos 10.6 success 30 Jul 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, macos 10.6 success
|
As of svn rev 4794, midas builds, runs and should be fully usable on MacOS 10.6.4. Previous revisions did
not compile due to assorted Linuxisms and did not run because of a sizeof() problem in ss_gettid(). Also
one of the system header files (mtio.h?) present in MacOS 10.5 vanished from 10.6.
Please continue reporting all problems with midas on macos to this forum.
K.O. |
 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, macos 10.6 success 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, macos 10.6 success
|
> As of svn rev 4794, midas builds, runs and should be fully usable on MacOS 10.6.4. Previous revisions did
> not compile due to assorted Linuxisms and did not run because of a sizeof() problem in ss_gettid(). Also
> one of the system header files (mtio.h?) present in MacOS 10.5 vanished from 10.6.
It turns out that on MacOS 10.6 the default maximum SYSV shared memory size is about 2 Mbytes, too small even for the default MIDAS SYSTEM
event buffer.
Svn revision 4807 implements POSIX shared memory, which does not seem to have such a small size limit and makes it the default on MacOS.
This update fixes the last issue that I am aware of for running MIDAS on MacOS.
svn rev 4807
K.O. |
 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Experimental POSIX shared memory support 31 Aug 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Experimental POSIX shared memory support
|
As of svn rev 4807, src/system.c has an experimental implementation of POSIX shared memory. It is
similar to the already existing implementation of MMAP shared memory, but uses POSIX shm_open()
instead of directly mmapping the .xxx.SHM file.
There are several benefits to using POSIX shared memory:
1) on MacOS, the (unchangable?) maximum SYSV shared memory is about 2 Mbytes, too small for most
MIDAS experiments. POSIX shared memory does not seem to have such a limit;
2) on Linux, when using SYSV shared memory, the .xxx.SHM files are tied to the shared memory keys
using ftok(). If the .xxx.SHM files are located on an NFS-mounted filesystem, ftok() has been observed
to malfunction and return the same key for different shared memory buffers, causing mighty confusing
behaviour of MIDAS. (while "man ftok" discusses a theoretical possibility for such collisions, I have
observed ftok() collisions first hand on a running experiment and it cost us several hours to understand
why all the events go into the wrong event buffers). The present POSIX shared memory implementation
does not have such a problem.
This implementation has received limited testing on Linux and MacOS, and it is now the default shared
memory implementation on MacOS. Linux continues to use SYSV shared memory (ipcs & co). Windows
uses it's own implementation of shared memory (same as mmap, the best I can tell).
svn 4807
K.O. |
 24 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 24 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
Dear All,
This is my first time running an experiment on separate computers. I followed
the documentation (https://midas.psi.ch/htmldoc/quickstart.html) to setup the
files:
/etc/services
/etc/xinetd.d/midas
/etc/ld.so.conf
/etc/exptab
but when I started the frontend program in the front-end computer I got the
following error (computerB is my back-end):
[midas.c:8623:rpc_server_connect,ERROR] mserver subprocess could not be started
(check path)
[mfe.c:2573:mainFE,ERROR] Cannot connect to experiment '' on host 'computerB',
status 503
In both front-end and back-end computers only a file '.SYSMSG.SHM' was created
after the attempt. If I start the frontend program somewhere in the back-end
computer by connecting to 'localhost', seven .SHM files are created in the
experiment directory together with a .RPC.SHM in the directory where I run the
frontend program.
Is that I misconfigure something? I cannot find a solution...
Thanks.
Best Regards,
Jimmy |
 26 Jun 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 26 Jun 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
> This is my first time running an experiment on separate computers. I followed
> the documentation (https://midas.psi.ch/htmldoc/quickstart.html) to setup the
> files:
> /etc/services
> /etc/xinetd.d/midas
Hi, there. I have not recently run mserver through inetd, and we usually do not do
that at TRIUMF. We do this:
a) on the main computer: start mserver: "mserver -p 7070 -D" (note - use non-default
port - can use different ports for different experiments)
b) on remote computer: "odbedit -h main:7070" ("main" is the hostname of your main
computer). Use same "-h" switch for all other programs, including the frontends.
This works well when all computers are on the same network, but if you have some
midas clients running on private networks you may get into trouble when they try to
connect to each other and fail because network routing is funny.
K.O. |
 27 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 27 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
> Hi, there. I have not recently run mserver through inetd, and we usually do not do
> that at TRIUMF. We do this:
>
> a) on the main computer: start mserver: "mserver -p 7070 -D" (note - use non-default
> port - can use different ports for different experiments)
> b) on remote computer: "odbedit -h main:7070" ("main" is the hostname of your main
> computer). Use same "-h" switch for all other programs, including the frontends.
>
> This works well when all computers are on the same network, but if you have some
> midas clients running on private networks you may get into trouble when they try to
> connect to each other and fail because network routing is funny.
Hi K.O.,
Thanks for your reply. I have tried your way but I got the same error:
[midas.c:8623:rpc_server_connect,ERROR] mserver subprocess could not be started
(check path)
My front-end and back-end computers are on the same network connected by a router. I
have allowed port 7070 in the firewall and done the port forwarding in the router (for
connecting from outside the network). From the error message it seems that some
processes can not be started automatically. Could it be related to some security
settings such as the SELinux?
Best Regards,
Jimmy |
 28 Jun 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 28 Jun 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
> > Hi, there. I have not recently run mserver through inetd, and we usually do not do
> > that at TRIUMF. We do this:
> >
> > a) on the main computer: start mserver: "mserver -p 7070 -D" (note - use non-default
> > port - can use different ports for different experiments)
> > b) on remote computer: "odbedit -h main:7070" ("main" is the hostname of your main
> > computer). Use same "-h" switch for all other programs, including the frontends.
> >
> > This works well when all computers are on the same network, but if you have some
> > midas clients running on private networks you may get into trouble when they try to
> > connect to each other and fail because network routing is funny.
>
> Hi K.O.,
>
> Thanks for your reply. I have tried your way but I got the same error:
>
> [midas.c:8623:rpc_server_connect,ERROR] mserver subprocess could not be started
> (check path)
>
> My front-end and back-end computers are on the same network connected by a router. I
> have allowed port 7070 in the firewall and done the port forwarding in the router (for
> connecting from outside the network). From the error message it seems that some
> processes can not be started automatically. Could it be related to some security
> settings such as the SELinux?
The way connections work under Midas is there is a callback scheme. The client starts
mserver on the back-end, then the back-end connects back to the front-end on three
different ports. These ports are assigned dynamically by the operating system and are
typically in the range 40000-60000. So you also have to allow the reverse connection on
your firewalls. |
 28 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 28 Jun 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
> The way connections work under Midas is there is a callback scheme. The client starts
> mserver on the back-end, then the back-end connects back to the front-end on three
> different ports. These ports are assigned dynamically by the operating system and are
> typically in the range 40000-60000. So you also have to allow the reverse connection on
> your firewalls.
It works now after allowing ports 40000-60000 in the front-end computer. Thanks!
Best Regards,
Jimmy |
 29 Jun 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer 29 Jun 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Forum, Error connecting to back-end computer
|
> > The way connections work under Midas is there is a callback scheme. The client starts
> > mserver on the back-end, then the back-end connects back to the front-end on three
> > different ports. These ports are assigned dynamically by the operating system and are
> > typically in the range 40000-60000. So you also have to allow the reverse connection on
> > your firewalls.
>
> It works now after allowing ports 40000-60000 in the front-end computer. Thanks!
Yes, right. Midas networking does not like firewalls.
In the nutshell, TCP connections on all TCP ports have to be open between all computers
running MIDAS. I think in practice it is not a problem: you only ever have a finite (a small
integer) number of computers running MIDAS and you can be added them as exceptions to the
firewall rules. These exceptions should not create any security problem because you still have
the MIDAS computers firewalled from the outside world and one hopes that they will not be
attacking each other.
P.S. Permitting ports 40000-60000 is not good enough. TCP ports are allocated to TCP
connections semi-randomly from a 16-bit address space (0..65535) and your system will bomb
whenever port numbers like 39999 or 60001 get used.
K.O. |
 12 Jun 2010, hai qu, Forum, crash on start run 12 Jun 2010, hai qu, Forum, crash on start run
|
Dear experts,
I use fedora 12 and midas 4680. there is problem to start run when the frontend
application runs fine.
# odbedit -c start
Starting run #18
[midas.c:8423:rpc_client_connect,ERROR] timeout on receive remote computer info:
[midas.c:3659:cm_transition,ERROR] cannot connect to client
"feTPCPacketReceiver" on host tpcdaq0, port 36663, status 503
[midas.c:8423:rpc_client_connect,ERROR] timeout on receive remote computer info:
[midas.c:4880:cm_shutdown,ERROR] Cannot connect to client 'frontend' on host
'hostname', port 36663
[midas.c:4883:cm_shutdown,ERROR] Killing and Deleting client
'feTPCPacketReceiver' pid 24516
[midas.c:3857:cm_transition,ERROR] Could not start a run: cm_transition() status
503, message 'Cannot connect to client 'frontend''
Run #18 start aborted
Error: Cannot connect to client 'frontend'
11:03:42 [Logger,INFO] Deleting previous file "/home/daq/Run/online/run00018.mid"
11:03:42 [Logger,INFO] Client 'feTPCPacketReceiver' on buffer 'SYSMSG' removed
by cm_watchdog because client pid 24516 does not exist
11:03:42 [Logger,ERROR] [system.c:563:ss_shm_close,ERROR]
shmctl(shmid=7274511,IPC_RMID) failed, errno 1 (Operation not permitted)
11:03:42 [ODBEdit,INFO] Run #18 start aborted
==========================================================================
there are several ethernet cards on the host machine. eth0 connect the host
machine to the gateway machine and the front end application listen to eth1 for
the incoming data packets:
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
inet addr:10.0.1.1 Bcast:10.0.1.63 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::f6ce:46ff:fe99:709b/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:470870 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:515987 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:345000246 (329.0 MiB) TX bytes:377269124 (359.7 MiB)
Interrupt:17
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
inet addr:10.0.1.2 Bcast:10.255.255.255 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::226:55ff:fed6:56a9/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:15 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:1836 (1.7 KiB)
Memory:ec180000-ec1a0000
thanks for hints |
 14 Jun 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, crash on start run 14 Jun 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, crash on start run
|
> I use fedora 12 and midas 4680. there is problem to start run when the frontend
> application runs fine.
I don't know exactly what is wrong, but I would check following things:
- does your feTCPPacketReceiver die during the start-of-run? Maybe you do some segfault
int he begin-of-run routine. Can you STOP a run?
- is there any network problem due to your two cards? When you try to stop your fe from
odbedit with
# odbedit -c "shutdown feTCPPacketReceiver"
do you then get the same error? The shutdown functionality uses the same RPC channel as
the start/stop run. Some people had firewall problems, on both sides (host AND client),
so make sure all firewalls are disabled.
- if you disable one network card, do you still get the same problem? |
 14 Jun 2010, hai qu, Forum, crash on start run 14 Jun 2010, hai qu, Forum, crash on start run
|
> - does your feTCPPacketReceiver die during the start-of-run? Maybe you do some segfault
> int he begin-of-run routine. Can you STOP a run?
when start a run, it bring the mtransition process and I guess the server try to talk to the
client, then it fails and the frontend application get killed since not response.
>> When you try to stop your fe from
> odbedit with # odbedit -c "shutdown feTCPPacketReceiver"
it gets
[midas.c:8423:rpc_client_connect,ERROR] timeout on receive remote computer info:
[midas.c:4880:cm_shutdown,ERROR] Cannot connect to client
"feTPCPacketReceiver" on host 'tpcdaq0', port 35865
[midas.c:4883:cm_shutdown,ERROR] Killing and Deleting client
'feTPCPacketReceiver' pid 27250
Client feTPCPacketReceiver not active
what does this error mean? :
11:03:42 [Logger,ERROR] [system.c:563:ss_shm_close,ERROR]
shmctl(shmid=7274511,IPC_RMID) failed, errno 1 (Operation not permitted)
thanks
hai
p.s. that code runs fine on my laptop with ubuntu 9, so that also be possible that somewhere
my configuration not right to cause problem |
 08 Jun 2010, nicholas, Forum, check out from svn 08 Jun 2010, nicholas, Forum, check out from svn
|
do: svn co svn+ssh://svn@savannah.psi.ch/afs/psi.ch/project/meg/svn/midas/trunk
midas
shows: ssh: connect to host savannah.psi.ch port 22: Connection timed out
svn: Connection closed unexpectedly |
 08 Jun 2010, nicholas, Forum, check out from svn 08 Jun 2010, nicholas, Forum, check out from svn
|
> do: svn co svn+ssh://svn@savannah.psi.ch/afs/psi.ch/project/meg/svn/midas/trunk
> midas
> shows: ssh: connect to host savannah.psi.ch port 22: Connection timed out
> svn: Connection closed unexpectedly
sorry, my side network problem.
N. |
 22 Apr 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Customized "Start" page 22 Apr 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Customized "Start" page
|
Dear All,
After clicking the "Start" button, there is a page for the operator to change some
ODB values. I have created "/Experiment/Edit on start" and added some links there.
If the link is pointed to a boolean type key, a check box will appear in the
"Start" page, which is great. But how about if I want to have some radio buttons
or pull-down menus for the operator to select among different calibration sources
or running modes?
Thanks,
Jimmy |
 08 Apr 2010, Exaos Lee, Forum, How to stop a run with a timer? 08 Apr 2010, Exaos Lee, Forum, How to stop a run with a timer?
|
I want to let the run stop and start periodically. But I looked through the ODB
and didn't find anything may help. I also checked the FAQ online and didn't find
answer either. Who can help me? Thank you. |
 22 Apr 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, How to stop a run with a timer? 22 Apr 2010, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, How to stop a run with a timer?
|
Hi Exaos,
This may help: https://ladd00.triumf.ca/elog/Midas/645
You need to set the following keys:
/Logger/Run duration
/Logger/Auto restart
/Logger/Auto restart delay
Regards,
Jimmy
> I want to let the run stop and start periodically. But I looked through the ODB
> and didn't find anything may help. I also checked the FAQ online and didn't find
> answer either. Who can help me? Thank you. |
 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, New '/Experiment/Menu buttons' 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, New '/Experiment/Menu buttons'
|
The mhttpd program shows some standard buttons in the top row for
starting/stopping runs, accessing the ODB, Alarms, etc. Since not all experiments
make use of all buttons, they have been customized. By default mhttpd creates
following entry in the ODB:
/Experiment/Menu Buttons = Start, ODB, Messages, ELog, Alarms, Programs, History,
Config, Help
Which is the standard set (except the old CNAF). People can customize this now by
removing unnecessary buttons or by changing their order. The "Start" entry above
actually causes the whole set of Start/Stop/Pause/Resume buttons to appear,
depending on the current run state. |
 11 Mar 2010, Stefan Ritt, Info, New '/Experiment/Menu buttons' 11 Mar 2010, Stefan Ritt, Info, New '/Experiment/Menu buttons'
|
> The mhttpd program shows some standard buttons in the top row for
> starting/stopping runs, accessing the ODB, Alarms, etc. Since not all experiments
> make use of all buttons, they have been customized. By default mhttpd creates
> following entry in the ODB:
>
> /Experiment/Menu Buttons = Start, ODB, Messages, ELog, Alarms, Programs, History,
> Config, Help
>
> Which is the standard set (except the old CNAF). People can customize this now by
> removing unnecessary buttons or by changing their order. The "Start" entry above
> actually causes the whole set of Start/Stop/Pause/Resume buttons to appear,
> depending on the current run state.
Upon request the set of Menu Buttons has been extended to
/Experiment/Menu Buttons = Start, Pause, ODB, Messages, ELog, Alarms, Programs,
History, Config, Help
by adding the additional "Pause" string. Without "Pause" being present in the list of
menu buttons, the run cannot be paused/resumed, but only started/stopped. This is
required by some experiments. If "/Experiment/Menu Buttons" is not present in the ODB,
it gets created with the above default. If it is there from the previous update, the
"Pause" string might be missing, so it must be added by hand if required. The
modification is committed as revision #4684. |
 04 Mar 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Notes on MIDAS Alarm system 04 Mar 2010, Konstantin Olchanski, Info, Notes on MIDAS Alarm system
|
Notes on the implementation of the MIDAS alarm system.
Alarms are checked inside alarm.c::al_check(). This function is called by
cm_yield() every 10 seconds and by rpc_server_thread(), also every 10 seconds.
For remote midas clients, their al_check() issues an RPC_AL_CHECK RPC call into
the mserver, where rpc_server_dispatch() calls the local al_check().
As result, all alarm checks run inside a process directly attached to the local
midas shared memory (inside a local client or inside an mserver process for a
remote client).
Each and every midas client runs the alarm checks. To prevent race conditions
between different midas clients, access to al_check() is serialized using the
ALARM semaphore.
Inside al_check(), alarms are triggered using al_trigger_alarm(), which in turn
calls al_trigger_class(). Inside al_trigger_class(), the alarm is recorded into
an elog or into midas.log using cm_msg(MTALK).
Special note should be made of the ODB setting "/Alarm/Classes/xxx/System
message interval", which has a surprising effect - after an alarm is recorded
into system messages (using cm_msg(MTALK)), no record is made of any subsequent
alarms until the time interval set by this variable elapses. With default value
of 60 seconds, after one alarm, no more alarms are recorded for 60 seconds.
Also, because all the alarms are checked at the same time, only the first
triggered alarm will be recorded.
As of alarm.c rev 4683, "System message interval" set to 0 ensures that every
alarm is recorded into the midas log file. (In previous revisions, this setting
may still miss some alarms).
There are 3 types of alarms:
1) "program not running" alarms.
These alarms are enabled in ODB by setting "/Programs/ppp/Alarm class". Each
time al_check() runs, every program listed in "/Programs" is tested using
"cm_exist()" and if the program is not running, the time of first failure is
remembered in "/Programs/ppp/First failed".
If the program has not been running for longer than the time set in ODB
"/Programs/ppp/Check interval", an alarm is triggered (if enabled by
"/Programs/ppp/Alarm class" and the program is restarted (if enabled by
"/Programs/ppp/Auto restart").
The "not running" condition is tested every 10 seconds (each time al_check() is
called), but the frequency of "program not running" alarms can be reduced by
increasing the value of "/Alarms/Alarms/ppp/Check interval" (default value 60
seconds). This can be useful if "System message interval" is set to zero.
2) "evaluated" alarms
3) "periodic" alarms
There is nothing surprising in these alarms. Each alarm is checked with a time
period set by "/Alarm/xxx/Check interval". The value of an evaluated alarm is
computed using al_evaluate_condition().
K.O. |
 27 Jan 2010, Suzannah Daviel, Forum, custom page - flashing filled area 27 Jan 2010, Suzannah Daviel, Forum, custom page - flashing filled area
|
Hi,
On a custom web page, can a "filled" area be made to flash (i.e. cycle between
two colours)? This area would have to update faster than the whole page update.
I have a custom page representing a gas system, and the users
want the heaters to flash when they are on, as is done in their EPICS page.
Thanks,
Suzannah |
 09 Feb 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, custom page - flashing filled area 09 Feb 2010, Stefan Ritt, Forum, custom page - flashing filled area   
|
| One possibility is to use small GIF images for each valve, which have several frames (called 'animated GIF'). Depending on the state you can use a static GIF or the flashing GIF. An alternate approach is to use a static background image, and display a valve with different color on top of the background in regular intervals using JavaScript. I tried that with the attached page. Just create a custom page
/Custom/Valve = valve.html
and put all three attachments into your mhttpd directory. The JavaScript displays the red valve on top of the background with a 3 Hz frequency. The only trick is to position the overlay image exactly on top of the background image. This is done using the 'absolute' position in the style sheet. It needs a bit playing to find the proper position, but then it works fine. |
 01 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Redesign of status page links 01 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Redesign of status page links 
|
The custom and alias links in the standard midas status page were shown as HTML
links so far. If there are many links with names having spaces in their names,
it's a bit hard to distinguish between them. Therefore, they are packed now into
individual buttons (see attachment) starting from SVN revision 4633 on. This makes
also the look more homogeneous. If there is any problem with that, please report. |
 22 Dec 2009, Suzannah Daviel, Suggestion, Redesign of status page links 22 Dec 2009, Suzannah Daviel, Suggestion, Redesign of status page links
|
> The custom and alias links in the standard midas status page were shown as HTML
> links so far. If there are many links with names having spaces in their names,
> it's a bit hard to distinguish between them. Therefore, they are packed now into
> individual buttons (see attachment) starting from SVN revision 4633 on. This makes
> also the look more homogeneous. If there is any problem with that, please report.
Would you consider using a different colour for the alias buttons (or background
colour)? At present it's hard to know whether a button is an alias link, a custom page
link or a user-button especially if you are not familiar with the button layout. |
 11 Jan 2010, Stefan Ritt, Suggestion, Redesign of status page links 11 Jan 2010, Stefan Ritt, Suggestion, Redesign of status page links 
|
> > The custom and alias links in the standard midas status page were shown as HTML
> > links so far. If there are many links with names having spaces in their names,
> > it's a bit hard to distinguish between them. Therefore, they are packed now into
> > individual buttons (see attachment) starting from SVN revision 4633 on. This makes
> > also the look more homogeneous. If there is any problem with that, please report.
>
> Would you consider using a different colour for the alias buttons (or background
> colour)? At present it's hard to know whether a button is an alias link, a custom page
> link or a user-button especially if you are not familiar with the button layout.
Ok, I changed the background colors for the button rows. There are now four different
colors: Main menu buttons, Scripts, Manually triggered events, Alias & Custom pages. Hope
this is ok. Of course one could have each button in a different color, but then it gets
complicated... In that case I would recommend to make a dedicated custom page with all these
buttons, which you can then tailor exactly to your needs. |
 12 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, New MSCB page implementation 12 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, New MSCB page implementation 
|
A new page has been implemented in mhttpd. This allows web access to all devices from an MSCB system and their variables:
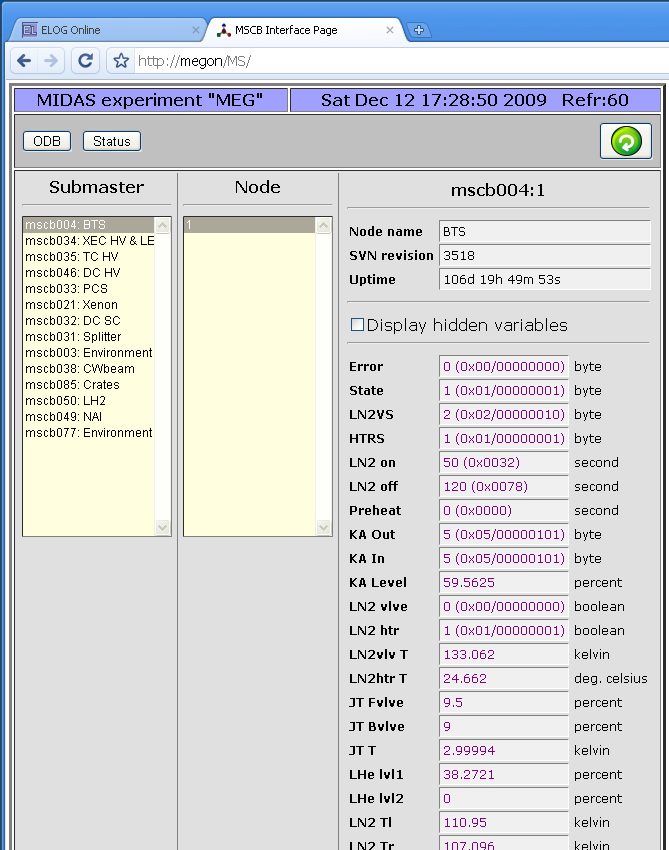
All you need to turn on the magic is to add a -DHAVE_MSCB to your Makefile for mhttpd. This is now the default in the Makefile from SVN, but it can be taken out for experiments not using MSCB. If it's present, mhttpd is linked against midas/mscb/mscb.c and gets direct access to all mscb ethernet submasters (USB access is currently disabled on purpose there). To show the MSCB button on the status page, you need following ODB entry:
/Experiment/Menu Buttons = Start, ODB, Messages, ELog, Alarms, Programs, History, MSCB, Config, Help
containing the "MSCB" entry in the list. If there is no "Menu Buttons" entry present in the ODB, mhttpd will create the above one, if it's compile with the -DHAVE_MSCB flag.
The MSCB page use the ODB Tree /MSCB/Submasters/... to get a list of all available submasters:
[local:MEG:R]/MSCB>ls -r
MSCB
Submaster
mscb004
Pwd xxxxx
Comment BTS
Address 1
mscb034
Pwd xxxxx
Comment XEC HV & LED
Address
0
1
2
Each submaster tree contains an optional password needed by that submaster, an optional comment (which just gets displayed on the 'Submaster' list on the web page), and an array of node addresses.
These trees can be created by hand, but they are also created automatically by mhttpd if the /MSCB/Submaster entry is not present in the ODB. In this case, the equipment list is scanned and all MSCB devices and addresses are collected from locations such as
/Equipment/<name>/Settings/Devices/Input/Device
or
/Equipment/<name>/Settings/Devices/<name>/MSCB Device
which are the locations for MSCB submasters used by the mscbdev.c and mscbhvr.c device drivers. Once the tree is created, it does not get touched again by mhttpd, so one can remove or reorder devices by hand.
The new system is currently successfully used at PSI, but I cannot guarantee that there are not issues. So in case of problems don't hesitate to contact me. |
 06 Nov 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 06 Nov 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host
|
Dear All,
I want to run two frontend programs (one for trigger and one for slow control)
concurrently on the same computer, but I failed. The second frontend said:
Semaphore already present
There is another process using the semaphore.
Or a process using the semaphore exited abnormally.
In That case try to manually release the semaphore with:
ipcrm sem XXX.
The two frontends are connected to the same experiment. Is there any way I can
overcome this problem?
Thanks!
Jimmy |
 27 Nov 2009, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 27 Nov 2009, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host
|
> Dear All,
>
> I want to run two frontend programs (one for trigger and one for slow control)
> concurrently on the same computer, but I failed. The second frontend said:
>
> Semaphore already present
> There is another process using the semaphore.
> Or a process using the semaphore exited abnormally.
> In That case try to manually release the semaphore with:
> ipcrm sem XXX.
>
> The two frontends are connected to the same experiment. Is there any way I can
> overcome this problem?
That might be related to the RPC mutex, which gets created system wide now. I
modified this in midas.c rev. 4628, so there will be one mutex per process. Can you
try that temporary patch and tell me if it works for you? |
 07 Dec 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 07 Dec 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host
|
Dear Stefan,
Thanks for the reply. I have tried your patch and it didn't solve my problem. Maybe I
have not written my question clearly. The two frontends could run on the same computer
if I use the remote method, i.e. by setting up the mserver and connect to the
experiment by specifying "-h localhost", also the frontend programs need to be put in
different directory. What I want to know is whether I can simply start multiple
frontends in the same directory without setting up the mserver etc. I noticed that
there are several *.SHM files, I'm not familiar with semaphore, but I guess they are
the key to the problem. Please correct me if I misunderstood something.
Best Regards,
Jimmy
> > Dear All,
> >
> > I want to run two frontend programs (one for trigger and one for slow control)
> > concurrently on the same computer, but I failed. The second frontend said:
> >
> > Semaphore already present
> > There is another process using the semaphore.
> > Or a process using the semaphore exited abnormally.
> > In That case try to manually release the semaphore with:
> > ipcrm sem XXX.
> >
> > The two frontends are connected to the same experiment. Is there any way I can
> > overcome this problem?
>
> That might be related to the RPC mutex, which gets created system wide now. I
> modified this in midas.c rev. 4628, so there will be one mutex per process. Can you
> try that temporary patch and tell me if it works for you? |
 08 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 08 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 
|
Hi Jimmy,
ok, now I understand. Well, I don't see your problem. I just tried with the
current SVN
version to start
midas/examples/experiment/frontend
midas/examples/slowcont/scfe
in the same directory (without "-h localhost") and it works just fine (see
attachemnt). I even started them from the same directory. Yes there are *.SHM
files and they correspond to shared memory, but both front-ends use this shared
memory together (that's why it's called 'shared').
Your error message 'Semaphore already present' is strange. The string is not
contained in any midas program, so it must come from somewhere else. Do you
maybe try to access the same hardware with the two front-end programs?
I would propose you do the following: Use the two front-ends from the
distribution (see above). They do not access any hardware. See if you can run
them with the current SVN version of midas. If not, report back to me.
Best regards,
Stefan
> Dear Stefan,
>
> Thanks for the reply. I have tried your patch and it didn't solve my problem.
Maybe I
> have not written my question clearly. The two frontends could run on the same
computer
> if I use the remote method, i.e. by setting up the mserver and connect to the
> experiment by specifying "-h localhost", also the frontend programs need to be
put in
> different directory. What I want to know is whether I can simply start
multiple
> frontends in the same directory without setting up the mserver etc. I noticed
that
> there are several *.SHM files, I'm not familiar with semaphore, but I guess
they are
> the key to the problem. Please correct me if I misunderstood something.
>
> Best Regards,
> Jimmy
>
>
> > > Dear All,
> > >
> > > I want to run two frontend programs (one for trigger and one for slow
control)
> > > concurrently on the same computer, but I failed. The second frontend said:
> > >
> > > Semaphore already present
> > > There is another process using the semaphore.
> > > Or a process using the semaphore exited abnormally.
> > > In That case try to manually release the semaphore with:
> > > ipcrm sem XXX.
> > >
> > > The two frontends are connected to the same experiment. Is there any way I
can
> > > overcome this problem?
> >
> > That might be related to the RPC mutex, which gets created system wide now.
I
> > modified this in midas.c rev. 4628, so there will be one mutex per process.
Can you
> > try that temporary patch and tell me if it works for you? |
 12 Dec 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host 12 Dec 2009, Jimmy Ngai, Forum, Run multiple frontend on the same host
|
Dear Stefan,
I followed your suggestion to try the sample front-ends from the distribution and
they work fine. They also work fine with any one of my front-ends. Only my two
front-ends cannot run concurrently in the same directory. I later found that the
problem is in the CAEN HV wrapper library. The problem arises when the front-ends
are both linked to that library and it is solved now.
Thanks & Best Regards,
Jimmy
> Hi Jimmy,
>
> ok, now I understand. Well, I don't see your problem. I just tried with the
> current SVN
> version to start
>
> midas/examples/experiment/frontend
> midas/examples/slowcont/scfe
>
> in the same directory (without "-h localhost") and it works just fine (see
> attachemnt). I even started them from the same directory. Yes there are *.SHM
> files and they correspond to shared memory, but both front-ends use this shared
> memory together (that's why it's called 'shared').
>
> Your error message 'Semaphore already present' is strange. The string is not
> contained in any midas program, so it must come from somewhere else. Do you
> maybe try to access the same hardware with the two front-end programs?
>
> I would propose you do the following: Use the two front-ends from the
> distribution (see above). They do not access any hardware. See if you can run
> them with the current SVN version of midas. If not, report back to me.
>
> Best regards,
>
> Stefan
>
>
> > Dear Stefan,
> >
> > Thanks for the reply. I have tried your patch and it didn't solve my problem.
> Maybe I
> > have not written my question clearly. The two frontends could run on the same
> computer
> > if I use the remote method, i.e. by setting up the mserver and connect to the
> > experiment by specifying "-h localhost", also the frontend programs need to be
> put in
> > different directory. What I want to know is whether I can simply start
> multiple
> > frontends in the same directory without setting up the mserver etc. I noticed
> that
> > there are several *.SHM files, I'm not familiar with semaphore, but I guess
> they are
> > the key to the problem. Please correct me if I misunderstood something.
> >
> > Best Regards,
> > Jimmy
> >
> >
> > > > Dear All,
> > > >
> > > > I want to run two frontend programs (one for trigger and one for slow
> control)
> > > > concurrently on the same computer, but I failed. The second frontend said:
> > > >
> > > > Semaphore already present
> > > > There is another process using the semaphore.
> > > > Or a process using the semaphore exited abnormally.
> > > > In That case try to manually release the semaphore with:
> > > > ipcrm sem XXX.
> > > >
> > > > The two frontends are connected to the same experiment. Is there any way I
> can
> > > > overcome this problem?
> > >
> > > That might be related to the RPC mutex, which gets created system wide now.
> I
> > > modified this in midas.c rev. 4628, so there will be one mutex per process.
> Can you
> > > try that temporary patch and tell me if it works for you? |
 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page showing ROOT analyzer output 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Custom page showing ROOT analyzer output  
|
Many midas experiments work with ROOT based analyzers today. One problem there is that the graphical output of the root analyzer can only be seen through the X server and not through the web. At the MEG experiment, we solved this problem in an elegant way: The ROOT analyzer runs in the background, using a "virtual" X server called Xvfb. It plots its output (several panels) normally using this X server, then saves this panels every ten seconds into GIF files. These GIF files are then served through mhttpd using a custom page. The output looks like this:
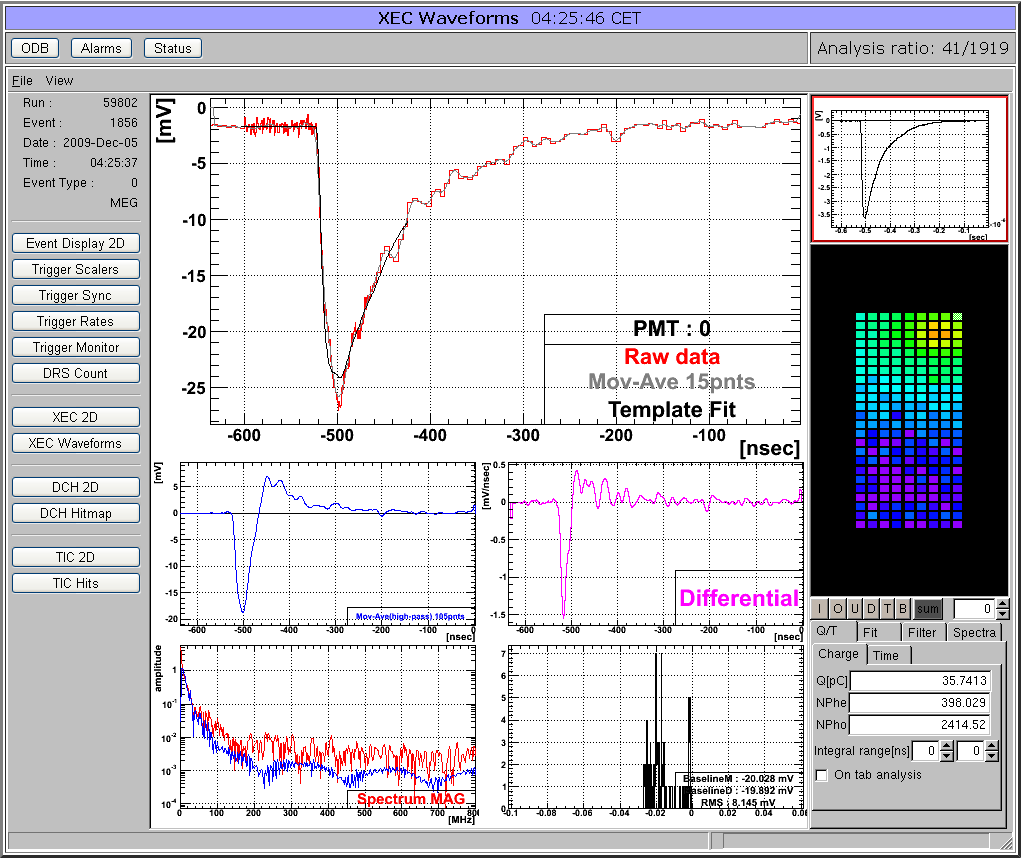
The buttons on the left sides are actually HTML buttons on that custom page overlaid to the GIF image, which in this case shows one of our 800 PMT channels digitized at 1.6 GSPS. With these buttons one can cycle through the different GIF images, which then automatically update ever ten seconds. Of course it is not possible to feed interaction back to the analyzer (like the waveform cannot be fitted interactively) but for monitoring an experiment in production mode this tools is extremely helpful, since it is seamlessly integrated into mhttpd. All the magic is done with JavaScript, and the buttons are overlaid to the graphics using CSS with absolute positioning. The analysis ratio on the top right is also done with JavaScript pulling the right info out of the ODB.
The used custom page file is attached. For details using Xvfb server, please contact Ryu Sawada <sawada@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp>. |
 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Redesign of status page columns 04 Dec 2009, Stefan Ritt, Info, Redesign of status page columns 
|
Since the column on the main midas status page with fraction of analyzed events is
barely used, I decided to drop it. Anyhow it does not make sense for all slow
control events. If this feature is required in some experiment, I propose to move it
into a custom page and calculate this ratio in JavaScript, where one has much more
flexibility.
This modification frees up more space on the status page for the "Status" column, where
front-end programs can report errors etc. |
 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken
|
I notice that "mserver -s" (a non-default mode of operation) does not work right
- if I connect odbedit for the first time, all is okey, if I connect the second
time, mserver crashes - because after the first connection closed,
rpc_deregister_functions() was called, rpc_list is deleted and causes a crash
later on. Because everybody uses the default "mserver -m" mode, I am not sure
how important it is to fix this.
K.O. |
 27 Nov 2009, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken 27 Nov 2009, Stefan Ritt, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken
|
> I notice that "mserver -s" (a non-default mode of operation) does not work right
> - if I connect odbedit for the first time, all is okey, if I connect the second
> time, mserver crashes - because after the first connection closed,
> rpc_deregister_functions() was called, rpc_list is deleted and causes a crash
> later on. Because everybody uses the default "mserver -m" mode, I am not sure
> how important it is to fix this.
> K.O.
"mserver -s" is there for historical reasons and for debugging. I started originally
with a single process server back in the 90's, and only afterwards developed the multi
process scheme. The single process server now only works for one connection and then
crashes, as you described. But it can be used for debugging any server connection,
since you don't have to follow the creation of a subprocess with your debugger, and
therefore it's much easier. But after the first connection has been closed, you have
to restart that single server process. Maybe one could add some warning about that, or
even fix it, but it's nowhere used in production mode. |
 27 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken 27 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Report, "mserver -s" is broken
|
>
> "mserver -s" is there for historical reasons and for debugging.
>
I confirm that my modification also works for "mserver -s". I also added an assert() to the
place in midas.c were it eventually crashes, to make it more obvious for the next guys.
K.O. |
 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Fix, mserver network routing fix 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Fix, mserver network routing fix
|
mserver update svn rev 4625 fixes an anomaly in the MIDAS RPC network code where
in some network configurations MIDAS mserver connections work, but some RPC
transactions, such as starting and stopping runs, do not (use the wrong network
names or are routed over the wrong network).
The problem is a possible discrepancy between network addresses used to
establish the mserver connection and the value of "/System/Clients/xxx/Host"
which is ultimately set to the value of "hostname" of the remote client. This
ODB setting is then used to establish additional network connections, for
example to start or stop runs.
Use the client "hostname" setting works well for standard configurations, when
there is only one network interface in the machine, with only one IP address,
and with "hostname" set to the value that this IP address resolves to using DNS.
However, if there are private networks, multiple network interfaces, or multiple
network routes between machines, "/System/Clients/xxx/Host" may become set to an
undesirable value resulting in asymmetrical network routing or complete failure
to establish RPC connections.
Svn rev 4625 updates mserver.c to automatically set "/System/clients/xxx/Host"
to the same network name as was used to establish the original mserver connection.
As always with networking, any fix always breaks something somewhere for
somebody, in which case the old behavior can be restored by "setenv
MIDAS_MSERVER_DO_NOT_USE_CALLBACK_ADDR 1" before starting mserver.
The specific problem fixed by this change is when the MIDAS client and server
are on machines connected by 2 separate networks ("client.triumf.ca" and
"client.daq"; "server.triumf.ca" and "server.daq"). The ".triumf.ca" network
carries the normal SSH, NFS, etc traffic, and the ".daq" network carries MIDAS
data traffic.
The client would use the "server.daq" name to connect to the server and this
traffic would go over the data network (good).
However, previously, the client "/System/Clients/xxx/Host" would be set to
"client.triumf.ca" and any reverse connections (i.e. RPC to start/stop runs)
would go over the normal ".triumf.ca" network (bad).
With this modification, mserver will set "/System/Clients/xxx/Host" to
"client.daq" (the IP address of the interface on the ".daq" network) and all
reverse connections would also go over the ".daq" network (good).
P.S. This modification definitely works only for the default "mserver -m" mode,
but I do not think this is a problem as using "-s" and "-t" modes is not
recommended, and the "-s" mode is definitely broken (see my previous message).
svn rev 4625
K.O. |
 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Fix, mdump max number of banks and dump of 32-bit banks 26 Nov 2009, Konstantin Olchanski, Bug Fix, mdump max number of banks and dump of 32-bit banks
|
By request from Renee, I increased the MIDAS BANKLIST_MAX from 64 to 1024 and
after fixing a few buglets where YB_BANKLIST_MAX is used instead of (now bigger)
BANKLIST_MAX, I can do a full dump of ND280 FGD events (96 banks).
I also noticed that "mdump -b BANK" did not work, it turns out that it could not
handle 32bit-banks at all. This is now fixed, too.
svn rev 4624
K.O. |
|